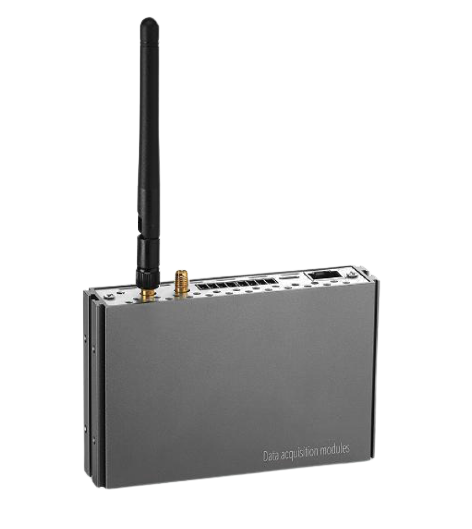
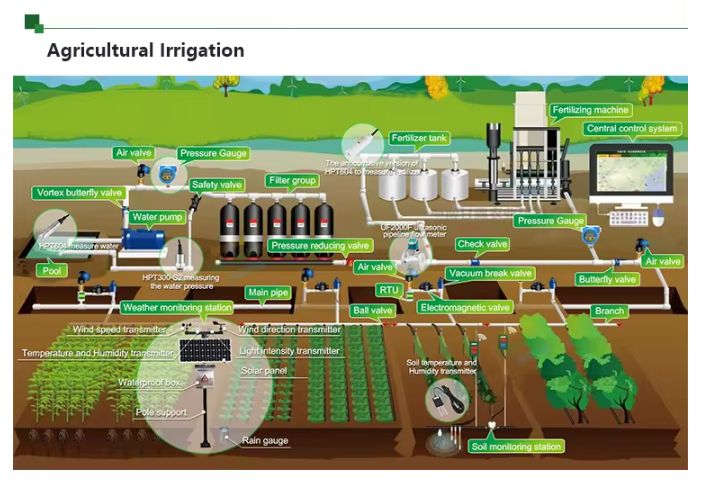
Description
A wireless gateway with Modbus RS485 communication capabilities is a device used in industrial automation and control systems like Temperature Sensors, Pressure Sensors, Level Sensors and Flow Meters that are wireless configured to enable communication between Modbus devices over a wireless network. Here is a breakdown of its key components and functionality:
Components of Wireless Gateways
Wireless Gateway Connectivity:
The gateway is equipped with wireless communication protocols such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, or Zigbee to connect to Modbus devices wirelessly.
RS485 Interface:
The gateway includes an RS485 interface, a common serial communication protocol used in industrial automation, to connect with Modbus devices using a wired connection.
Processors:
The gateway houses a processor responsible for handling data exchange between Modbus devices and translating the data for the wireless network.
Power Supply:
It requires a power supply to operate and may be designed for both AC and DC power sources commonly found in industrial settings.
Antennas:
Antennas are integrated into the gateway to ensure reliable wireless communication within the specified range.
Functionality of Wireless Gateways
Data Conversion:
The gateway acts as a bridge between Modbus RTU or Modbus TCP devices connected via RS485 and the wireless network, converting Modbus data packets for transmission over the wireless protocol.
Remote Monitoring and Control:
By incorporating connectivity, the gateway enables remote monitoring and control of Modbus devices from a centralized location using a computer or smart device.
Data Logging:
Some gateways provide data logging capabilities to store historical data from Modbus devices, enabling analysis and troubleshooting.
Security Features:
To ensure data integrity and secure communication, the gateway may incorporate encryption and authentication mechanisms to protect sensitive information.
Scalability:
They are designed to be scalable, allowing easy integration with existing Modbus systems and the addition of new devices as needed.
Configuration Options:
Users can typically configure settings such as data transmission rates, network parameters, and security protocols to tailor the gateway to specific industrial applications.
Overall, a gateway with Modbus RS485 communication enhances flexibility, scalability, and convenience in industrial environments, enabling efficient and reliable communication between Modbus devices over a wireless network.
Specifications
| Wireless Technology
& Parameters |
Wireless spectrum |
ZigBee:ISM(2.4~2.5)GHz(IEEE 802.15.4 DSSS) |
| Wireless HART:ISM(2.4~2.5)GHz(IEEE 802.15.4 DSSS) |
| GPRS/CDMA:Meet the standard of GPRS/CDMA 1x Regulations |
| Wireless authentication |
Zigbee:FCC ID: MCQ-XBS2C,IC: 1846A-XBS2C |
| WirelessHART:IEC 62591 HART,GB/T 29910.1~ 6-2013 HART |
| GPRS/CDMA: Meet the Standard of ETSI GSM Phase 2+、 FCC/SAR and CDG 1/2&3 Standards |
| Wireless Protocol |
Zigbee:Zigbee 2007( compatible with CNPC’S A11-GRM Communication Protocol) |
| WirelessHART:IEC62591 |
| GPRS/CDMA:Meet the Standard of GPRS/CDMA 1x Regulations |
| Receive Sensibility |
ZigBee:-100dBm |
| WirelessHART:-95dBm |
| GPRS/CDMA: Meet the standard of GPRS/CDMA 1x Regulations |
| Transmit Power |
ZigBee:8dBm(6.3mW) |
| WirelessHART:8dBm(6.3mW) |
| GPRS/CDMA:Meet the Standard of GPRS/CDMA 1x Regulation |
| Communication Distance |
ZigBee:300m、800m |
| WirelessHART:300m、800m |
|
|
GPRS/CDMA:Meet the standard of GPRS/CDMA 1x Regulations |
| Network
Security |
AES-128 encryption algorithm, network authentication
and network authorization |
| Interference
resistant ability |
Automatic frequency hopping |
| Uplink
communication interface |
RS485(MODBUS-RTU) |
| Ethernet Interface (MODBUS-TCP) |
| Output Signal |
8 Wires (4 ~ 20) mA output, output accuracy: 0.2%FS |
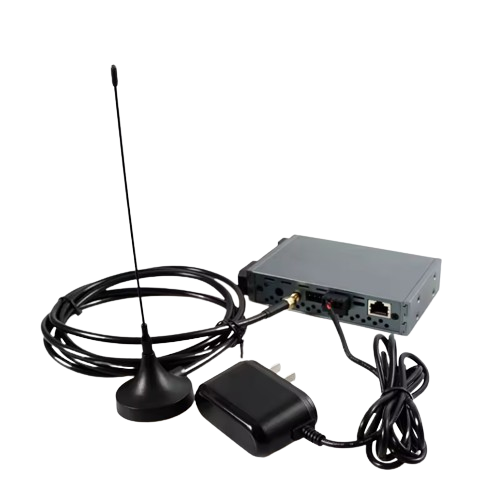
| Power Supply |
(12~30)V DC |
| Whole System
Power |
< 3W |
| Environmental
Temperature |
(-30~70)℃ |
| Relative
Humidity |
<90% |
| Atmospheric
Pressure |
(86~106)kPa |
| Protection
Grade |
IP65 |
| Antenna |
Short stick type fixed antenna, extended wire type
suction cup antenna |
| Dimension (Unit: mm) |
Q&A
Q: What is a Wireless Gateway?
A: A Wireless Gateway is a device that acts as a bridge between wireless sensors or instruments and a central control system, enabling data communication without the need for physical wires.
Q: How does a Gateway benefit industrial instrumentation?
A: Wireless Gateways allow for easier installation, reduced maintenance costs, and improved flexibility in industrial settings. They enable remote monitoring, control, and data collection from sensors spread throughout a facility.
Q: What types of communication protocols are typically supported by Wireless Gateways
A: Wireless Gateways can support various protocols like Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, LoRa, and others depending on the specific requirements of the industrial application.
Q: How secure are Gateways for industrial use?
A: Security is essential in industrial settings. Wireless Gateways incorporate encryption, authentication, and other security measures to ensure the integrity and confidentiality of data transmitted wirelessly.
Q: Can a Wireless Gateway integrate with existing industrial control systems?
A: Yes, Wireless Gateways are designed to seamlessly integrate with existing control systems through standard interfaces and protocols, enabling a smooth transition to wireless communication.
Q: What factors should be considered when selecting a Wireless Gateway for industrial instrumentation?
A: Factors to consider include range and reliability of wireless communication, compatibility with existing infrastructure, data processing capabilities, security features, scalability, and vendor support.
Feel free to customize these questions or add more based on the specific details of the Wireless Gateway you are interested in! If you need more assistance with this topic, feel free to ask.
Advantages / Disadvantages
Advantages of Wireless Gateways for Industrial Instrumentation:
Increased Flexibility: Wireless Gateways eliminate the need for physical wiring, allowing for easier installation and reconfiguration of sensors and instruments in industrial settings.
Cost-Effective: Wireless Gateways can lower installation and maintenance costs associated with physical cabling, especially in large industrial facilities where wiring can be complex and expensive.
Scalability: Wireless Gateways offer scalability, allowing for easy expansion or modification of the network by adding more sensors or devices without the constraints of wired infrastructure.
Remote Monitoring: With Wireless Gateways, industrial processes, and equipment can be remotely monitored in real-time, enabling quick decision-making, predictive maintenance, and improved operational efficiency.
Improved Safety: Wireless Gateways enhance safety by providing continuous monitoring of critical parameters, machinery conditions, and environmental factors without the need for manual checks in hazardous or hard-to-reach areas.
Data Accessibility: Wireless Gateways facilitate the collection and transmission of data from sensors to centralized control systems, enabling better data analysis, visualization, and decision support for industrial operations.
Disadvantages of Wireless Gateways for Industrial Instrumentation:
Interference and Signal Strength: Wireless communication can be susceptible to interference from other devices or physical obstacles, potentially affecting signal strength and data transmission reliability.
Security Concerns: Although security features are implemented in Wireless Gateways, there is always a risk of unauthorized access, data breaches, or potential cyber threats that need to be addressed to ensure the integrity of industrial data.
Compatibility Issues: Integrating Wireless Gateways with existing industrial systems or protocols may present compatibility challenges, requiring careful planning and potentially additional configuration or adaptation.
Limited Range: The range of wireless communication supported by Wireless Gateways may be limited, especially in large industrial environments, which can impact the coverage area and necessitate strategic placement of gateways or repeaters.
Power Requirements: Wireless Gateways require a power source to operate, which may pose challenges in locations where access to electrical outlets or battery replacement is not convenient or feasible.
Data Latency: In some cases, wireless communication may introduce latency in data transmission, which can be a concern for time-sensitive industrial applications that require real-time responsiveness.
Overall, the advantages of Wireless Gateways for industrial instrumentation often outweigh the disadvantages, especially when considering the enhanced flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and operational efficiencies they can bring to industrial processes. Understanding and mitigating the potential challenges associated with wireless technology is crucial for successful implementation in industrial settings. If you need more specific information or have further questions, feel free to ask for assistance!
Applications
Here are some common applications where Wireless Gateways for industrial instrumentation are beneficial:
Remote Monitoring and Control: Gateways enable real-time monitoring and control of industrial processes, equipment, and environmental conditions from a central location, improving operational efficiency and reducing downtime.
Asset Tracking: In industries where tracking the location and status of assets is crucial, Wireless Gateways can be used to connect with sensors and tags attached to equipment, inventory, or vehicles, providing accurate and up-to-date information.
Environmental Monitoring: Wireless Gateways can be deployed for monitoring environmental parameters such as temperature, humidity, air quality, and vibration in industrial facilities to ensure compliance with regulations and maintain optimal working conditions.
Predictive Maintenance: By integrating Wireless Gateways with sensors on machinery and equipment, predictive maintenance strategies can be implemented, detecting potential issues early and scheduling maintenance tasks before costly breakdowns occur.
Energy Management: Wireless Gateways can collect data from energy meters, sensors, and control systems to optimize energy usage, identify areas for improvement, and reduce operational costs in industrial facilities.
Safety and Security: Implementing Wireless Gateways for surveillance cameras, access control systems, and emergency response devices enhances safety and security measures in industrial settings, offering real-time alerts and monitoring capabilities.
Inventory Management: Wireless Gateways play a vital role in inventory tracking and management by providing visibility into inventory levels, movement of goods, expiration dates, and reorder points, streamlining supply chain operations.
Process Automation: Wireless Gateways facilitate process automation by connecting sensors and actuators to control systems, enabling efficient operation of manufacturing processes, material handling systems, and industrial machinery.
These are just a few examples of the wide range of applications where Wireless Gateways for industrial instrumentation can make a significant impact. Each industry and use case may have specific requirements that can be optimized with the right choice of Wireless Gateway technology. If you have a particular application in mind or need more detailed information, feel free to ask!
Drawings
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.






Reviews
There are no reviews yet.