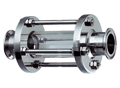
Description
Inline Sight Glasses is a transparent or semi-transparent device used in industrial processes to visually inspect the flow of fluids. Operators also use it to detect the presence of foreign particles within a pipeline. Typically, it consists of mounting a strong, transparent glass or plastic tube in line with the pipeline. This allows operators to observe the contents of the pipe without interrupting the flow.
The main components of an inline sight glass include the transparent tube, gaskets, and metal or plastic housing. Materials like borosilicate glass or acrylic, which are resistant to corrosion and capable of withstanding high temperatures and pressures, typically make the transparent tube. The housing securely holds the tube in place, typically made of stainless steel, carbon steel, or PVC for durability and compatibility with different types of fluids.
Gaskets
Operators use gaskets to create a tight seal between the sight glass and the pipeline, preventing leaks and ensuring the proper functioning of the device. Depending on the application and the fluid being monitored, different types of gaskets such as EPDM, PTFE, or Viton. Operators may use this to maintain compatibility and prevent contamination of the process fluid.
Inline sight glasses come in various sizes and configurations to suit different applications and flow rates. Operators can equip them with additional features such as illumination, wipers, and pressure indicators to enhance visibility. It will also enhance monitoring capabilities. Illuminated sight glasses use built-in LED lights or external light sources to improve visibility in low-light conditions. Operators also use it when inspecting opaque fluids.
Industrial Settings for Sight Glasses
In industrial settings, operators use inline sight glasses in a wide range of applications across various industries. These industries include food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, petrochemicals, and water treatment. Operators commonly install them in pipelines to monitor the flow of liquids, gases, or powders. They are also used to verify the effectiveness of filtration systems or the presence of contaminants.
The installation of an inline sight glass is a relatively straightforward process that involves cutting the pipeline and inserting the sight glass between two pipe flanges. Using bolts or clamps, operators secure the device in place. Furthermore, this involves compressing the gaskets to establish a tight seal. Finally, proper installation and maintenance of the sight glass are essential to prevent leaks, ensure accurate monitoring, and prolong the operational life of the device.
In summary, an inline sight glass is a valuable tool for process monitoring and quality control in industrial pipelines. By providing a visual indication of the flow of fluids and the condition of the process stream. As a result, the sight glasses help operators optimize production processes. It also helps with troubleshooting issues and ensures the safety and efficiency of industrial operations.
Specifications
| For Use With |
Hydrocarbons / Water / Oils |
| Body Material |
304SS / 316SS |
| Connection Type |
Pipe |
| Pipe Connection Type |
Threaded |
| Pipe Size |
Selectable when purchasing |
| Gender |
Female |
| Temperature Range |
-20° to 250° F |
| Window Type |
Tubular |
| Window Material |
Glass |
| Maximum Pressure |
150 psi @ 70° F |
| Mounting |
|
| Location |
Inline |
| Orientation |
Any Position |
| Direction of Flow |
Any Direction |
| Indicator Type |
No Indicator |
Installation
Installing an industrial inline sight glass involves several important steps to ensure proper function and safety. Here’s a general procedure for the installation:
Preparation
Read Manufacturer’s Instructions: Always start by reading the manufacturer’s installation instructions specific to your sight glass model.
Inspect Components: Check all components for any damage or defects before installation.
Gather Tools and Materials: You’ll need wrenches, gaskets, sealants, and possibly a pipe wrench or spanner.
Shut Down and Drain System
Shut Down Equipment: Ensure the system is completely shut down and isolated from any power sources.
Drain the System: Fully drain the pipeline where the sight glass will be installed to avoid any spillage and to ensure a clean installation area.
Prepare the Pipe
Clean the Flange Faces: Clean the flange faces where the sight glass will be installed. Remove any old gaskets, debris, or rust.
Check Pipe Alignment: Ensure that the pipe ends are properly aligned. Misalignment can cause damage to the sight glass.
Install the Gaskets
Apply Gaskets: Place new gaskets on the flanges. Make sure they are correctly positioned and free from any folds or damage.
Install the Sight Glass
Position the Sight Glass: Carefully position the sight glass between the flanges. Ensure it is properly aligned with the bolt holes.
Secure the Sight Glass: Insert and tighten the bolts evenly in a cross pattern to avoid warping. Follow the manufacturer’s recommended torque specifications for the bolts.
Check for Leaks
Re-fill the System: Slowly re-fill the system with the appropriate fluid or gas.
Inspect for Leaks: Check around the sight glass for any leaks. If any are found, tighten bolts as necessary or inspect for proper gasket seating.
System Startup
Gradual Startup: Gradually bring the system back online, monitoring the sight glass for any signs of issues.
Monitor Operation: Observe the sight glass during operation to ensure it’s functioning correctly and there are no leaks.
Final Checks
Verify Operation: Ensure the sight glass is providing clear visibility as intended.
Document Installation: Record the installation details for future reference and maintenance.
Safety Tips
- Wear Protective Gear: Use appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) during installation.
- Handle with Care: Sight glasses are often made of glass or other delicate materials that can be easily damaged.
- Consult Professionals: If unsure about any part of the installation process, consult with a professional or the manufacturer for guidance.
Following these steps will help ensure a proper and safe installation of an inline sight glass.
Maintenance
Maintaining an industrial inline sight glass is crucial for ensuring its proper function and longevity. Here’s a comprehensive maintenance procedure to follow:
Routine Inspection
- Frequency: Perform visual inspections at regular intervals based on the operating conditions and manufacturer’s recommendations.
- Check for Leaks: Examine the sight glass and surrounding flanges for any signs of leakage.
- Inspect Glass Condition: Look for any cracks, chips, or other signs of damage on the sight glass.
Cleaning
- Frequency: Clean the sight glass periodically or as needed based on the type of fluid being handled and the operating conditions.
Cleaning Procedure:
Shut Down System: Ensure the system is turned off and the pressure is relieved.
Drain Fluid: If required, drain the fluid from the pipeline to avoid spills.
Remove Sight Glass: Carefully remove the sight glass from the pipeline.
Clean the Glass: Use a non-abrasive cleaner and a soft cloth or sponge to clean the glass. Avoid harsh chemicals that could damage the glass or gaskets.
Clean Flanges: Clean the flange surfaces where the sight glass mounts to ensure a good seal during reinstallation.
Check Gaskets and Seals
- Inspect for Wear: Examine gaskets and seals for signs of wear, damage, or deformation.
- Replace if Necessary: Replace gaskets or seals if they show any signs of deterioration or if leaks are detected.
Reinstallation
- Inspect Components: Before reinstalling, inspect the sight glass and all associated components for damage or wear.
Reinstall Sight Glass:
Reapply Gaskets: Place new gaskets if needed.
Align and Secure: Align the sight glass with the flange holes and secure it with bolts. Tighten bolts evenly in a cross pattern to avoid distortion.
Check Alignment: Ensure the sight glass is properly aligned and centered in the pipeline.
System Testing
- Pressure Test: If applicable, conduct a pressure test to ensure there are no leaks and the sight glass is properly sealed.
- Operational Check: Observe the sight glass during system startup to ensure it functions correctly and provides a clear view.
Documentation
- Record Maintenance: Document all maintenance activities, including inspections, cleaning, and replacements. This helps in tracking the history of the sight glass and planning future maintenance.
Safety Considerations
- Personal Protective Equipment: Always wear appropriate PPE, such as gloves and safety goggles, when handling and cleaning the sight glass.
- Handle with Care: Sight glasses are delicate and should be handled carefully to avoid damage.
Troubleshooting
- Cloudy or Dirty Glass: If the glass becomes cloudy or dirty despite cleaning, check for residual build-up or contamination in the fluid. Consider additional filtration if needed.
- Cracking or Leaking: If you observe cracks or leaks, shut down the system immediately and replace the sight glass or any damaged components.
Regular maintenance of the sight glass ensures optimal performance and helps in preventing unexpected downtime and potential hazards. Always refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines for specific maintenance recommendations related to your sight glass model.
Q&A
Q: What is an industrial sight glass?
A: An industrial sight glass is a transparent or translucent window typically made of glass or durable material that allows visual observation of processes, fluids, or components within industrial equipment or systems.
Q: Where are industrial sight glasses commonly used?
A: Industrial sight glasses are commonly used in various industrial applications, including pipelines, tanks, pressure vessels, boilers, reactors, and other equipment where visual inspection of fluids, levels, or processes is necessary.
Q: What are the primary purposes of industrial sight glasses?
A: The primary purposes of industrial sight glasses are to provide a visual indication of fluid levels, color, clarity, flow, or conditions inside equipment, facilitating monitoring, inspection, and maintenance of industrial processes.
Q: What are the different types of industrial sight glasses available?
A: Industrial sight glasses come in various types, such as flat sight glasses, cylindrical sight glasses, reflex sight glasses, tubular sight glasses, and armored sight glasses, each designed for specific applications and operating conditions.
Q: How are industrial sight glasses installed and maintained?
A: Industrial sight glasses are typically installed by attaching them to flanged connections or directly onto equipment using gaskets and seals. Maintenance involves regular cleaning, inspection for cracks or damage, and replacement of sight glass components when necessary.
Q: What are the benefits of using industrial sight glasses in industrial processes?
A: Industrial sight glasses offer visual transparency, allowing operators to monitor processes in real-time, detect leaks, observe fluid interfaces, assess mixing efficiency, and ensure safety by visually inspecting equipment under operating conditions.
Q: How do industrial sight glasses enhance operational efficiency and safety?
A: By providing a visual window into industrial processes, sight glasses enable operators to make informed decisions, troubleshoot issues, prevent overflows or spills, optimize processes, and ensure compliance with safety regulations.
Q: Are there specialized sight glasses for high-pressure or corrosive environments?
A: Yes, there are sight glasses designed specifically for high-pressure, high-temperature, or corrosive environments, constructed with materials such as borosilicate glass, tempered glass, or specialized metals to withstand demanding industrial conditions.
Feel free to ask if you have more specific questions or require additional information on industrial sight glasses or related topics!
Advantages / Disadvantages
An inline sight glass, also known as an inline viewport or flow indicator, is a specific type of sight glass that is integrated directly into a pipeline or process system. It offers several advantages and disadvantages:
Advantages of Sight Glasses
Real-time visibility
An inline sight glass provides instant visual observation of the flow within the pipeline or process system. This allows operators to monitor the movement, behavior, and characteristics of the fluid in real-time.
Process optimization
By visually assessing the flow patterns and conditions, operators can identify any abnormalities or issues that may impact the efficiency or performance of the system. This enables timely adjustments, troubleshooting, and optimization of the processes as required.
Safety and troubleshooting
Inline sight glasses offer a means to visually inspect the movement of fluids. This helps operators identify any potential blockages, leaks, or irregularities. Furthermore, it may lead to safety hazards or system failures. Additionally, this facilitates prompt action and preventive maintenance, reducing the risk of accidents or equipment damage.
Compact design
Inline sight glasses are designed to be installed directly into the pipeline. It helps save valuable space and can be particularly beneficial in applications where limited space is available.
Versatile applications
Inline sight glasses can be used in various industries and applications, including chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, food and beverage, oil and gas, and more. Finally, their adaptability allows for monitoring a wide range of fluid types and process conditions.
Disadvantages of Sight Glasses
Limited access for cleaning and maintenance
Installing an inline sight glass directly into the pipeline may make it challenging to access and clean the sight glass itself. Also, regular cleaning and maintenance are essential to maintain visibility and prevent any obstruction. During this, it may require additional effort, such as disassembling parts of the system or using specialized cleaning equipment.
Risk of breakage or damage
Inline sight glasses are exposed to the full flow pressure, temperature, and process conditions within the pipeline. Therefore, there is an inherent risk of breakage or damage due to mechanical stress, pressure surges, thermal expansion, or chemical attack. In conclusion, selecting robust materials and proper installation techniques are crucial to mitigate this risk.
Limited visibility in some applications
Depending on the flow characteristics or fluid properties, the visibility through the inline sight glass may be limited. Moreover, for example, if the fluid is opaque or contains solid particles that obstruct visibility. If this occurs, the effectiveness of the sight glass may be compromised.
Pressure and temperature limitations
Inline sight glasses have specific pressure and temperature limitations based on their design and material of construction. Additionally, in applications with extreme conditions, such as high pressures or temperatures. Under these conditions, specialized sight glasses may be required to ensure reliable and accurate visibility.
It’s important to note the advantages and disadvantages outlined above. This may vary depending on the specific design, material selection, and application requirements of the inline sight glass. Additionally, it’s recommended to consult and work with knowledgeable professionals and manufacturers. If you do, it will help you choose the most suitable sight glass for your particular needs.
Applications
Common Sight Glass Applications
There are several uses for sight glasses and the varying forms they can take. A sight glass is especially useful for monitoring fluids in pipe systems. It helps you keep an eye on the pressure in boilers, and ensure that the pilot lights and heating elements are functioning properly in heating systems.
Sight glasses are used across a huge range of industries, including:
- Utilities and power
- Pharmaceuticals
- Food and beverage
- Biofuels
- Wastewater treatment and management
- And chemical/petrochemical
The most well-known application for sight glasses is monitoring fluids since companies of all kinds must monitor fluids. This will ensure optimal quality and safety; after all, everything from petrochemical industries to craft breweries work with liquids.
This makes sight glasses critical components for ensuring operations run smoothly and safely. Liquid level gauges, another form of sight glass, are often used in industries with storage tanks or containment systems designed to mix or ferment.
Sight glasses and sight glass windows, as mentioned earlier, are commonly used in industries that use pressurized systems. This includes steam boilers and steam generators are found in a wide variety of industries, such as utilities and power generation, cement production, food and beverage, and dry cleaning.
Pressurized
All processes that require pressurized systems or vaporization use sight glass windows in some manner. They are used for monitoring liquids and ensuring optimal safety. Boiler systems also use a more specialized type of sight glass, called boiler sight glass. It is used to monitor the pressure within.
Industries that utilize heat or heat transfer make use of sight glasses as well. Many of the heating systems in these applications contain a viewport or sight port to ensure the system is functioning properly.
In these scenarios, the operators certainly can’t look directly inside the heating system. This is to make sure the pilot lights or heating elements are still working. This is why the viewport is such a critical component in the overall system.
Downloads
Drawings