Specifications
| Product Name |
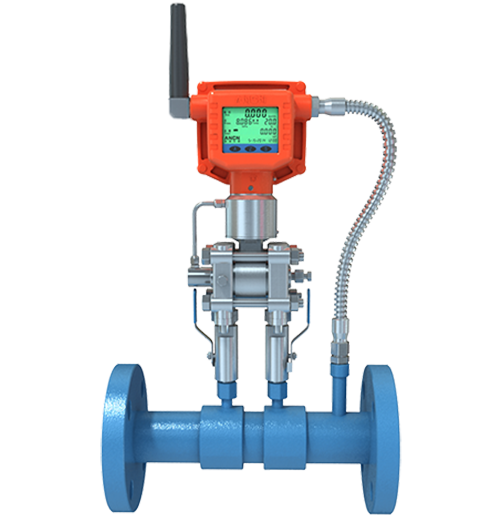
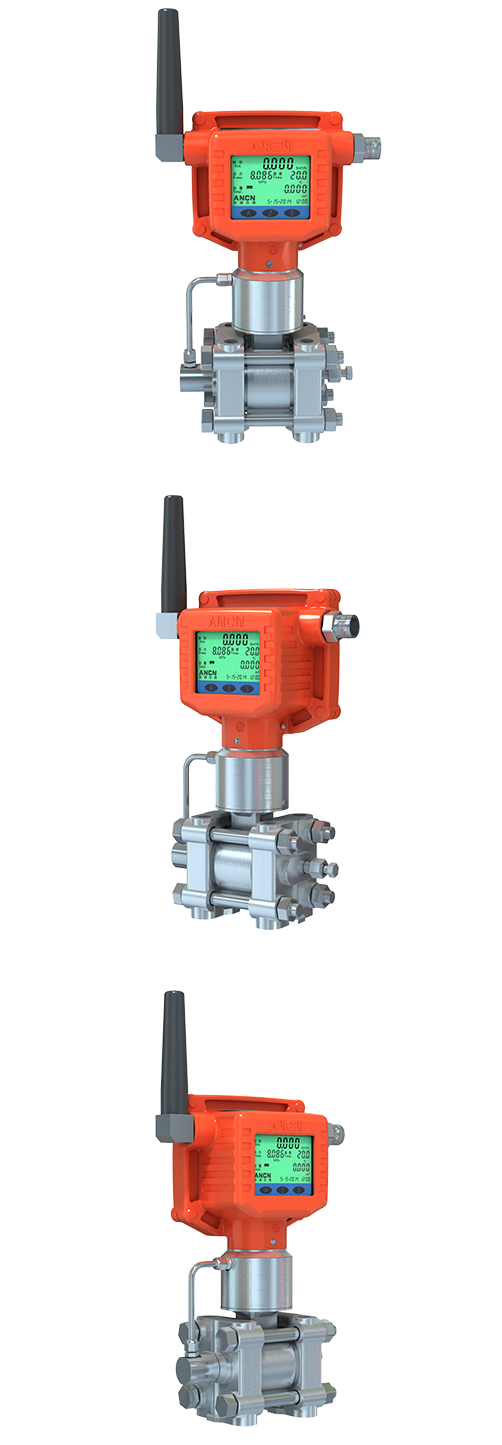
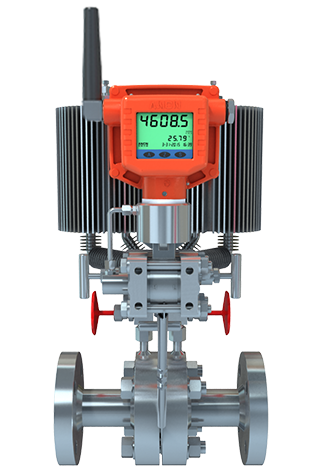
Wireless Flow Meter Sensor |
| Pressure Range |
0 ~ 1500 GPM |
| Configuration method |
Local USB / remote configuration |
| Working power |
3.6V,19Ah |
| Battery Life |
5 years (send data every hour) |
| Power consumption |
Normal work 70mA sleep is less than 0.1mA, data sending and receiving 330mA |
| Display |
large size LCD screen |
| Network format |
NB-IOT/GPRS/4G/LoRa |
| Antenna |
External waterproof antenna |
| SIM Card |
Built-in SIM card |
| Sampling interval |
1 Time / Min |
| Wake-up mode |
Buttons, Timing, USB |
| Upload information |
Flow, Temperature, Signal, Battery Power |
| Working temperature |
-30℃~+70℃ (Medium does not crystallize) |
| Accuracy |
0.5 |
| Temperature influence |
0.015% F.S/℃ |
| Waterproof level |
General Duty / Explosion-Proof |
| Installation |
Vertical and horizontal installation |
| Certificate |
CE, RoHS, Ex d IIB T6 Gb |
Communication Options
LoRa (Long Range), NB-IoT (Narrowband IoT), and 4G are different wireless communication technologies, each with unique characteristics and use cases:
LoRa
- LoRa is a low-power, long-range wireless communication technology designed for connecting battery-operated devices over long distances.
- It operates in the unlicensed radio spectrum, offering long-range connectivity with minimal power consumption, making it suitable for Internet of Things (IoT) applications such as smart city infrastructure, agriculture, and industrial monitoring.
- LoRa is known for its ability to penetrate obstacles and provide reliable communication in challenging environments.
NB-IoT
- NB-IoT, or Narrowband IoT, is a Low Power Wide Area Network (LPWAN) technology designed for long-range, low-power IoT applications using licensed cellular bands.
- It provides deeper coverage compared to traditional cellular networks and is optimized for efficient data transmission from a large number of IoT devices.
- NB-IoT is well-suited for applications that require long battery life, such as asset tracking, smart meters, and remote monitoring.
4G
- 4G is a standard for wireless broadband communication, providing high-speed data transmission and low latency for mobile devices and applications.
- It operates in licensed bands and is commonly used for high-bandwidth applications, such as mobile internet access, video streaming, and voice communication.
- 4G offers fast and reliable data connectivity, making it suitable for applications that require real-time data transmission and high-speed internet access.
In summary, LoRa and NB-IoT are tailored for low-power, long-range IoT applications, with the former working in unlicensed spectrum and the latter leveraging licensed cellular bands. On the other hand, 4G provides high-speed, high-bandwidth communication for mobile and data-centric applications. The choice of technology depends on the specific requirements of the application, such as range, power consumption, and data transmission speed.
Q&A
A Q&A Wireless Flow Meter, which stands for “question and answer for a Wireless Flow Meter,” is a format commonly used to facilitate communication and exchange of information. In a Q&A Wireless Flow Meters, one person asks a question, and another person or group provides an answer or response to that question. This format is widely used in various contexts, such as interviews, discussions, presentations, or online forums. It allows for a structured and organized way of addressing inquiries and obtaining relevant information. Is there anything specific you would like to know about Q&A Wireless Flow Meters?
Q: What is a wireless flow meter?
A: A wireless meter is a type of flow meter that transmits data wirelessly to a remote location. The meter uses sensors to measure the flow of fluid in a pipeline or other system. After that, it sends the data to a receiver or other device using wireless technology such as Bluetooth or Wi-Fi.
Q: What are the benefits of using wireless flow meters?
A: The benefits of using wireless flow meters include increased convenience, flexibility, and accuracy. Wireless meters eliminate the need for complex wiring and can be installed in remote or hard-to-reach locations. They can also be easily moved or repositioned as needed. Additionally, wireless meters can provide real-time data that can be used to monitor system performance. This will also identify potential issues before they become major problems.
Q: What types of fluids can be measured with Q&A Wireless Flow Meters?
A: Wireless meters can be used to measure a wide range of fluids, including liquids and gases. Some meters are designed specifically for use with certain types of fluids. Others are more versatile and can be used with a variety of fluids.
Q: How accurate are wireless meters?
A: The accuracy of wireless flow meters varies depending on factors such as the type of meter, the fluid being measured, and the conditions in which the meter is used. In general, wireless flow meters are highly accurate and can provide precise measurements even in challenging environments.
Q: What is the range of a wireless meter?
A: The range of a wireless meter depends on the specific technology used and the environment in which the meter is used. Some meters have a range of just a few feet, while others can transmit data over long distances. In general, the range of a wireless meter can be extended by using repeaters or other signal boosters.
Q: What is the installation process for a wireless meter?
A: The installation process for a wireless flow meter varies depending on the specific meter and the system being measured. In general, the meter must be placed in a location where it can accurately measure the flow of fluid. After that, it is connected to the wireless network using the appropriate technology. Some wireless meters are designed to be easy to install and can be set up in just a few minutes. Many other types may require more extensive installation and configuration.
Q: Can wireless meters be integrated with other systems?
A: Yes, wireless flow meters can be integrated with other systems, such as SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems or building automation systems. The integration allows for real-time monitoring and control of the flow of fluids in a system. This can also help to improve efficiency and reduce waste.
Q: Are wireless meters more expensive than wired meters?
A: Wireless meters can be more expensive than wired meters due to the additional technology required for wireless communication. However, the cost of wireless meters has decreased over time as the technology has become more widespread and affordable. In some cases, the cost of wireless meters may be offset by the savings in installation costs compared to wired meters.
Q: What is the maintenance required for Q&A Wireless Flow Meters?
A: The maintenance required for wireless flow meters depends on the specific meter and the environment in which it is used. In general, wireless meters require less maintenance than wired meters. This is due to the lack of wiring and connections that can degrade over time. However, regular calibration and cleaning of the meter may be necessary to ensure accurate measurements.
Q: What are the security risks associated with wireless meters?
A: Wireless meters can be vulnerable to hacking or other security threats if they are not properly secured. To mitigate these risks, wireless meters should be encrypted and secured with strong passwords. Additionally, it is important to regularly update the firmware and software used with the meter. This is to ensure that any security vulnerabilities are addressed.
Q: Can flow meters be used in hazardous environments?
A: Yes, wireless flow meters can be used in hazardous environments as long as they are designed and certified for use in such environments. In these cases, the meters may need to meet specific safety standards. Many of these meters are designed to operate in environments with potentially explosive gases or other hazardous materials.
Buy Wireless Flow Meters
Advantages / Disadvantages
Advantages of a Wireless Flow Meter
One of the primary advantages of wireless flow meters is their ability to provide accurate and reliable measurements across different operating conditions. Unlike traditional flow meters, wireless meters allow for continuous monitoring, enabling users to detect any abnormalities or variations in flow rates promptly. This real-time data provides valuable insights for process optimization, maintenance scheduling, and troubleshooting.
Another benefit of wireless flow meters is their remote monitoring capability. As the data is transmitted wirelessly, users can access the information from a central control room, a computer, or even a mobile device, thus ensuring the accessibility of the data at all times. This remote monitoring feature allows for efficient data management, enabling timely decision-making and reducing the need for on-site visits and manual data retrieval.
The wireless nature of these flow meters also contributes to improved safety in industrial settings. With no physical connections, there is a lower risk of leaks, corrosion, or accidents caused by damaged cables. Additionally, wireless meters eliminate the need for workers to access hazardous areas for data retrieval, reducing potential employee exposure to dangerous environments.
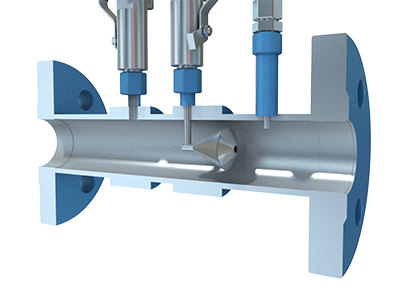
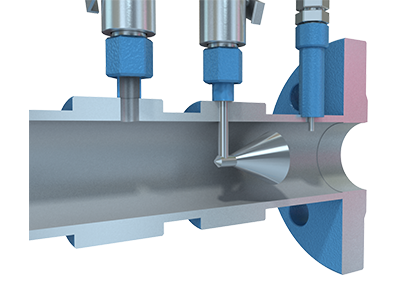
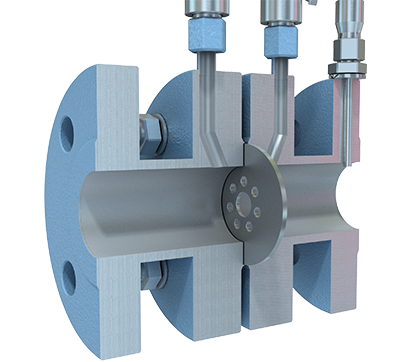
Realize the remote real-time monitoring, wireless transmission, no need site wiring, saves on the ordinary instrument field wiring required. It will save manpower and construction costs. The instrument is advanced in design, has complete specifications, and is easy to install and use. This is the ideal upgrade product for a traditional pressure transmitter. The Wireless Flow Meter is the revolutionary innovation of the traditional differential pressure flow meter system.
Also, wireless products are the future technology of industrial control systems. Physical wiring was used in the past and will always be used on higher power-required applications. Wireless on Temperature, Pressure, Level, and flow are low-power applications and easily converted to wireless signals.
Easy Installation: Wireless flow meters are typically easier to install compared to wired counterparts since there is no need for extensive wiring, conduits, or cables.
Remote Monitoring: Wireless flow meters allow for convenient remote monitoring of flow data, enabling real-time insights and adjustments from a distance.
Cost-Effective: In some cases, wireless flow meters can be more cost-effective to install and maintain, especially in scenarios where wiring can be expensive or challenging.
Scalability: Wireless systems are often easier to expand or modify, allowing for scalability as monitoring needs evolve or new measurement points are added.
Reduced Downtime: Wireless flow meters can help reduce downtime during installation or maintenance, as they can be easily relocated or replaced without disrupting existing infrastructure.
Disadvantages of a Wireless Flow Meter
Signal Interference: Wireless flow meters may be susceptible to signal interference from other wireless devices or environmental factors, which can impact data accuracy or transmission reliability.
Power Requirements: Some wireless flow meters require power sources like batteries or charging, which may need to be regularly maintained or replaced.
Data Security: Wireless transmission of flow data may pose security concerns, as data could be vulnerable to interception or unauthorized access without proper encryption measures.
Limited Range: Depending on the wireless technology used, there may be limitations to the range over which data can be reliably transmitted, especially in large or complex environments.
Compatibility Issues: Compatibility with existing systems or protocols may be a challenge when integrating wireless flow meters into an existing monitoring infrastructure, requiring additional configuration or adapters.
These advantages and disadvantages can vary depending on the specific wireless flow meter technology, application, and environmental factors. It’s essential to consider these factors when choosing a wireless flow meter for a particular use case.
Applications
Industries and Applications
Wireless flow meters are highly versatile and can be utilized in a wide range of industries and applications. They find applications in sectors such as oil and gas, water and wastewater management, chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, food and beverage, HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning), and many more. In these industries, wireless flow meters are essential for monitoring and controlling flow rates, ensuring optimal efficiency and compliance with regulatory standards.
Oil and Gas
In the oil and gas industry, for example, wireless flow meters are used for measuring the flow of crude oil, natural gas, refined products, and various chemicals. These measurements are crucial for production optimization, custody transfer, and leakage detection. With their wireless capabilities, these meters enable real-time monitoring across vast oil fields, ensuring early detection and mitigation of issues that could potentially impact operations.
Water and Wastewater
Water and wastewater management is another application where wireless flow meters play a vital role. These meters allow for continuous monitoring of water flow within pipelines, reservoirs, and treatment plants. This data helps in identifying leakage points, minimizing water loss, and optimizing the distribution networks. Similarly, in the food and beverage industry, wireless flow meters assist in maintaining accurate flow measurements during processes such as mixing, blending, and bottling, ensuring product consistency and quality.
In conclusion, the wireless flow meter offers numerous advantages over traditional meters by providing accurate, real-time flow measurements, remote monitoring capabilities, and enhanced safety. Their versatility makes them suitable for a wide range of applications across various industries. With continuous advancements in wireless technology, these meters are poised to revolutionize the way flow measurements are conducted, helping industries optimize processes, reduce costs, and improve overall efficiency.
Downloads
Drawings
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.











Reviews
There are no reviews yet.