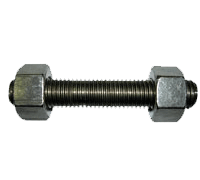
Description
An In-Depth Overview of Stud Bolts with Nuts
Introduction
Stud bolts and stud nuts are crucial components in mechanical and structural assemblies, widely used in various industries including construction, automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing. Additionally, these fasteners play an essential role in ensuring the stability and integrity of joints and connections. Furthermore, understanding their design, application, and installation can significantly impact the performance and safety of engineered systems.
Stud Bolts
Definition and Design
A stud bolt is a cylindrical fastener with threads along its entire length or a portion of it. Unlike traditional bolts with a head, stud bolts lack a head and are designed for insertion into a threaded hole or nut. Additionally, use them where high-strength and precise fastening are required. Furthermore, stud bolts can come in various grades and materials, tailored to meet specific requirements of strength, corrosion resistance, and temperature tolerance.
Types of Stud Bolts
- Fully Threaded Studs: Also, these have threads running the entire length, allowing for flexibility in the length of the engagement in nuts or threaded holes.
- Partially Threaded Studs: In addition, these feature threads only on part of their length, with the unthreaded section often used for aligning or positioning parts.
- Double Ended Studs: These studs have threads at both ends, allowing for attachment of nuts on both sides of the joint.
- Tap-End Studs: Also, designed with a tapered end, which makes them suitable for situations requiring easy alignment and insertion.
Materials and Coatings
Stud bolts are manufactured from a variety of materials depending on the application:
- Carbon Steel: Commonly used for general-purpose applications due to its affordability and strength.
- Alloy Steel: Used in high-stress applications for enhanced strength and durability.
- Stainless Steel: Provides excellent corrosion resistance, making it suitable for harsh environments.
- High-Temperature Alloys: Such as Inconel or Monel, used in extreme temperature applications.
Apply coatings like zinc plating, hot-dip galvanizing, and black oxide to enhance corrosion resistance and wear properties.
Applications
- Structural Engineering: Used in construction and civil engineering to join structural elements like beams and columns.
- Automotive Industry: Applied in engine assemblies and chassis components for robust and reliable connections.
- Oil and Gas: Utilized in pipelines and drilling rigs where high strength and corrosion resistance are critical.
- Aerospace: Employed in aircraft and spacecraft for lightweight and high-strength applications.
Stud Nuts
Definition and Design
A stud nut is a type of nut specifically designed to fit onto a stud bolt. Moreover, unlike standard nuts, stud nuts often have a design that accommodates the threaded portion of the stud bolt. Finally, they come in various forms including hexagonal, round, and flanged, depending on the application requirements.
Types of Stud Nuts
- Hex Nuts: The most common type, featuring a six-sided design that allows for easy tightening and loosening with standard wrenches.
- Lock Nuts: Designed with features such as nylon inserts or deformed threads to prevent loosening due to vibrations.
- Flange Nuts: Equipped with a flange that distributes the load over a larger area, reducing the risk of damage to the mating surface.
- Coupling Nuts: Used to join two studs or extend the length of a stud.
Materials and Coatings
Manufacturers make stud nuts from materials compatible with the stud bolts to ensure a secure fit and resistance to environmental conditions.
- Carbon Steel: Provides strength for general applications.
- Stainless Steel: Offers resistance to corrosion, suitable for use in harsh environments.
- Brass and Bronze: Used in applications where non-ferrous materials are required for conductivity or corrosion resistance.
Apply coatings such as zinc plating, cadmium plating, and anodizing to enhance the performance of stud nuts in various environments.
Applications
- Construction: Used in structural steelwork to secure components and provide stability.
- Machinery: Applied in industrial machinery for reliable connections under vibration and load.
- Automotive: Employed in vehicle assembly to secure engine and transmission components.
- Marine: Utilized in shipbuilding and offshore platforms to withstand marine conditions.
Installation and Maintenance
Installation Procedures
- Preparation: Ensure that the threads on both the stud bolt and the stud nut are clean and free from debris. Also, this ensures a proper fit and reduces the risk of cross-threading.
- Alignment: Insert the stud bolt into the threaded hole or nut and ensure you align it properly. Use alignment tools if necessary.
- Tightening: Use appropriate tools, such as torque wrenches, to tighten the stud nut to the recommended torque specifications. Furthermore, this ensures the joint achieves the desired clamping force without over-tightening.
Maintenance of Stud Bolts and Nuts
- Inspection: Regularly inspect stud bolts and nuts for signs of wear, corrosion, or damage. Replace any components that show signs of deterioration.
- Lubrication: Apply anti-seize lubricant to the threads of stud bolts and nuts to prevent seizing and make future disassembly easier.
- Retightening: In applications subject to vibration or temperature changes, periodically check and retighten the nuts to maintain proper tension.
Conclusion
Stud bolts and stud nuts are essential components in a wide range of applications, from construction and automotive to aerospace and marine industries. In addition, their ability to provide strong, reliable connections makes them invaluable in ensuring the integrity and safety of mechanical systems. Finally, understanding their design, material options, and proper installation and maintenance practices helps in selecting the right components for specific applications and ensuring their optimal performance over time.
You might be interested in other materials:
Piping
Fittings
Specifications
General Description
Stud bolts with nuts are fasteners used to create strong, reliable connections between components in various industrial and engineering applications. Stud bolts are cylindrical, threaded rods without heads, and nuts are used to secure them in place. This combination is crucial for applications requiring high strength, precise alignment, and resistance to environmental factors.
Materials
- Carbon Steel:
- Grade: ASTM A193 B7 or equivalent.
- Properties: High tensile strength, used for general-purpose applications.
- Coating: Hot dip galvanized, or zinc plated for corrosion resistance.
- Alloy Steel:
- Grade: ASTM A193 B16 or equivalent.
- Properties: Enhanced strength and hardness, suitable for high-stress environments.
- Coating: Black oxide or phosphate for protection against corrosion.
- Stainless Steel:
- Grade: AISI 304, 316, or equivalent.
- Properties: Excellent corrosion resistance, suitable for harsh environments.
- Coating: Typically, uncoated but can be passivated for extra protection.
- Special Alloys:
- Grade: Inconel, Monel, or other high-temperature alloys.
- Properties: Designed for extreme temperature and corrosive conditions.
- Coating: Often not required due to inherent material properties.
Dimensions
- Thread Size:
- Range: Typically, from M6 to M64 or ¼” to 2” nominal diameter.
- Standard: Metric (ISO) or Unified Thread Standard (UTS) depending on regional requirements.
- Length:
- Range: Custom lengths available, with standard lengths commonly ranging from 1” to 12” (25mm to 300mm).
- Thread Type:
- Metric Threads: ISO M series.
- Unified Threads: UNC (Coarse) and UNF (Fine).
- Nut Dimensions:
- Type: Hexagonal, flanged, lock nuts, or coupling nuts.
- Standard: Sizes to match corresponding stud bolts, with standard hex nuts typically conforming to ANSI B18.2.2 or ISO 4032.
Mechanical Properties
- Tensile Strength:
- Carbon Steel: Minimum 125 ksi (860 MPa) for ASTM A193 B7.
- Alloy Steel: Minimum 150 ksi (1035 MPa) for ASTM A193 B16.
- Stainless Steel: Minimum 70 ksi (485 MPa) for AISI 304.
- Yield Strength:
- Carbon Steel: Minimum 105 ksi (720 MPa) for ASTM A193 B7.
- Alloy Steel: Minimum 130 ksi (895 MPa) for ASTM A193 B16.
- Stainless Steel: Minimum 30 ksi (205 MPa) for AISI 304.
- Hardness:
- Carbon Steel: Typically, Rockwell C25-C32.
- Alloy Steel: Typically, Rockwell C30-C36.
- Stainless Steel: Typically, Rockwell B70-B90.
Coatings and Finishes
- Zinc Plating: Provides basic corrosion resistance and is commonly used for carbon steel fasteners.
- Hot-Dip Galvanizing: Offers a thicker coating for enhanced protection against rust and corrosion.
- Black Oxide: Provides a thin, non-reflective finish for improved corrosion resistance and wear properties.
- Passivation: Enhances the natural oxide layer on stainless steel for improved corrosion resistance.
Standards and Certifications
- Standards:
- ASTM: A193, A320, A194, A307.
- ISO: ISO 898, ISO 3506.
- ANSI: B18.2.1, B18.2.2.
- Certifications:
- Quality Assurance: Must meet the quality control standards outlined by relevant industry certifications.
- Material Certification: Certificates of compliance (CoC) to verify material properties and performance.
Application Guidelines
- Installation: Ensure proper alignment and thread engagement. Use torque wrenches to apply the recommended torque values to prevent over-tightening or under-tightening.
- Maintenance: Regularly inspect for signs of wear, corrosion, or damage. Replace any defective components to maintain structural integrity.
Safety and Handling
- Handling: Use appropriate tools and techniques to handle and install stud bolts and nuts. Avoid dropping or mishandling to prevent damage.
- Safety: Follow all relevant safety guidelines and procedures during installation and maintenance to ensure safe working conditions.
These specifications provide a comprehensive overview of the requirements and properties for stud bolts and nuts, ensuring their proper application and performance in various industrial and engineering contexts.
Installation
Preparation
- Select the Correct Size and Type: Ensure that the stud bolts and nuts you are using are the correct size and type for your application. Check the specifications and requirements for both the stud bolts and nuts to confirm compatibility.
- Inspect Components: Before installation, inspect all components for damage or defects. Ensure that the threads on both the stud bolts and nuts are clean and free of debris.
Surface Preparation
- Clean the Threads: Use a wire brush or thread-cleaning tool to remove any dirt, rust, or other contaminants from the threads of the stud bolts and nuts.
- Check Alignment: Ensure that the surfaces where the stud bolts will be installed are properly aligned and in good condition. Misalignment can cause uneven load distribution and potential failure.
Installation
- Insert the Stud Bolt: Thread the stud bolt into the designated hole or nut. If you are using a blind hole, make sure the stud bolt is properly engaged and seated. For through-holes, insert the stud bolt and ensure it passes through the assembly.
- Align the Components: Ensure that the components being joined are properly aligned. Use alignment tools if necessary to maintain accurate positioning.
- Thread on the Nut: Hand-thread the nut onto the stud bolt until it is finger-tight. For applications requiring precise torque, use a torque wrench to achieve the specified torque value.
Tightening
- Apply Torque: Use a calibrated torque wrench to tighten the nut to the recommended torque specification. Follow the appropriate torque sequence if tightening multiple nuts to ensure even load distribution. Tighten gradually in a crisscross pattern if applicable.
- Check for Proper Engagement: Verify that the nut is properly engaged on the stud bolt and that there is no movement or wobbling. Ensure that the threads are fully seated and that the nut is snug against the surface.
Post-Installation Checks
- Inspect the Installation: After tightening, inspect the assembly to ensure that the stud bolt and nut are securely in place and that there is no visible deformation or damage.
- Verify Torque: Recheck the torque settings if necessary to ensure that they meet the specifications. Some applications may require a final torque check after a period of use.
Safety Considerations
- Use Proper Tools: Always use appropriate and well-calibrated tools for installation to avoid damaging the components.
- Avoid Over-Tightening: Do not exceed the recommended torque specifications as over-tightening can damage the threads or the components.
- Follow Safety Guidelines: Adhere to all relevant safety guidelines and procedures during installation to ensure a safe working environment.
Maintenance
- Regular Inspections: Periodically inspect the installed stud bolts and nuts for signs of wear, corrosion, or loosening. Replace any defective or damaged components as needed.
- Lubrication: Apply anti-seize lubricant to the threads if required to facilitate future disassembly and prevent seizing.
Following these installation procedures will help ensure that stud bolts and nuts are installed correctly and function effectively, contributing to the overall reliability and safety of the assembled system.
Q&A
Q1: What are stud bolts and how do they differ from regular bolts?
A1: Stud bolts are cylindrical fasteners with threads along their length but without a head. They differ from regular bolts, which have a head and are typically used with a single nut. Stud bolts are designed to be inserted into threaded holes or paired with nuts on both ends, providing strong and precise connections. They are commonly used where high-strength and alignment are crucial.
Q2: What types of materials are commonly used for manufacturing stud bolts and nuts?
A2: Stud bolts and nuts are commonly made from materials such as carbon steel, alloy steel, and stainless steel. Carbon steel is used for general applications, alloy steel for high-stress environments, and stainless steel for corrosion resistance. Special alloys may be used for extreme temperatures or corrosive environments.
Q3: How do I choose the right size of stud bolt and nut for my application?
A3: Choose the size of stud bolt and nut based on the requirements of your application, including the load they need to support and the conditions they will be exposed to. Refer to the specifications provided for the components and ensure they match the thread size, length, and material requirements for your assembly.
Q4: What is the proper torque specification for installing stud bolts and nuts?
A4: The proper torque specification depends on the size and material of the stud bolt and nut, as well as the requirements of your specific application. Refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines or industry standards for recommended torque values. Use a calibrated torque wrench to apply the correct amount of torque to ensure a secure connection.
Q5: How can I ensure that stud bolts and nuts are properly aligned during installation?
A5: Ensure proper alignment by checking that the components being joined are correctly positioned and aligned before threading the stud bolts. Use alignment tools or guides if necessary. During installation, hand-thread the nuts initially to verify alignment, and then tighten with a torque wrench.
Q6: What are the common coatings applied to stud bolts and nuts, and why are they used?
A6: Common coatings for stud bolts and nuts include zinc plating, hot-dip galvanizing, and black oxide. Zinc plating and hot-dip galvanizing enhance corrosion resistance, while black oxide provides improved wear properties. Coatings protect the components from environmental factors and extend their service life.
Q7: How often should I inspect stud bolts and nuts after installation?
A7: Regular inspections are recommended to ensure that stud bolts and nuts remain in good condition. Check for signs of wear, corrosion, or loosening periodically, and after any significant stress or vibration. Replace any damaged or defective components as needed.
Q8: What should I do if I notice a stud bolt or nut is damaged or corroded?
A8: If you notice that a stud bolt or nut is damaged or corroded, replace it immediately to maintain the integrity of the connection. Inspect the surrounding components to ensure that no additional damage has occurred and address any underlying issues that may have caused the damage or corrosion.
Q9: Can I use stud bolts and nuts in high-temperature or high-pressure applications?
A9: Yes, stud bolts and nuts can be used in high-temperature or high-pressure applications if they are made from suitable materials and meet the necessary specifications. For such conditions, select high-strength materials and coatings that are specifically designed to withstand extreme environments.
Q10: What safety precautions should I take during the installation of stud bolts and nuts?
A10: During installation, use appropriate tools and follow safety guidelines to prevent accidents. Avoid over-tightening, which can damage the threads or components. Ensure that you are working in a safe environment and that all personnel are aware of the procedures and potential hazards. Always use calibrated tools and protective equipment as needed.
This Q&A covers common questions and concerns related to stud bolts and nuts, providing guidance on their selection, installation, and maintenance.
Advantages / Disadvantages
Advantages
High Strength and Load Capacity:
-
- Advantage: Stud bolts are designed to handle high tensile loads, making them ideal for applications that require strong and reliable connections. Their lack of a head allows them to accommodate large clamping forces and withstand significant stresses.
Flexibility in Installation:
-
- Advantage: Stud bolts can be installed from either end, which offers flexibility in tight spaces where access to one side may be limited. This makes them useful in assemblies where traditional bolts might be difficult to install or remove.
Enhanced Alignment:
-
- Advantage: By using stud bolts and nuts, you can achieve precise alignment between components. This is particularly important in critical applications where maintaining exact alignment is necessary to ensure proper function and prevent mechanical failure.
Resistance to Vibration:
-
- Advantage: Properly installed stud bolts and nuts can resist loosening due to vibrations. They often come with locking mechanisms or can be used with locking nuts to prevent self-loosening in dynamic environments.
Corrosion Resistance:
-
- Advantage: Stud bolts and nuts made from stainless steel or coated with protective finishes, such as zinc plating or hot-dip galvanizing, offer excellent resistance to corrosion and environmental degradation, extending their service life in harsh conditions.
Ease of Maintenance:
-
- Advantage: Stud bolts can be easily replaced or adjusted without removing the entire component, which simplifies maintenance and repairs. This reduces downtime and labor costs associated with component replacement.
Disadvantages
Installation Complexity:
-
- Disadvantage: Installing stud bolts and nuts can be more complex compared to traditional bolts, particularly in terms of ensuring proper alignment and torque. Special tools and careful procedures are required to achieve the correct fit and load distribution.
Cost:
-
- Disadvantage: Stud bolts and nuts, especially those made from high-grade materials or with special coatings, can be more expensive than standard bolts and nuts. This higher cost can impact budget constraints for large-scale projects.
Potential for Thread Damage:
-
- Disadvantage: Improper installation or excessive torque can damage the threads of stud bolts or nuts, leading to reduced performance and potential failures. It is essential to use the correct torque values and installation procedures to avoid such issues.
Limited Access:
-
- Disadvantage: In some applications, the need to access both ends of the stud bolt for installation or adjustment may be restrictive. This can be a challenge in tightly confined spaces or assemblies with limited accessibility.
Risk of Over-tightening:
-
- Disadvantage: Over-tightening stud bolts can cause deformation or failure of both the bolt and the components being fastened. It is crucial to adhere to recommended torque specifications to avoid such problems.
Handling and Transport:
-
- Disadvantage: Stud bolts can be prone to bending or damage during handling and transport due to their elongated shape. Proper care and handling practices are necessary to prevent damage before installation.
In summary, stud bolts and nuts offer numerous advantages such as high strength, flexibility, and resistance to environmental factors, making them suitable for demanding applications. However, they also come with challenges including installation complexity, cost, and potential risks of thread damage or over-tightening. Proper understanding and management of these factors can help leverage their benefits while mitigating disadvantages.
Applications
Oil and Gas Industry
- Application: Stud bolts and nuts are extensively used in the oil and gas industry for connecting flanges, valves, pumps, and other equipment in high-pressure and high-temperature environments. Their ability to withstand extreme conditions makes them ideal for pipeline systems and drilling operations.
Aerospace Industry
- Application: In aerospace, stud bolts and nuts are employed in aircraft assemblies and engines where high strength and precision are critical. They are used in structural connections, engine mounts, and various other components that require reliable and robust fastening.
Automotive Industry
- Application: Stud bolts and nuts are commonly used in automotive manufacturing and maintenance for engine assemblies, chassis components, and transmission systems. Their strong load-bearing capacity is essential for ensuring the durability and safety of vehicle parts.
Construction Industry
- Application: In construction, stud bolts and nuts are used in the assembly of structural steel frameworks, bridges, and high-rise buildings. They provide strong and stable connections for beams, columns, and other structural elements subject to significant loads and stresses.
Manufacturing Industry
- Application: Stud bolts and nuts are vital in manufacturing processes for securing machinery, conveyors, and equipment. They ensure that components remain firmly attached and can handle the operational forces encountered during production.
Power Generation
- Application: Stud bolts and nuts play a crucial role in power generation facilities, including turbines, generators, and boilers. Their high strength and resistance to extreme conditions are essential for maintaining the integrity and safety of critical power plant components.
Marine Industry
- Application: In marine applications, stud bolts and nuts are used in shipbuilding and maintenance for hulls, propeller shafts, and engine assemblies. Their corrosion resistance is particularly important for withstanding harsh marine environments and saltwater exposure.
Chemical Processing
- Application: Stud bolts and nuts are utilized in chemical processing plants where resistance to corrosive substances is required. They secure flanges and other equipment in chemical reactors, pipelines, and storage tanks, ensuring the safe handling of aggressive chemicals.
Railway Industry
- Application: In the railway industry, stud bolts and nuts are used for track assembly, rail fastening, and securing various components in locomotives and railcars. Their strength and durability are crucial for maintaining the safety and stability of rail infrastructure.
HVAC Systems
- Application: Stud bolts and nuts are used in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems to secure ductwork, equipment mounts, and support structures. Their reliability ensures that HVAC systems operate efficiently and remain securely assembled.
Renewable Energy
- Application: In renewable energy sectors, such as wind and solar power, stud bolts and nuts are employed in the construction of wind turbine towers, solar panel mounts, and other infrastructure. Their strength and resistance to environmental factors are essential for the stability and longevity of renewable energy systems.
Defense Industry
- Application: Stud bolts and nuts are used in defense applications for assembling military vehicles, weapon systems, and other critical equipment. Their robustness and precision are vital for ensuring the reliability and performance of defense technology.
In summary, stud bolts and nuts find applications across a wide range of industries due to their high strength, durability, and ability to perform under extreme conditions. Their versatility makes them essential components in numerous high-stress and high-performance environments.
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.








Reviews
There are no reviews yet.