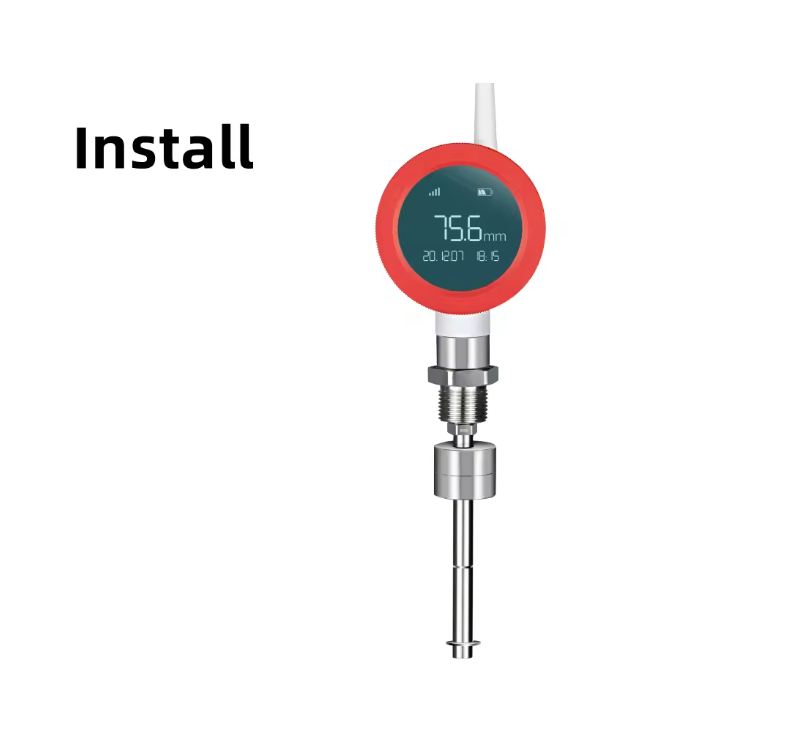
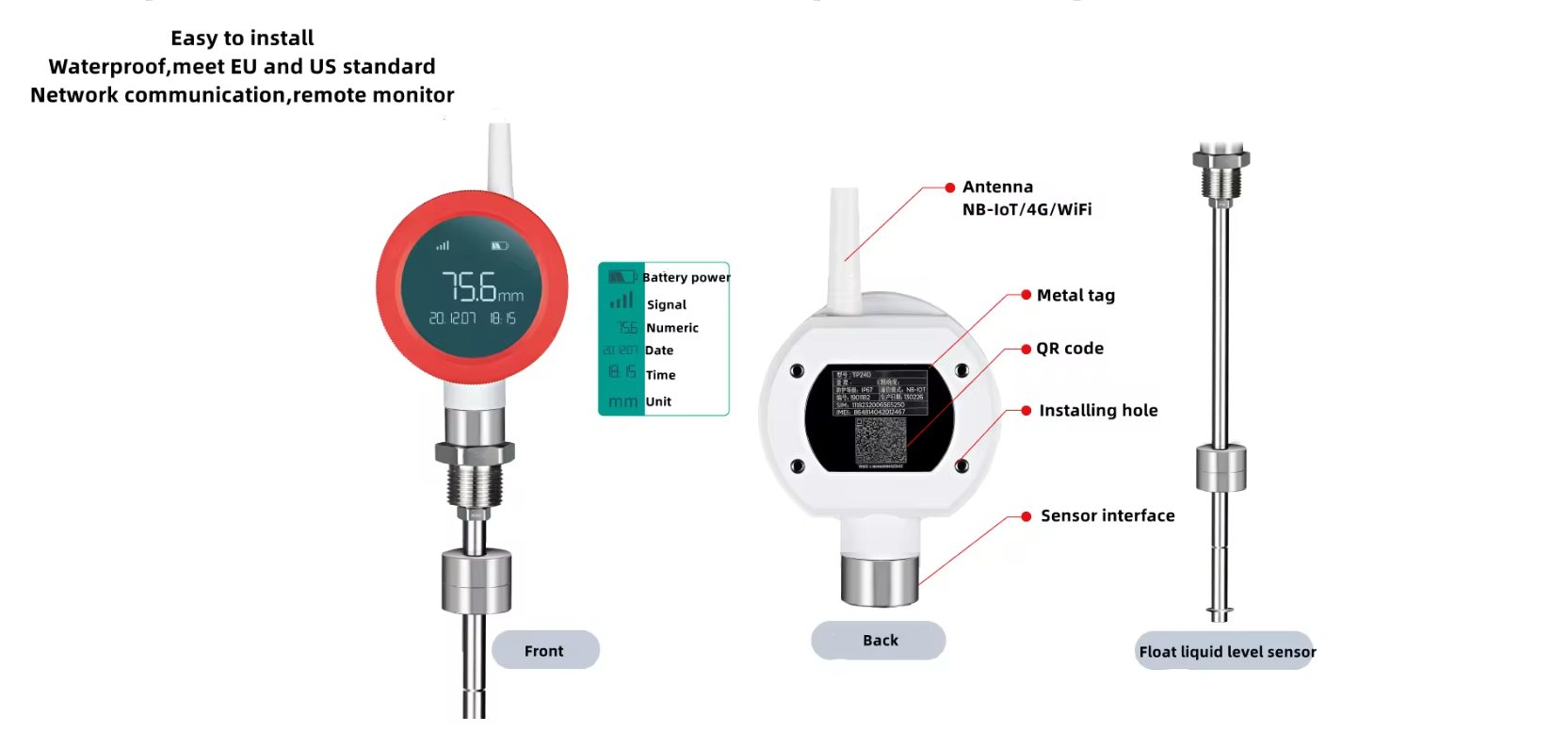
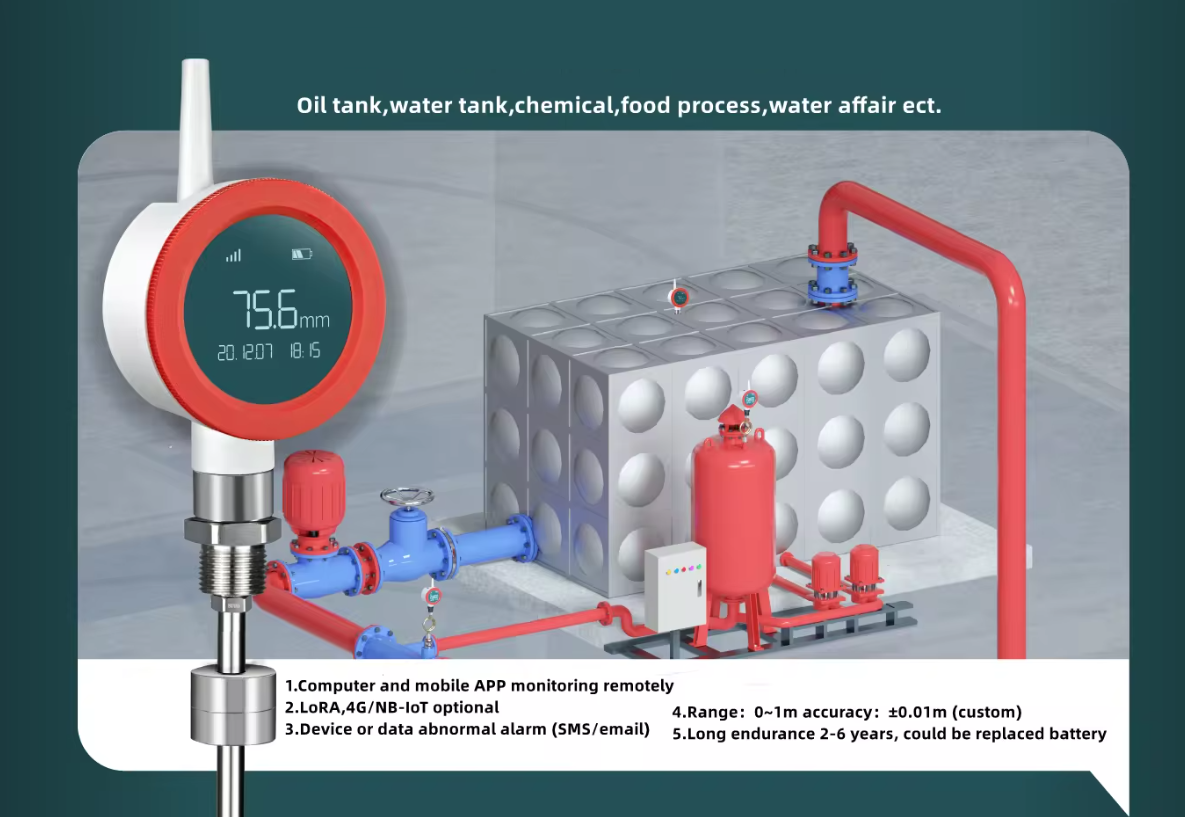
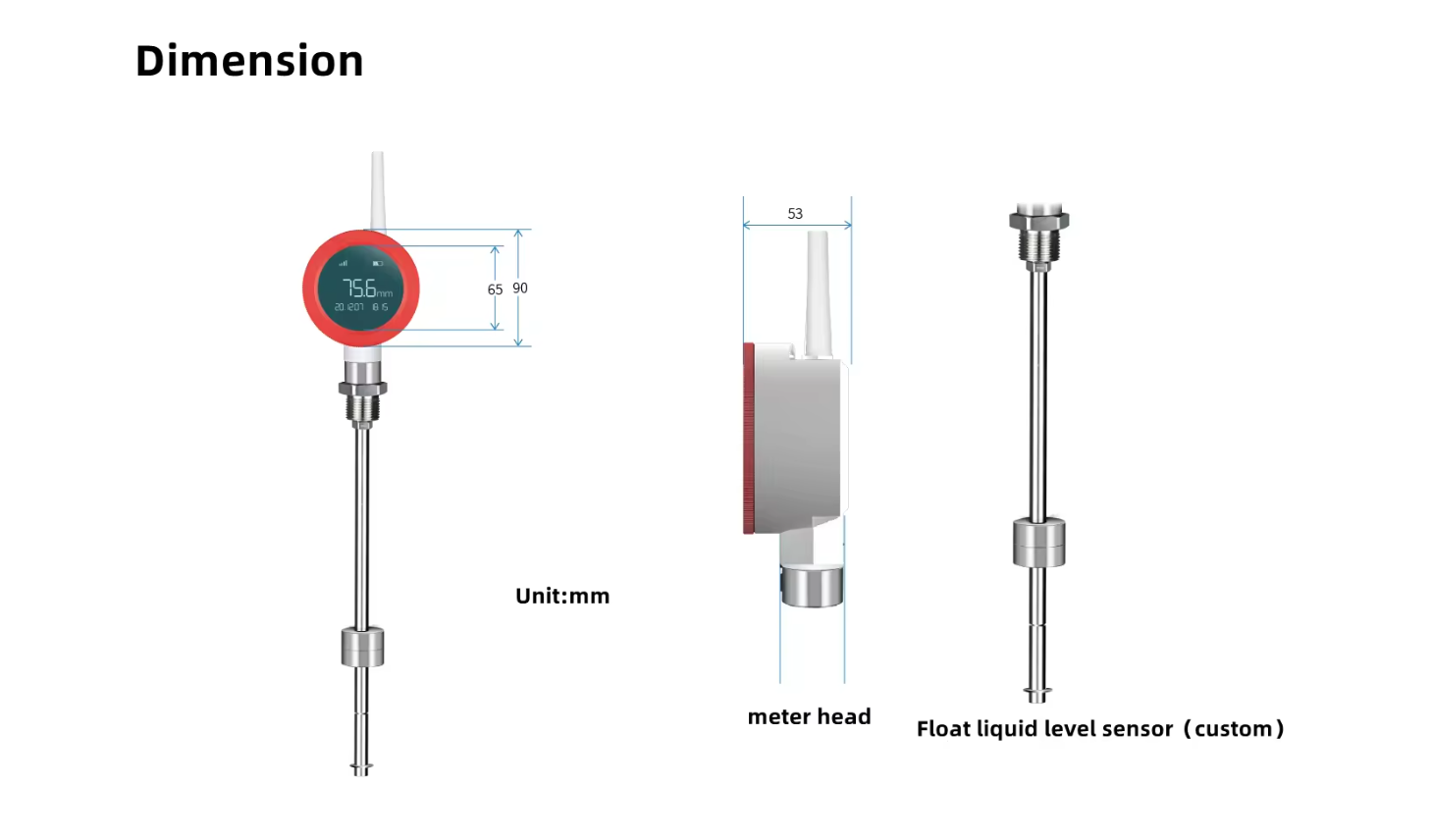
Wireless Level Float Transmitter
$ 1,422.00 – $ 1,852.00Price range: $ 1,422.00 through $ 1,852.00
A Wireless Level Float Transmitter is a cutting-edge device designed to accurately measure liquid levels in various applications. This sensor operates wirelessly, eliminating the need for physical connections and allowing for remote monitoring capabilities. The sensor consists of a buoyant element equipped with sensors that detect changes in liquid levels with high precision. These sensors transmit data wirelessly to a central monitoring system, enabling real-time tracking of liquid levels.
The key benefits of a wireless floating level sensor include continuous monitoring without manual intervention, early warning alerts to prevent overflow or underflow situations, and seamless integration with existing monitoring systems. The sensor is constructed from durable materials to withstand harsh environmental conditions and may feature advanced functionalities such as temperature compensation, self-calibration, and data-logging capabilities. Easy to install and configure, the sensor provides reliable and accurate measurements, offering an efficient solution for liquid-level monitoring in various industrial and commercial settings.
Description
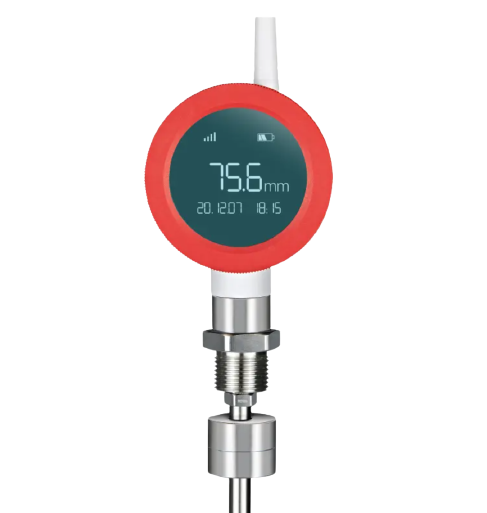 A Wireless Level Float Transmitter is a sophisticated device designed to accurately measure liquid levels in various applications, creating a seamless and efficient monitoring system. This sensor operates using cutting-edge wireless technology, eliminating the need for physical connections and allowing for remote monitoring capabilities. With a focus on precision and reliability, the sensor offers real-time data transmission, ensuring up-to-date information on liquid levels for enhanced control and management.
A Wireless Level Float Transmitter is a sophisticated device designed to accurately measure liquid levels in various applications, creating a seamless and efficient monitoring system. This sensor operates using cutting-edge wireless technology, eliminating the need for physical connections and allowing for remote monitoring capabilities. With a focus on precision and reliability, the sensor offers real-time data transmission, ensuring up-to-date information on liquid levels for enhanced control and management.
A Wireless Level Float Transmitter typically includes a buoyant element that floats on the surface of the liquid being measured. The sensors on this element detect changes in liquid levels with high accuracy. The transmitter then wirelessly sends the data to a central monitoring system, where operators can analyze and act on it in real time.
Continuous Monitoring of Wireless Level Float Transmitter
One of the key benefits of a Wireless Level Float Transmitter is its ability to provide continuous monitoring without the need for manual intervention. This automation not only improves efficiency but also minimizes the risk of human error. Whether used in industrial tanks, reservoirs, or other liquid containment systems, the sensor can help prevent overflow or underflow situations by providing early warnings and alerts.
In terms of technology, Wireless Level Float Transmitter may utilize various wireless communication protocols such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, 4G, or LoRaWAN to transmit data over short or long distances. These communication protocols ensure reliable connectivity and enable seamless integration with existing monitoring systems. Additionally, you can power the sensor with batteries or solar panels, offering flexibility in deployment and reducing maintenance requirements.
Engineers often design the wireless level float transmitter to be rugged and durable, enabling it to withstand harsh environmental conditions. Furthermore, the engineers commonly use materials such as stainless steel, PVC, or corrosion-resistant plastics to ensure longevity and reliability in challenging settings. Engineers may also design the sensor to be intrinsically safe for use in hazardous areas. Intrinsically safe is at the highest safety level where explosive gases or liquids are present.
Precise Level measurement
In applications where precise liquid level measurement is critical, engineers may equip the sensor with advanced features. Advanced features such as temperature compensation, self-calibration, and data logging capabilities. These features help ensure accurate and consistent measurements over time, even in changing environmental conditions.
The installation of a Wireless Level Float sensor is typically straightforward, requiring minimal setup and configuration. Depending on the specific requirements of the application, you can mount the sensor directly on the liquid surface. You can suspend it from a fixed point above the liquid. You can usually perform calibration procedures simply, either manually or automatically, depending on the sensor’s capabilities.
Once installed, the Wireless Level Float Transmitter begins gathering data immediately, providing real-time insights into liquid levels and trends. You can access this data remotely through web-based interfaces and mobile applications. You can integrate it into existing SCADA systems for centralized monitoring and control.
Overall, a Wireless Level Float Transmitter offers a reliable and cost-effective. In addition, this is an efficient solution for monitoring liquid levels in a wide range of applications. By leveraging wireless technology, advanced sensors, and robust construction, this device enhances operational efficiency. It Also improves safety, and enables better decision-making based on accurate and timely data.
Other Wireless Instruments
Wireless Pressure
Wireless Temperature
Specifications
|
Range
|
0-1M(custom)
|
|
Accuracy
|
±0.01m (custom)
|
|
Battery capacity
|
2pcs*8500mAh lithium battery
|
|
Battery lifespan
|
5 years
|
|
Communication
|
NB-IoT, LoRA, 4G
|
|
Awake mode
|
Timing, Button, Alarm
|
|
Waterproof grade
|
IP66
|
|
Weight(gauge head)
|
500g
|
|
Certificate
|
CE, RoHS
|
|
Uploading information
|
Battery capacity, liquid level, signal, card number
|
|
Configuration method
|
USB, remote configuration
|
|
Antenna
|
External
|
|
Display
|
TFT LCD screen
|
Installation
The installation of a wireless floating level sensor involves several steps to ensure proper functioning and accurate monitoring. Here are the general installation procedures:
Site Survey: Before installation, conduct a site survey to determine the best location for placing the sensor. Consider factors such as accessibility, visibility of liquid levels, and wireless signal strength for data transmission.
Mounting: Depending on the type of sensor, mount it directly on the liquid surface or suspend it from a fixed point above the liquid using mounting brackets or cables. Ensure the sensor is securely attached to prevent displacement.
Calibration: Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines to calibrate the sensor for accurate measurement. This may involve setting the zero point and span to match the specific liquid being monitored.
Power Supply: Connect the sensor to the power source, which could be batteries or solar panels, based on the sensor’s requirements. Ensure the power supply is sufficient for continuous operation.
Wireless Connectivity: Set up the wireless communication protocol, such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, or LoRaWAN, to establish a connection between the sensor and the central monitoring system. Configure the data transmission settings for seamless communication.
Testing: Once the sensor is installed and configured, conduct thorough testing to ensure it accurately measures liquid levels and transmits data effectively. Verify the readings against manual measurements for accuracy.
Integration: Integrate the sensor with the central monitoring system or SCADA platform for real-time data monitoring and analysis. Configure alerts and notifications to notify stakeholders of any critical changes in liquid levels.
Maintenance: Establish a maintenance schedule to regularly check and clean the sensor to prevent debris buildup or malfunctions. Replace batteries or perform necessary maintenance tasks as recommended by the manufacturer.
Documentation: Keep detailed records of the installation process, calibration settings, test results, and maintenance activities for future reference. This documentation will aid in troubleshooting and ensuring consistent performance.
By following these installation procedures diligently, you can effectively deploy a wireless floating level sensor for accurate and reliable liquid level monitoring in various industrial, commercial, or environmental settings.
Q&A
Q: What is a wireless floating-level sensor?
A: A wireless floating level sensor is a sophisticated device designed to accurately measure liquid levels in various applications using wireless technology.
Q: How does a wireless floating-level sensor work?
A: The sensor consists of a buoyant element with sensors that detect changes in liquid levels. These sensors transmit data wirelessly to a central monitoring system for real-time tracking.
Q: What are the benefits of using a wireless floating-level sensor?
A: Benefits include remote monitoring, precision measurement, automation, efficiency, real-time data transmission, and enhanced safety through early warning alerts.
Q: Where are wireless floating-level sensors commonly used?
A: They are used in industrial tanks, water management systems, oil refineries, agriculture, environmental monitoring, food processing plants, and various other industrial and commercial settings.
Q: How is a wireless floating-level sensor installed?
A: Installation involves mounting the sensor, calibrating it for accurate measurements, setting up wireless connectivity, testing the system, integrating with monitoring platforms, and establishing a maintenance schedule.
Q: What are the advantages of wireless floating-level sensors over traditional sensors?
A: Advantages include remote monitoring, accuracy, efficiency, safety, versatility, integration capabilities, and cost-effectiveness in monitoring liquid levels with ease.
Q: Are there any disadvantages to using wireless floating-level sensors?
A: Some disadvantages include initial cost, power dependency, potential interference issues, calibration requirements, security risks, environmental factors, compatibility challenges, and range limitations in wireless connectivity.
Advantages / Disadvantages
Advantages of Wireless Floating Level Sensors:
Remote Monitoring: Enables real-time monitoring of liquid levels from a distance, allowing for quick response to changes or emergencies.
Efficiency: Automation of data collection and transmission reduces manual effort and enhances operational efficiency.
Accuracy: Provides precise measurements of liquid levels, aiding in better decision-making and process optimization.
Safety: Early warning alerts help prevent overflows, leaks, or underflows, enhancing safety in industrial and environmental settings.
Versatility: Suitable for a wide range of applications across industries, offering flexibility in monitoring different types of liquids.
Integration: Seamless integration with existing monitoring systems, SCADA platforms, or IoT networks for comprehensive data analysis.
Cost-Effective: Minimizes maintenance costs by reducing the need for physical connections and manual monitoring.
Environmental Monitoring: Supports environmental conservation efforts by detecting pollution events and ensuring regulatory compliance.
Disadvantages of Wireless Floating Level Sensors:
Initial Cost: The upfront cost of purchasing and installing wireless floating-level sensors may be higher compared to traditional sensors.
Power Dependency: Sensors reliant on batteries or solar panels for power may require frequent maintenance to ensure continuous operation.
Interference: Wireless signal interference or connectivity issues may affect data transmission reliability in certain environments.
Calibration: Regular calibration of sensors is necessary to maintain accuracy, which can be time-consuming and require technical expertise.
Security Risks: Wireless communication may pose security risks such as data breaches or unauthorized access if proper encryption measures are not implemented.
Environmental Factors: Harsh environmental conditions like extreme temperatures or corrosive substances may impact sensor durability and performance.
Compatibility: Compatibility issues with existing monitoring systems or networks may arise, requiring additional adjustments or investments.
Range Limitations: Wireless signals have a limited range, which may necessitate additional signal boosters or repeaters for extended coverage in large facilities.
Despite these disadvantages, the advantages typically outweigh the drawbacks, making wireless floating-level sensors a valuable tool for efficient liquid-level monitoring in various applications.
Applications
Wireless floating level sensors find diverse applications across various industries and settings where accurate liquid level monitoring is crucial. Here are some key applications:
Industrial Tanks: In manufacturing facilities, wireless floating level sensors are used to monitor liquid levels in tanks storing chemicals, oils, or other fluids. This ensures proper inventory management, prevents overfilling or running out of stock, and enhances safety by detecting leaks or spills promptly.
Water Management: Municipalities and water treatment plants utilize these sensors to monitor water levels in reservoirs, dams, and water distribution systems. This data helps optimize water usage, predict demand, and manage water resources efficiently.
Oil & Gas Industry: In oil refineries and extraction sites, wireless floating level sensors provide real-time monitoring of oil levels in storage tanks, ensuring compliance with regulations, preventing spills, and optimizing inventory management.
Agriculture: Farmers use these sensors to monitor water levels in irrigation systems, ensuring crops receive adequate water supply. This helps in conserving water, optimizing irrigation schedules, and maximizing crop yield.
Environmental Monitoring: Environmental agencies deploy wireless floating level sensors in rivers, lakes, and seas to monitor water levels, detect pollution events, and study water flow patterns. This data aids in environmental conservation efforts and early warning systems for natural disasters.
Food & Beverage Industry: In food processing plants, these sensors monitor liquid levels in production tanks to ensure consistent product quality, prevent contamination, and streamline manufacturing processes.
Pharmaceuticals: Pharmaceutical companies use wireless floating-level sensors to monitor liquid levels in storage tanks containing critical ingredients or products. Accurate monitoring ensures compliance with strict quality standards and regulations.
Petrochemical Plants: These sensors play a vital role in monitoring levels of chemicals and liquids in various processes within petrochemical plants, helping maintain operational efficiency, prevent spills, and ensure worker safety.
Wastewater Treatment: Municipal wastewater treatment plants utilize these sensors to monitor levels in different stages of the treatment process. This data aids in optimizing treatment efficiency, managing flow rates, and ensuring regulatory compliance.
Smart Cities: In the context of smart city initiatives, wireless floating level sensors can be integrated into urban infrastructure to monitor water levels in drainage systems, reservoirs, and flood-prone areas, enabling proactive measures to prevent flooding and improve urban planning.
These applications highlight the versatility and importance of wireless floating-level sensors in various industries, contributing to improved efficiency, safety, and environmental sustainability.
Downloads
Drawings
 A Wireless Level Float Transmitter is a sophisticated device designed to accurately measure liquid levels in various applications, creating a seamless and efficient monitoring system. This sensor operates using cutting-edge wireless technology, eliminating the need for physical connections and allowing for remote monitoring capabilities. With a focus on precision and reliability, the sensor offers real-time data transmission, ensuring up-to-date information on liquid levels for enhanced control and management.
A Wireless Level Float Transmitter is a sophisticated device designed to accurately measure liquid levels in various applications, creating a seamless and efficient monitoring system. This sensor operates using cutting-edge wireless technology, eliminating the need for physical connections and allowing for remote monitoring capabilities. With a focus on precision and reliability, the sensor offers real-time data transmission, ensuring up-to-date information on liquid levels for enhanced control and management.