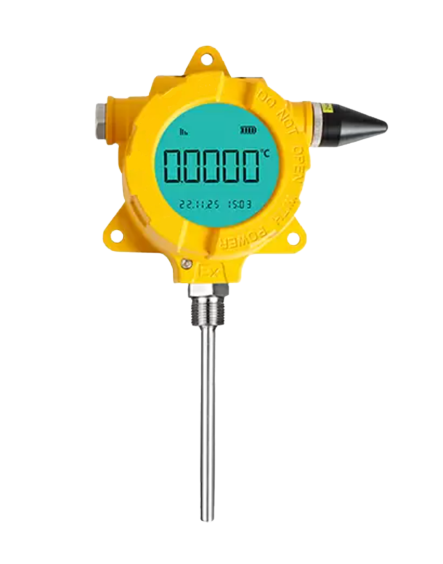
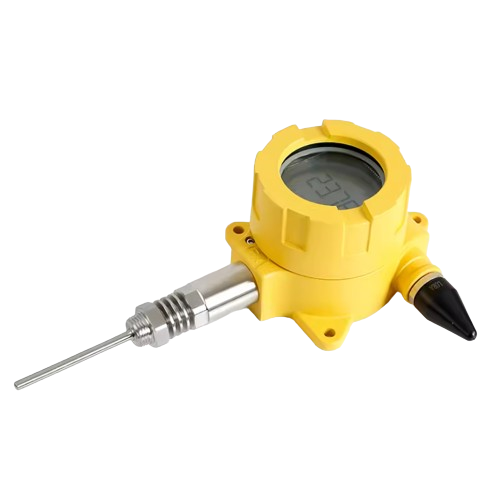
Description
 A wireless temperature transmitter is a device designed to measure temperature and wirelessly transmit this data to a central monitoring system or receiver. Also, these transmitters play a crucial role in various industries where monitoring and maintaining temperature levels is critical for operational efficiency, safety, and quality control.
A wireless temperature transmitter is a device designed to measure temperature and wirelessly transmit this data to a central monitoring system or receiver. Also, these transmitters play a crucial role in various industries where monitoring and maintaining temperature levels is critical for operational efficiency, safety, and quality control.
Here is a detailed breakdown of the components and functionality of a typical wireless temperature transmitter:
Sensor
A wireless temperature transmitter includes a sensor that detects temperature changes and converts them into electrical signals. In addition, common types of temperature sensors used include thermocouples, resistance temperature detectors (RTDs), and thermistors. Finally, the selection of the sensor type depends on factors like temperature range, accuracy, and environmental conditions.
Transmitter Unit
The transmitter unit processes the electrical signals from the sensor and transmits the data wirelessly to a receiver. It may include components such as a microprocessor, signal conditioning circuitry, and a radio frequency (RF) transmitter for wireless communication.
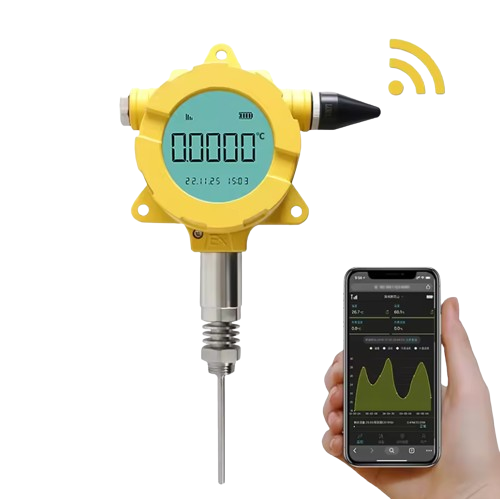
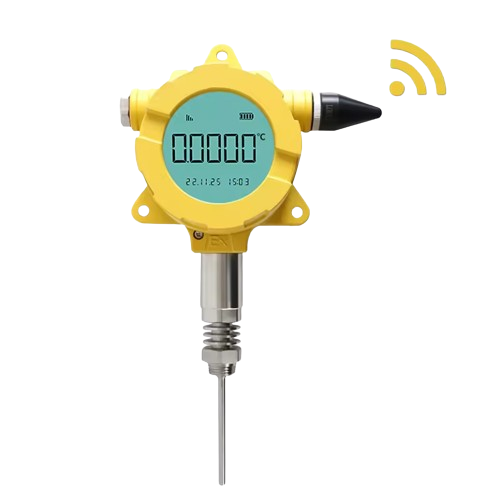
Wireless Communication
Wireless temperature transmitters utilize technologies like Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, Zigbee, or other proprietary wireless protocols to transmit temperature data. Moreover, this wireless connectivity eliminates the need for physical connections like cables, allowing for flexible installation and remote monitoring capabilities.
Power Source
Depending on the application and location of the transmitter, power is supplied through various means. Additionally, some transmitters use batteries, while others power them through energy harvesting systems, solar panels, or wired power sources.
Enclosures house the transmitter unit, protecting the internal components from environmental factors like dust, moisture, and temperature extremes. Manufacturers typically make enclosures out of materials like plastic, stainless steel, or aluminum based on the application requirements.
Installation and Calibration
Companies strategically install wireless temperature transmitters in crucial locations where temperature monitoring is essential. Proper calibration is essential to ensure accurate temperature readings, and some transmitters may support local or remote calibration capabilities.
Data Logging and Monitoring
A central monitoring system or receiver receives the temperature data transmitted wirelessly by the transmitter. This system collects, logs, and displays temperature information in real time. This allows operators to track temperature trends. Also, it sets alarm thresholds and makes informed decisions based on the data.
Wireless temperature transmitters find applications in various industries, including manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, food and beverage, HVAC, energy, and environmental monitoring. Furthermore, industries use them to monitor temperature in refrigeration units, industrial processes, storage facilities, laboratories, and more.
In summary, a wireless temperature transmitter is a sophisticated yet essential device that enables real-time temperature monitoring and data transmission without the constraints of wired connections. Finally, its versatility, accuracy, and remote monitoring capabilities make it a valuable tool. This tool allows for maintaining optimal temperature conditions in diverse industrial settings.
Specifications
- Input: Single sensor capability with universal sensor inputs (RTD, T/C, mV, ohms)
- Output Signal: Wireless HART / Zigbee protocol
- Housing: Dual-compartment field mount
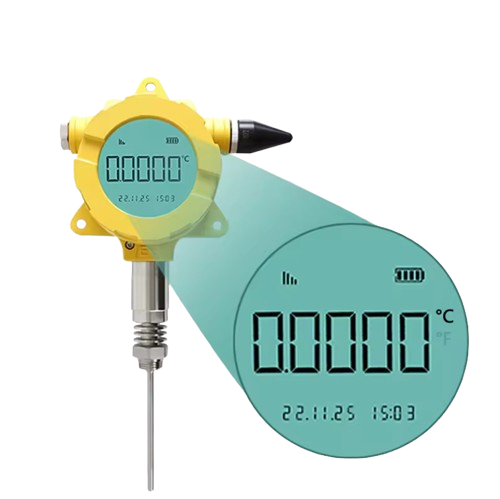
- Display/Interface: Large LCD with percent range graph
- Diagnostics: Basic diagnostics including open/short sensor diagnostics
- Calibration Options: Transmitter-sensor matching
- Certifications/Approvals: Hazardous location, marine type, see full specs for a complete list of certifications
- Update Rate: 1 sec. to 60 min., user selectable
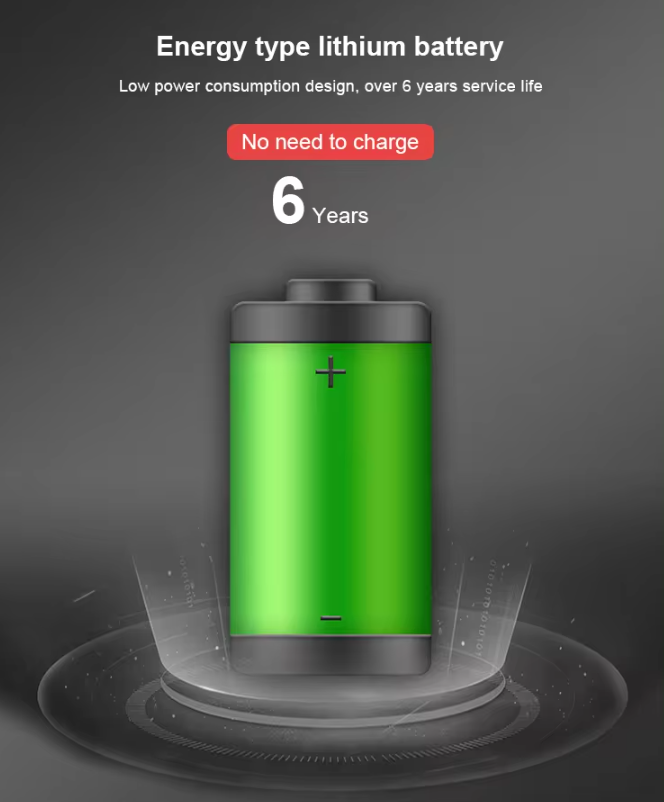
- Power Module Life: Up to 10-year life, field replaceable (order separately)Antenna Type: External (standard and extended range)
-
Wireless Temperature Transmitter HART / Zigbee technology is secure, cost-effective, and delivers >99% data reliability
- Best-in-class wireless accuracy and stability for process automationDurable dual-compartment housing offers added field reliabilityThe technology measures temperature without a process penetration for reduced design, installation, and maintenance costsWireless Temperature Transmitter sensor matching produces better accuracy, matching exact sensor characteristics with the transmitterLCD offers access to measurement and diagnostic information in the field, enhancing process visibilityThe internal module provides up to 5-year maintenance-free operation and field replacement without transmitter removalEasy installation enables quick instrumentation of measurement points without the cost of wiring
Communication Options
LoRa (Long Range), NB-IoT (Narrowband IoT), and 4G are different wireless communication technologies, each with unique characteristics and use cases:
LoRa
- LoRa is a low-power, long-range wireless communication technology designed for connecting battery-operated devices over long distances.
- It operates in the unlicensed radio spectrum, offering long-range connectivity with minimal power consumption, making it suitable for Internet of Things (IoT) applications such as smart city infrastructure, agriculture, and industrial monitoring.
- LoRa is known for its ability to penetrate obstacles and provide reliable communication in challenging environments.
NB-IoT
- NB-IoT, or Narrowband IoT, is a Low Power Wide Area Network (LPWAN) technology designed for long-range, low-power IoT applications using licensed cellular bands.
- It provides deeper coverage compared to traditional cellular networks and is optimized for efficient data transmission from a large number of IoT devices.
- NB-IoT is well-suited for applications that require long battery life, such as asset tracking, smart meters, and remote monitoring.
4G
- 4G is a standard for wireless broadband communication, providing high-speed data transmission and low latency for mobile devices and applications.
- It operates in licensed bands and is commonly used for high-bandwidth applications, such as mobile internet access, video streaming, and voice communication.
- 4G offers fast and reliable data connectivity, making it suitable for applications that require real-time data transmission and high-speed internet access.
In summary, LoRa and NB-IoT are tailored for low-power, long-range IoT applications, with the former working in unlicensed spectrum and the latter leveraging licensed cellular bands. On the other hand, 4G provides high-speed, high-bandwidth communication for mobile and data-centric applications. The choice of technology depends on the specific requirements of the application, such as range, power consumption, and data transmission speed.
Q&A
Q: What is a Wireless Temperature Transmitter?
A: A Wireless Temperature Transmitter is a device that measures temperature and wirelessly transmits the data to a monitoring system or control center without the need for physical wiring.
Q: How does a Wireless Temperature Transmitter benefit industrial applications?
A: Wireless Temperature Transmitters eliminate the need for wiring, enabling easy installation, remote monitoring, and real-time temperature data collection in industrial environments, improving efficiency and safety.
Q: What types of temperature sensors are commonly used in Wireless Temperature Transmitters?
A: Wireless Temperature Transmitters can utilize various types of temperature sensors such as thermocouples, RTDs (Resistance Temperature Detectors), thermistors, or infrared sensors based on the specific requirements of the application.
Q: What is the typical wireless range of a Wireless Temperature Transmitter?
A: The wireless range of a Wireless Temperature Transmitter can vary based on the technology used (e.g., Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, Zigbee) and environmental factors, but ranges of up to several hundred meters are common in industrial settings.
Q: How secure is the data transmission in Wireless Temperature Transmitters?
A: Data security is crucial in industrial applications. Wireless Temperature Transmitters incorporate encryption, authentication, and secure communication protocols to ensure the integrity and confidentiality of temperature data.
Q: Can multiple Wireless Temperature Transmitters be integrated to monitor different locations? A: Yes, multiple Wireless Temperature Transmitters can be deployed to monitor temperature variations at various locations within a facility, providing comprehensive temperature data for analysis and control.
Q: What factors should be considered when selecting a Wireless Temperature Transmitter?
A: Factors to consider include temperature range, accuracy, wireless range, battery life, data transmission frequency, compatibility with monitoring systems, and environmental conditions where the transmitter will be deployed.
Feel free to customize these questions or add more based on the specific details of the Wireless Temperature Transmitters you are interested in!
Advantages / Disadvantages
Advantages of Wireless Temperature Transmitters
Wireless temperature transmitters offer several advantages over their wired counterparts. They provide flexibility in terms of installation, enabling the monitoring of temperature in hard-to-reach or hazardous locations. The absence of physical wiring simplifies maintenance and reduces the risk of damage or interference with other equipment. Wireless transmitters can also be easily repositioned or relocated as needed.
In terms of maintenance and management, wireless temperature transmitters may incorporate self-diagnostic capabilities for identifying faults or irregularities in the measurement process. They can also support over-the-air (OTA) firmware updates, allowing for easy software upgrades and ensuring compatibility with evolving wireless protocols or security standards.
Ease of Installation: Wireless temperature transmitters eliminate the need for complex wiring, making installation quick and straightforward, especially in hard-to-reach or remote locations.
Flexibility: Wireless transmitters offer flexibility in terms of placement and relocation, allowing for easy adjustments to changes in the monitoring environment without the constraints of physical cables.
Remote Monitoring: Real-time temperature monitoring and data transmission enable remote access to critical temperature readings, allowing for prompt response to variations or anomalies without the need for on-site visits.
Cost Savings: Wireless temperature transmitters can reduce installation and maintenance costs associated with wiring, conduit, and labor, making them a cost-effective solution for temperature monitoring in industrial settings.
Scalability: Wireless systems can be easily scaled up by adding more transmitters as needed, allowing for expansion or modification of the monitoring network without significant infrastructure changes.
Disadvantages of Wireless Temperature Transmitters
Interference: Wireless signals may be prone to interference from other electronic devices, physical obstructions, or environmental factors, potentially affecting data accuracy and reliability.
Power Source Dependency: Wireless transmitters require a power source, which may be limited in remote or inaccessible locations, requiring careful consideration of power management and battery replacement.
Data Security Concerns: Transmitting temperature data wirelessly introduces security risks such as data interception or unauthorized access, necessitating robust encryption and authentication mechanisms to safeguard sensitive information.
Range Limitations: The wireless range of temperature transmitters may be limited, especially in large industrial facilities or areas with interference, requiring strategic placement of repeaters or signal boosters.
Latency: Wireless communication may introduce latency in data transmission, which could be a concern for applications requiring real-time temperature monitoring and immediate action based on the data received.
By understanding both the advantages and disadvantages of wireless temperature transmitters, businesses can make informed decisions about implementing these devices in their industrial temperature monitoring systems. Proper planning and consideration of these factors can help maximize the benefits and mitigate potential challenges associated with wireless temperature monitoring technologies. I
Applications
Wireless temperature transmitters are suitable for numerous applications across various industries where remote and real-time temperature monitoring is essential. Some common applications where wireless temperature transmitters are beneficial include:
Industrial Monitoring: Wireless temperature transmitters are ideal for monitoring temperature in industrial settings such as manufacturing plants, oil refineries, chemical processing facilities, and food production environments. They allow for continuous monitoring of critical temperatures without the need for manual checks.
HVAC Systems: In heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems, wireless temperature transmitters can be used to monitor and regulate temperature levels in buildings, offices, and commercial spaces, ensuring efficient operation and occupant comfort.
Cold Chain Management: For industries like pharmaceuticals, food storage, and logistics, wireless temperature transmitters help in monitoring temperature-sensitive products throughout the supply chain, ensuring that they are stored at optimal temperatures to maintain quality and safety.
Environmental Monitoring: Wireless temperature transmitters are utilized in environmental monitoring applications such as weather stations, agricultural settings, and research facilities to track temperature variations, analyze trends, and study climate changes.
Laboratories and Research: In scientific research, laboratories, and healthcare facilities, wireless temperature transmitters play a crucial role in monitoring temperature-sensitive experiments, samples, vaccines, and storage conditions to maintain integrity and compliance.
Energy Management: Wireless temperature transmitters help in energy management by monitoring temperature levels in heating and cooling systems, optimizing energy usage, and identifying areas for efficiency improvements in commercial and industrial buildings.
Data Centers: In data centers and server rooms, wireless temperature transmitters are used to monitor equipment temperature, prevent overheating, and ensure optimal conditions for the reliable operation of IT infrastructure.
Greenhouses and Agriculture: Wireless temperature transmitters are valuable in greenhouse monitoring for controlling and maintaining optimal growing conditions for plants, crops, and agricultural produce by monitoring temperature variations.
Equipment Monitoring: Wireless temperature transmitters are employed to monitor temperature-sensitive equipment, machinery, and processes in industries like aerospace, automotive, and electronics manufacturing to prevent overheating and avoid potential damage.
Safety Compliance: In environments where temperature monitoring is critical for safety and regulatory compliance, such as industrial ovens, chemical storage facilities, and clean rooms, wireless temperature transmitters ensure adherence to standards and prevent hazards.
These applications showcase the versatility and importance of wireless temperature transmitters in various sectors where accurate and reliable temperature monitoring is essential for operational efficiency, product quality, and maintaining safety standards. If you have a specific application in mind or need more detailed information, feel free to ask for further assistance!
Downloads
SRSACT-Z3 – Temperature Sensors
Drawings
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.
 A wireless temperature transmitter is a device designed to measure temperature and wirelessly transmit this data to a central monitoring system or receiver. Also, these transmitters play a crucial role in various industries where monitoring and maintaining temperature levels is critical for operational efficiency, safety, and quality control.
A wireless temperature transmitter is a device designed to measure temperature and wirelessly transmit this data to a central monitoring system or receiver. Also, these transmitters play a crucial role in various industries where monitoring and maintaining temperature levels is critical for operational efficiency, safety, and quality control.













Reviews
There are no reviews yet.