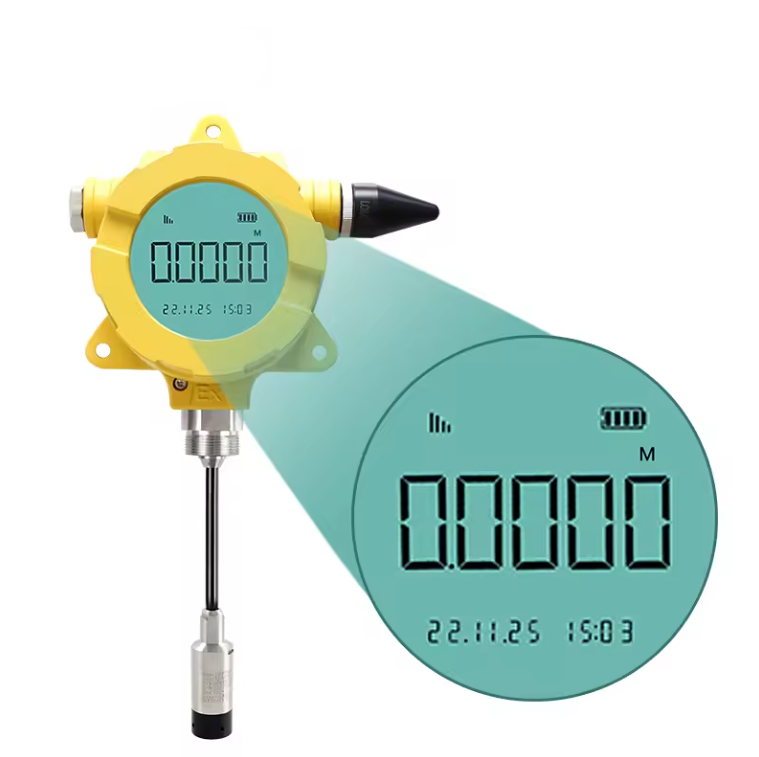
Wireless Level Probe Transmitter
$ 1,344.00 – $ 1,880.00
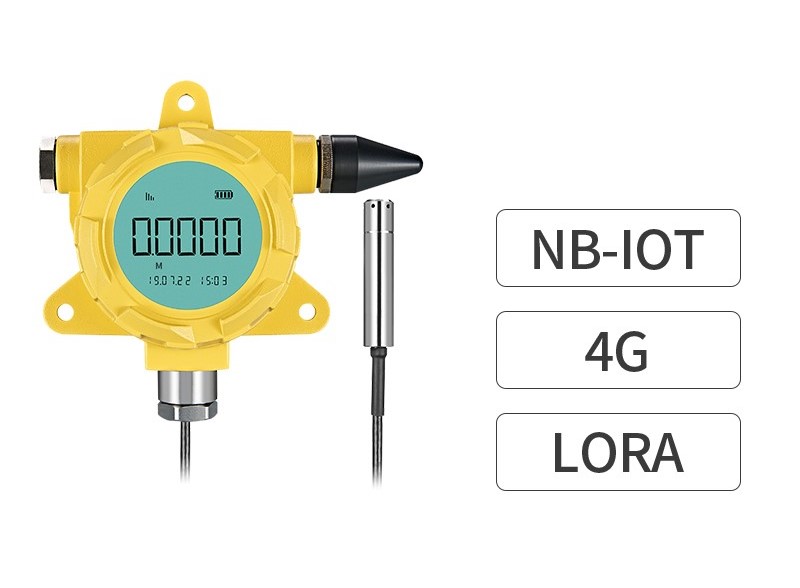
A wireless level probe transmitter is a device used to measure the level of liquids, solids, or slurry materials in tanks or silos without the need for direct physical wiring connections. It typically consists of a sensor that measures the substance’s level and a transmitter that wirelessly communicates this data to a central monitoring system. These transmitters offer easy installation, remote access to process data, and enhanced diagnostics for predictive maintenance.
Description
A Wireless Level Probe Transmitter is a device used to measure the level of liquids, solids, or slurry materials in tanks or silos without the need for direct physical wiring connections. Furthermore, it typically consists of the following components:
Sensor: The sensor is responsible for measuring the level of the substance in the tank. In addition, it can be an ultrasonic sensor, radar sensor, pressure sensor, or any other type of sensor suitable for the specific application.
Transmitter: The transmitter is the unit that processes the signal from the sensor and sends it wirelessly to a receiving unit or system. Furthermore, it may have built-in signal conditioning circuitry to enhance the accuracy and reliability of the measured data.
Wireless Level Probe Transmitter Communication Module
This module allows the transmitter to send the data wirelessly over a communication protocol such as 4G, LoRa, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, or proprietary radio frequency signals. Finally, it eliminates the need for complex wiring installations.
Power Source: The Wireless Level Probe Transmitter is typically powered by batteries or in some cases by solar panels. this is used to ensure continuous operation without relying on external power sources.
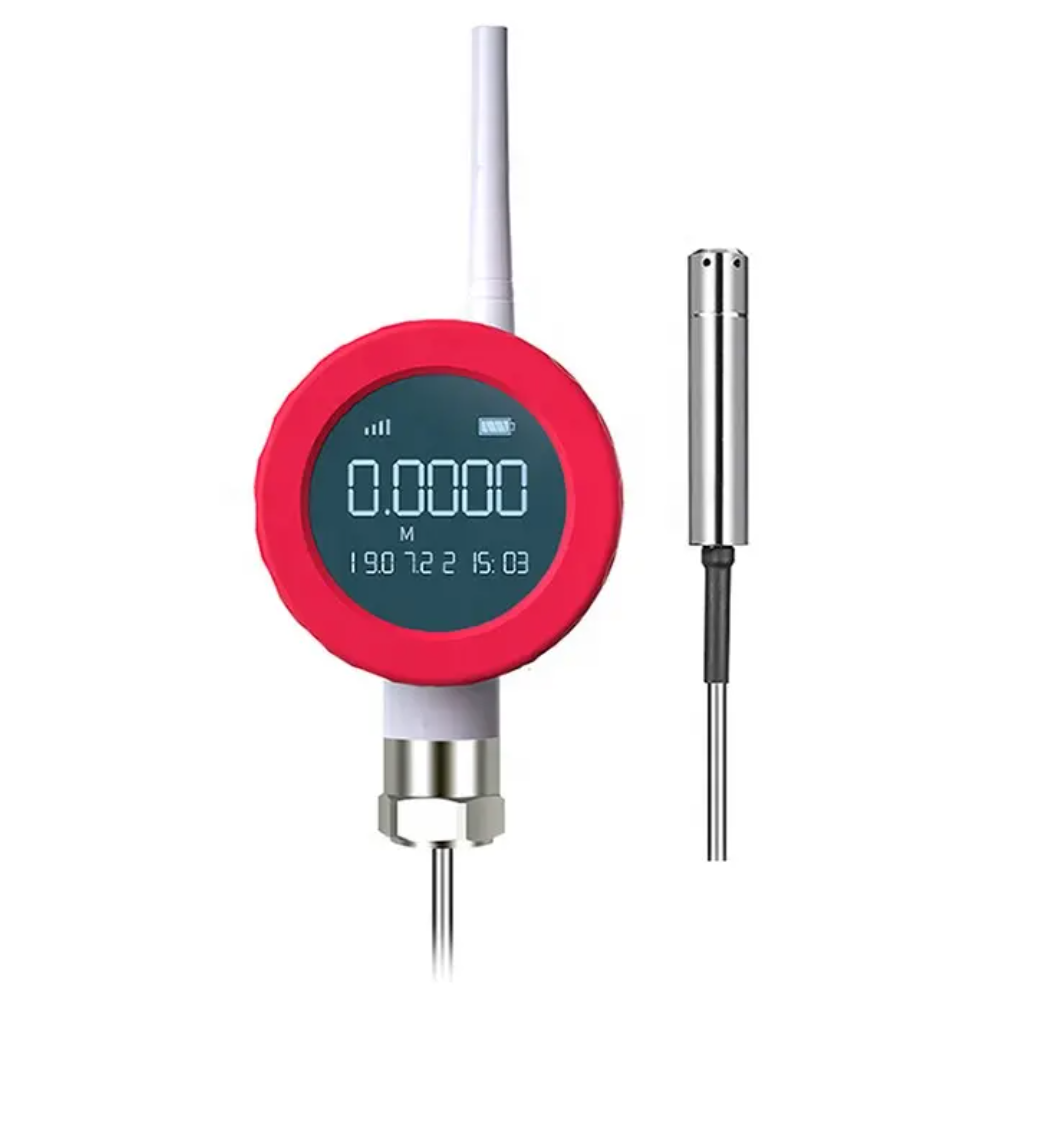
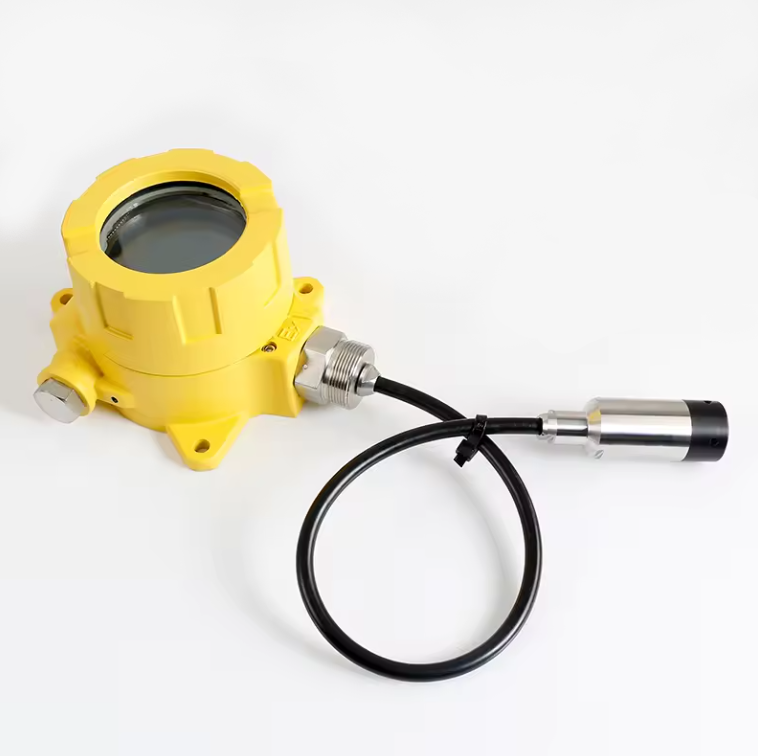
Enclosure: The transmitter and its components are enclosed in durable housing to protect them from environmental factors such as dust. It is also used to protect from moisture and temperature variations.
Display/Output: Some Wireless Level Probe Transmitter comes equipped with a display. This is used to show real-time level readings locally. Others transmit the data to a central control system where the information can be monitored and analyzed.
Overall, the Wireless Level Probe Transmitter offers the advantage of easy installation, and reduced maintenance costs. It is also good for improved safety by eliminating the need for physical wiring connections that can be prone to damage or pose safety hazards. In addition, this technology is widely used in industrial applications and wastewater management. Also, oil and gas refineries, and various other sectors where accurate level measurement is essential. Typically, level probes are essential in monitoring remote tank and vessel applications. This occurs when electrical is difficult to install.
Not what you are looking for?
Temperature Transmitter
Flow Meter
Ultrasonic Level Transmitter
Float Level Transmitter
Pressure Transmitter
Specifications
|
Product name
|
Wireless liquid level gauge
|
|
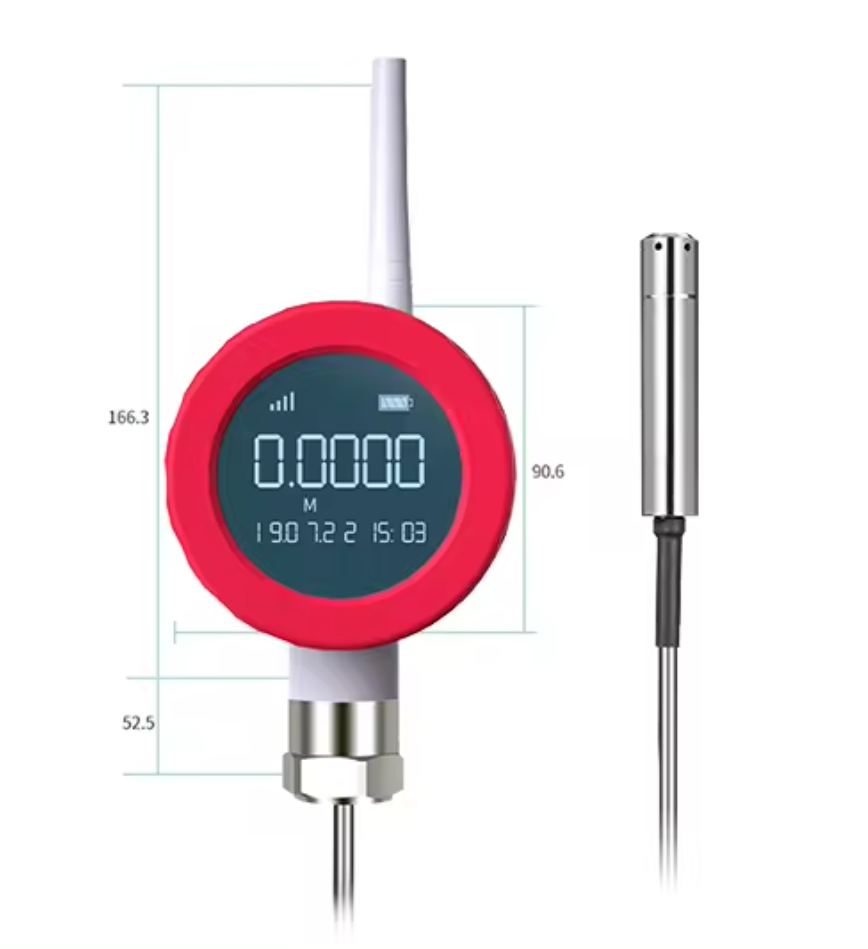
Size
|
218*90*58mm (not including the sensor)
|
|
Weight
|
0.70KG
|
|
Power supply
|
2 *8500mah Lithium battery
|
|
Display
|
2.4“ TFT LCD screen
|
|
Working time
|
5 years (sending data once an hour)
|
|
Power consumption
|
Standby current ≤80uA data average sending current≤150mA
|
|
Sampling interval
|
once per minute
|
|
Antenna
|
External
|
|
Protection level
|
IP66
|
|
Data transmission interval
|
2min-1440min
|
|
Configuration
|
USB, remote configuration
|
|
Range
|
0-100m
|
|
Accuracy
|
0.5
|
|
Uploading information
|
liquid level, temperature, battery power, signal, card number
|
|
Wakeup mode
|
Button, timing
|
|
Working temperature
|
-30℃-70℃
|
Installation
While I don’t have specific details about the exact model you’re using, I can provide general guidelines based on common practices:
Site Preparation:
- Choose an Optimal Location: Select a suitable location for the transmitter. Consider factors such as accessibility, visibility, and safety.
- Clear Obstructions: Ensure there are no obstacles or obstructions that might interfere with signal transmission.
- Power Source: If the transmitter requires power, ensure a reliable power source is available nearby.
Mounting and Support:
- Secure Mounting: Install the transmitter securely using appropriate brackets or supports.
- Avoid Vibration: Mount it away from sources of excessive vibration or mechanical stress.
- Proper Orientation: Align the transmitter properly (e.g., vertical for level measurement).
Cable and Wiring:
- Use Suitable Cable: Choose the right cable for wireless communication (if applicable).
- Avoid Interference: Keep the cable away from sources of electromagnetic interference.
- Proper Grounding: Ground the transmitter as per safety guidelines.
Antenna Placement:
- If the transmitter has an external antenna, position it optimally for signal strength.
- Avoid placing the antenna near metal structures or other potential signal blockers.
Configuration and Pairing:
- Follow the manufacturer’s instructions to configure the transmitter.
- Pair it with the corresponding receiver or monitoring system.
Testing and Commissioning:
- Signal Strength Test: Verify that the wireless signal strength is adequate.
- Functional Test: Ensure the transmitter communicates correctly with the receiver.
- Calibration: Calibrate the transmitter if necessary.
Remember to consult the specific installation manual provided by the manufacturer for detailed instructions related to your wireless-level probe transmitter. Safety and proper installation are crucial!
Maintenance
Here are the maintenance procedures for a wireless-level probe transmitter:
Regular Inspections:
- Conduct visual inspections periodically.
- Check for physical damage, loose connections, or signs of wear.
- Inspect the antenna (if applicable) for any issues.
Antenna Maintenance:
- Clean the antenna to remove dust, dirt, or debris.
- Ensure proper alignment for optimal signal strength.
- Inspect cables and connectors for damage.
Battery Replacement (if applicable):
- If the transmitter is battery-powered, replace batteries as needed.
- Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for battery type and replacement intervals.
Calibration:
- Regularly calibrate the transmitter to maintain accurate measurements.
- Use calibration standards and follow the calibration procedure provided by the manufacturer.
Signal Strength Testing:
- Periodically check the wireless signal strength.
- Verify that the transmitter communicates effectively with the receiver.
Environmental Considerations:
- Ensure the transmitter is protected from extreme temperatures, humidity, and corrosive substances.
- Address any environmental factors that could affect performance.
Documentation:
- Maintain a log of maintenance activities.
- Record inspection dates, calibration details, and any corrective actions taken.
Remember to consult the specific user manual or documentation provided by the transmitter manufacturer for detailed maintenance instructions.
Advantages / Disadvantages
Advantages
Wireless Communication:
- Eliminates Wiring: Wireless transmitters do not require physical cables, reducing installation complexity.
- Flexibility: Easy relocation or repositioning without rewiring.
Reduced Installation Costs:
- Labor Savings: No need for extensive cable routing and conduit installation.
- Time-Efficient: Faster setup compared to wired systems.
Scalability:
- Expandable Networks: Easily add more transmitters to the same wireless network.
- Adaptable: Suitable for both small-scale and large-scale applications.
Remote Monitoring:
- Access Anywhere: Monitor levels remotely via a central control system or mobile devices.
- Real-Time Alerts: Receive notifications for critical conditions.
Safety and Hazardous Areas:
- Intrinsically Safe Options: Some wireless transmitters are designed for hazardous environments.
- Reduced Risk: Minimized exposure to live wires during maintenance.
Disadvantages
Signal Interference:
- Environmental Factors: Obstacles (walls, structures) and interference (other wireless devices) can affect signal strength.
- Reliability Concerns: Signal dropouts may occur.
Power Source Dependency:
- Battery Life: Battery-powered transmitters require periodic battery replacement.
- External Power: Some models need an external power source.
Limited Range:
- Distance Constraints: Wireless signals have a finite range.
- Repeater Requirement: For extended coverage, additional repeaters may be necessary.
Security Risks:
- Unauthorized Access: Wireless networks are susceptible to hacking or unauthorized access.
- Encryption and Authentication: Proper security measures are essential.
Initial Cost:
- Higher Investment: Wireless transmitters may be more expensive upfront.
- Balancing Cost: Consider long-term benefits versus initial costs.
Remember that the choice between wired and wireless transmitters depends on specific application requirements, budget, and environmental factors.
Applications
Wireless level probe transmitters find applications in various industries where accurate level measurement is essential. Here are some common use cases:
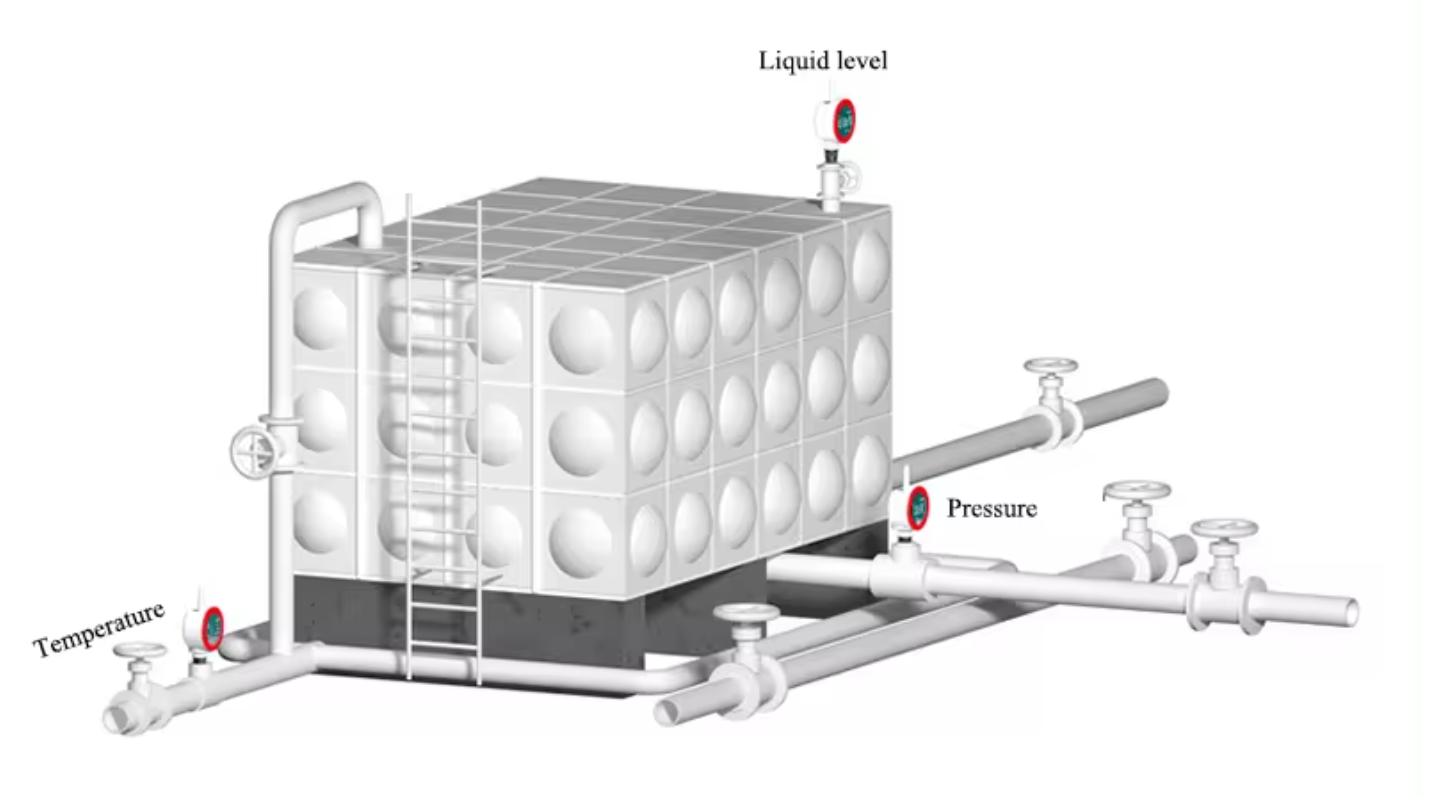
Industrial Processes:
- Monitor liquid levels in tanks, vessels, and silos.
- Control material flow in manufacturing and production lines.
- Ensure consistent levels in chemical reactors and mixing tanks.
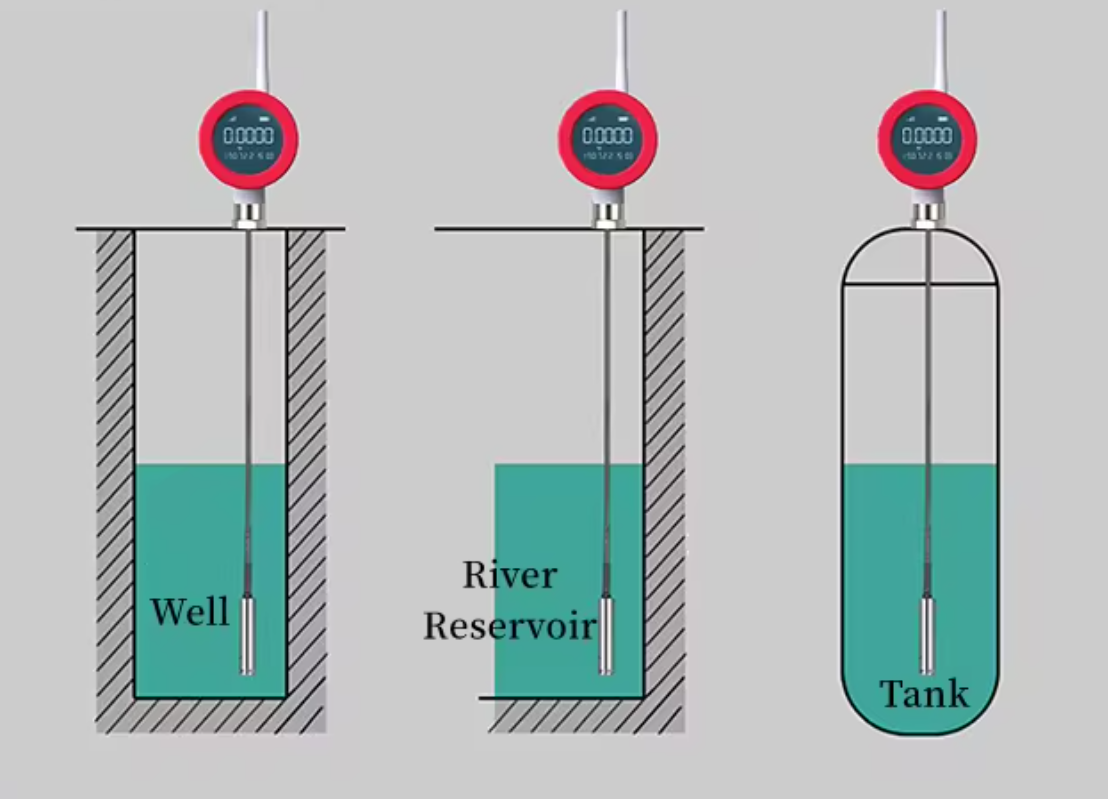
Water and Wastewater Management:
- Measure water levels in reservoirs, wells, and treatment plants.
- Detect overflow conditions to prevent flooding.
- Monitor sewage levels in lift stations.
Oil and Gas Refineries:
- Monitor oil and fuel levels in storage tanks.
- Detect leaks or spills promptly.
- Ensure safe operation in hazardous areas.
Food and Beverage Industry:
- Measure liquid levels in brewing tanks, fermentation vessels, and storage containers.
- Control filling processes in bottling plants.
Power Plants:
- Monitor water levels in cooling towers and boilers.
- Prevent low water conditions that could damage equipment.
Chemical Processing:
- Monitor chemical levels in reactors, distillation columns, and storage tanks.
- Ensure safety by detecting leaks or spills.
Pharmaceutical Manufacturing:
- Measure liquid levels in drug formulation tanks.
- Ensure accurate dosing and batch consistency.
Environmental Monitoring:
- Monitor water levels in rivers, lakes, and reservoirs.
- Detect changes in groundwater levels.
Mining and Minerals:
- Measure slurry levels in mining pits and tailings ponds.
- Control material flow in conveyor systems.
Pulp and Paper Industry:
- Monitor liquid levels in pulp digesters, paper machines, and chemical storage tanks.
- Optimize production processes.
Remember that wireless-level probe transmitters provide reliable measurements even in remote or hard-to-reach locations, making them valuable across various sectors!
Q&A
Q: What is a wireless-level probe transmitter?
A: A wireless level probe transmitter is a device used to measure the level of liquids, solids, or slurry materials in tanks or silos without the need for direct physical wiring connections. It typically consists of a sensor, transmitter, wireless communication module, power source, and enclosure.
Q: What types of sensors are commonly used in wireless-level transmitters?
A: Various sensors can be used, including ultrasonic sensors, radar sensors, guided microwave sensors, and pressure sensors. The choice depends on the specific application and the substance being measured.
Q: How does a wireless-level probe transmitter communicate data?
A: The transmitter processes the signal from the sensor and sends it wirelessly using communication protocols such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, or proprietary radio frequency signals. This eliminates the need for complex wiring installations.
Q: What are the advantages of using wireless-level transmitters?
A: Features
- Easy installation: No physical wiring is required.
- Reduced maintenance costs: Eliminates potential damage to wires.
- Improved safety: Avoids safety hazards associated with live wires.
Q: Where are wireless-level probe transmitters commonly used?
A: They find applications in industrial processes, water and wastewater management, oil and gas refineries, food and beverage production, environmental monitoring, and more.
Remember that wireless level probe transmitters offer flexibility, scalability, and remote monitoring capabilities, making them valuable tools for accurate level measurement!
Downloads
Drawings
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.














Reviews
There are no reviews yet.