Description
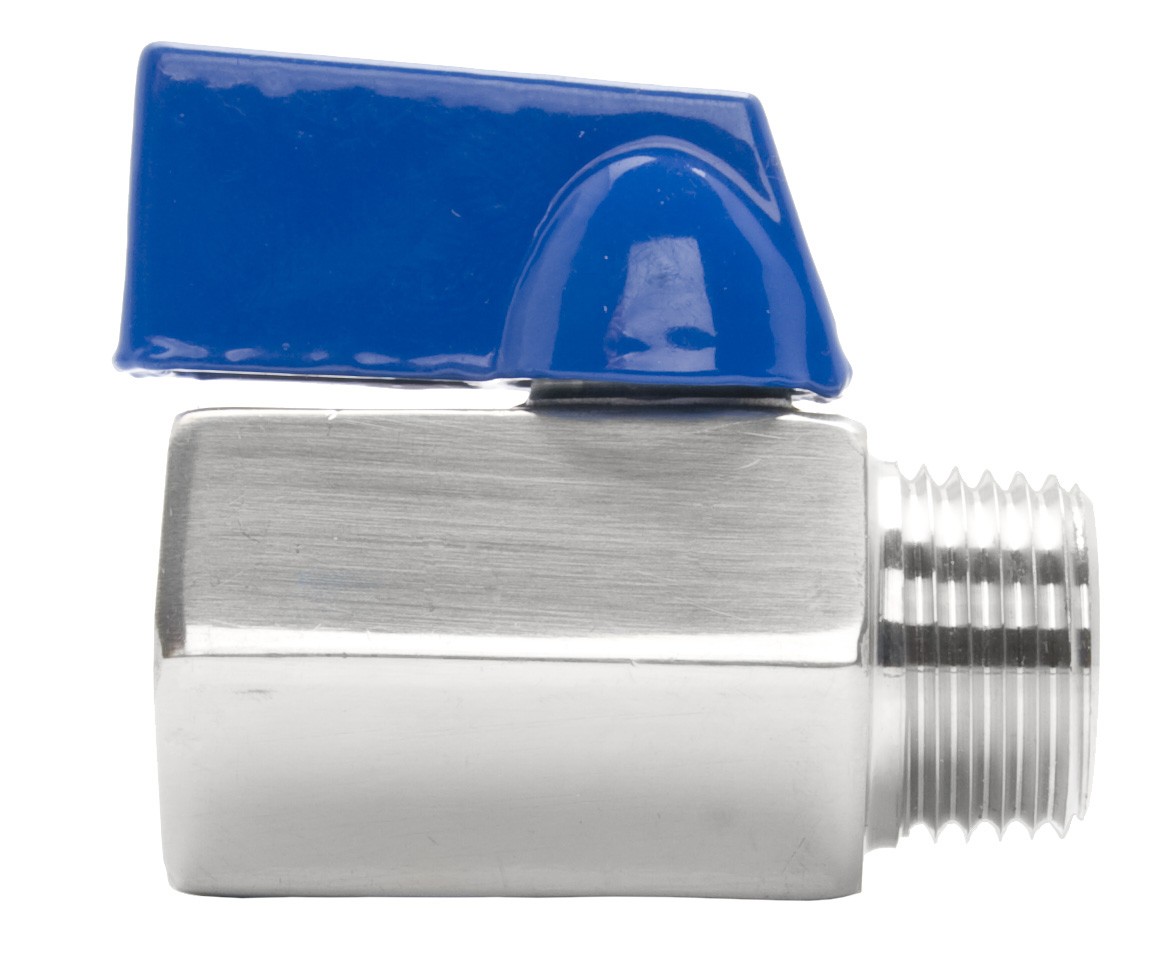
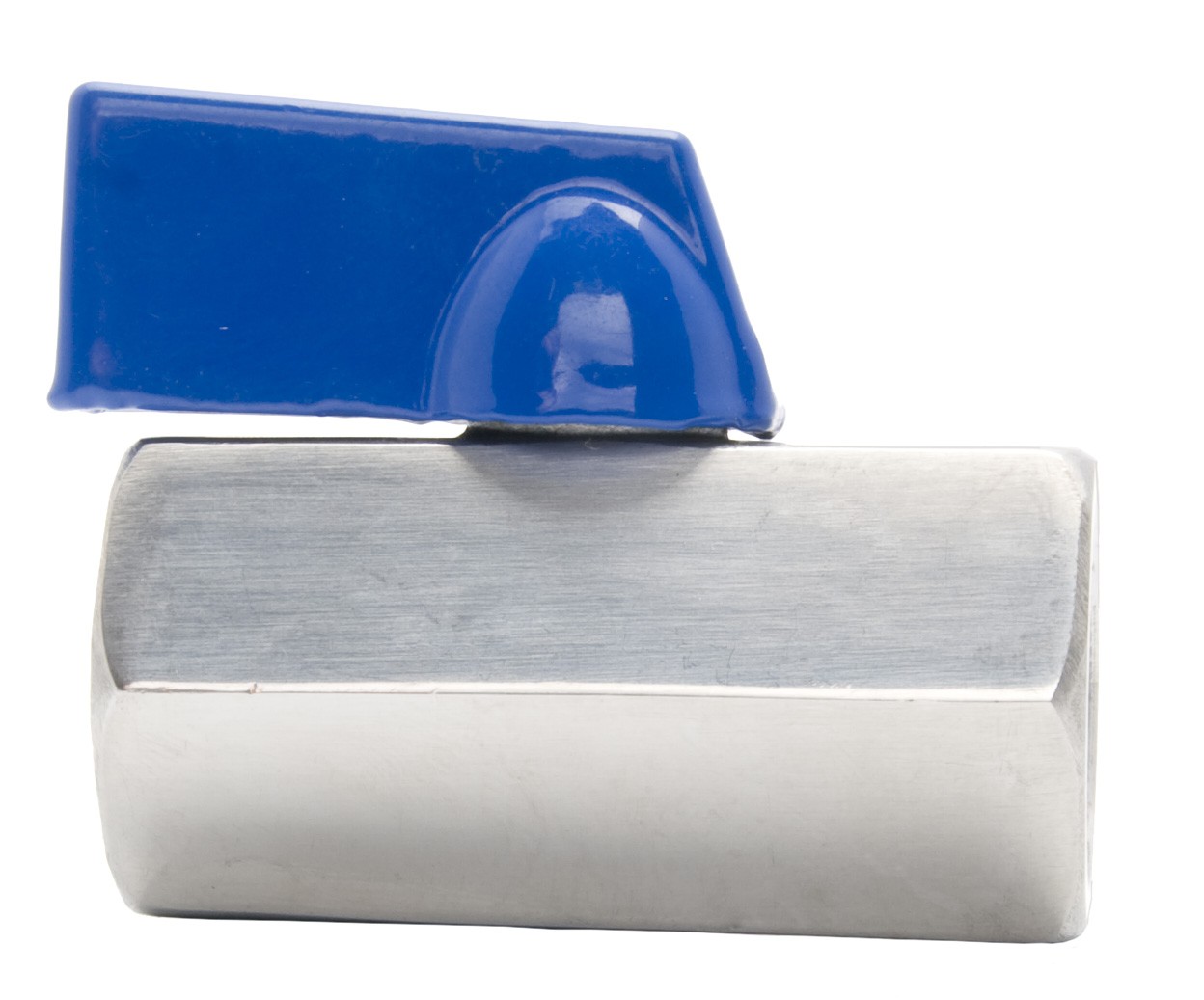
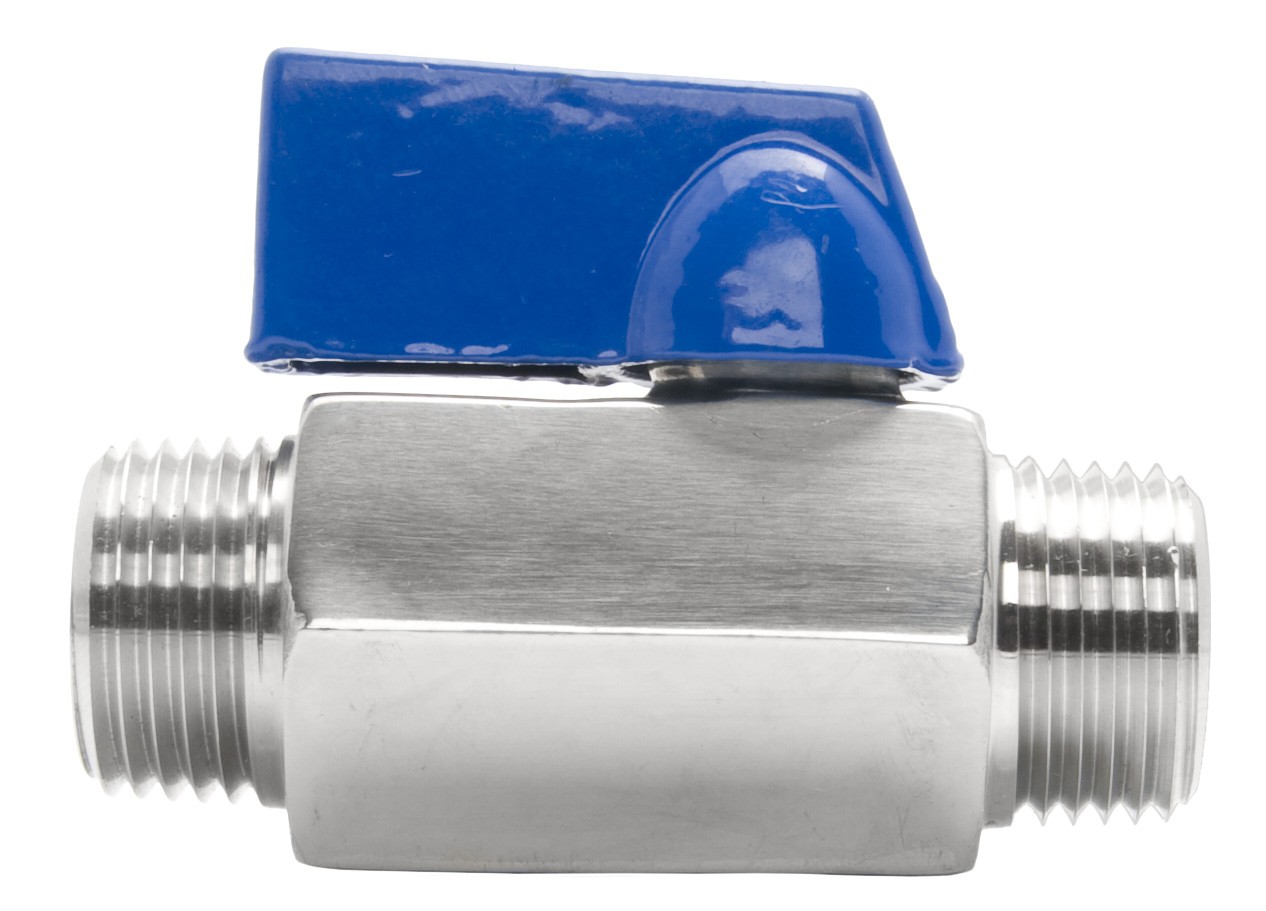
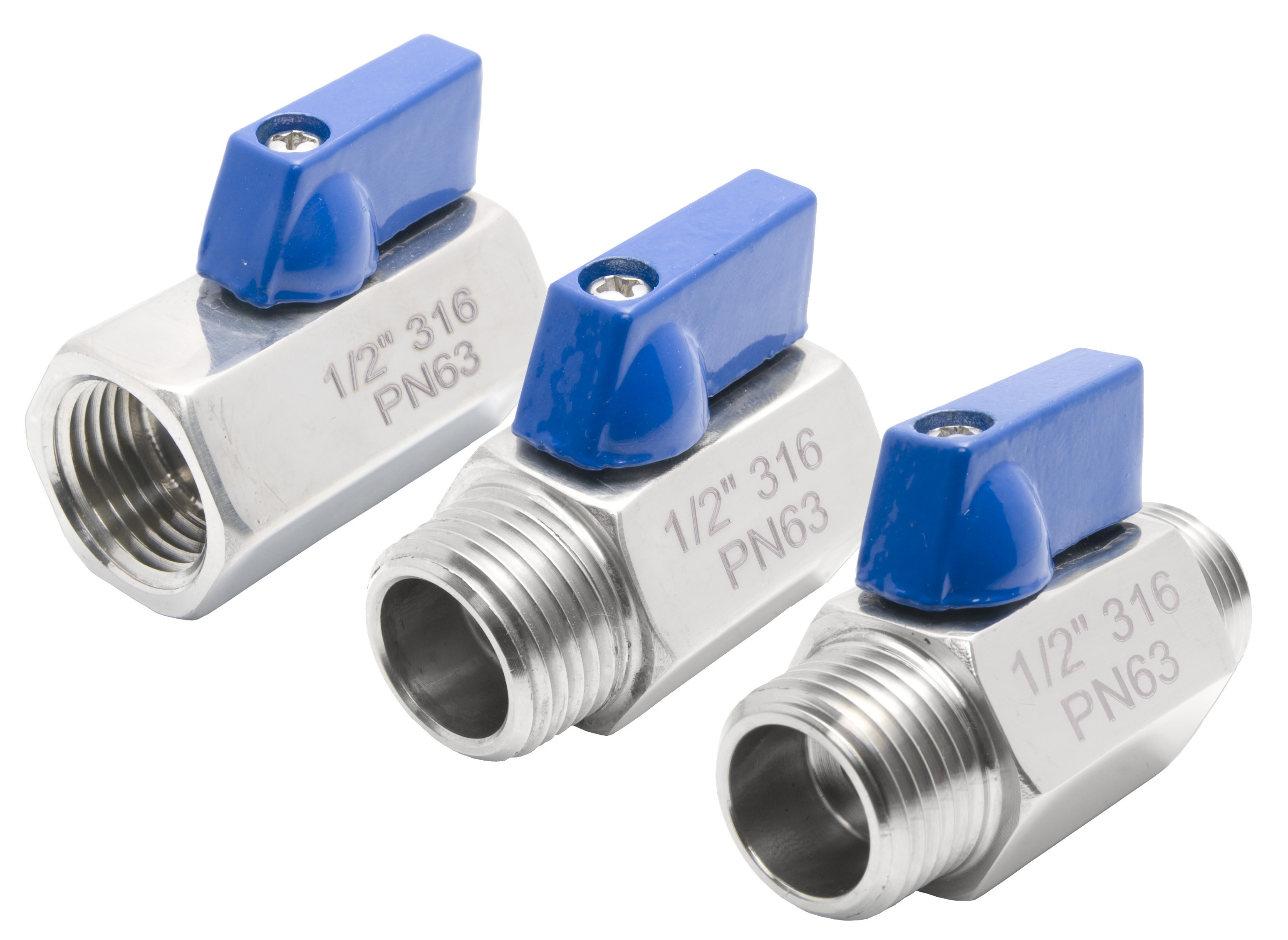 Mini ball valves are compact and versatile valves commonly used in various industrial applications where space is limited, or precise flow control is required. In addition, manufacturers construct these from high-quality materials like 304 stainless steel (304SS) or 316 stainless steels (316SS). This material is known for its corrosion resistance and durability in demanding environments. The choice of material depends on the specific requirements of the application, with 316SS offering greater resistance to corrosion and pitting compared to 304SS.
Mini ball valves are compact and versatile valves commonly used in various industrial applications where space is limited, or precise flow control is required. In addition, manufacturers construct these from high-quality materials like 304 stainless steel (304SS) or 316 stainless steels (316SS). This material is known for its corrosion resistance and durability in demanding environments. The choice of material depends on the specific requirements of the application, with 316SS offering greater resistance to corrosion and pitting compared to 304SS.
Mini ball valves are available in different configurations. These include FNPT to FNPT (Female National Pipe Thread to Female National Pipe Thread). Also, MNPT to MNPT (Male National Pipe Thread to Male National Pipe Thread). Finally, MNPT to FNPT (Male National Pipe Thread to Female National Pipe Thread). These variations allow for flexible installation options to meet specific piping requirements. This ensures compatibility with existing systems.
Design of Mini-Ball Valves
The design of mini ball valves includes a spherical closure element (the ball) with a bore through it. In addition, when the valve is in the open position, the bore aligns with the pipeline. This allows fluid to flow through. In addition, rotating the handle or lever attached to the ball 90 degrees closes the valve by positioning the bore perpendicular to the pipeline, blocking the flow of fluid.
When selecting a mini ball valve, factors to consider include pressure rating and temperature suitability. Also, ensure the material is compatible with the fluid being handled. Most important is the specific connection type required (FNPT, MNPT). Proper installation and maintenance are essential to ensure optimal performance and longevity of them in industrial processes. In addition, we recommend regularly inspecting seals, lubricating moving parts, and replacing worn components to prevent leakage and ensure efficient operation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, mini ball valves are reliable, compact, and versatile components widely used in industrial applications. In addition, users employ them for precise flow control and shut-off functions. With their robust construction and flexible configurations, these valves play a crucial role in maintaining the efficiency and reliability. This applies to various systems across industries.
Specifications
General Description
A mini ball valve is a compact, reliable valve designed for precise flow control in small-diameter piping systems. It features a spherical ball with a hole through the center, which rotates to open or close the flow path.
Materials
- Body Material: Stainless Steel (316), Brass, or Plastic (PVC/CPVC)
- Ball Material: Stainless Steel (316), Brass, or Plastic (PVC/CPVC)
- Seat Material: PTFE (Teflon), Nylon, or EPDM
- Handle Material: Plastic or Metal (Steel, Stainless Steel)
Size and Dimensions
- Nominal Size: 1/4 inch to 1 inch (6 mm to 25 mm)
- End Connections: Threaded (NPT/BSP), Compression, or Push-fit
- Overall Length: Typically ranges from 2 to 4 inches (50 to 100 mm)
- Overall Width: Typically ranges from 1.5 to 2.5 inches (38 to 63 mm)
- Height: Varies with handle type and size
Pressure and Temperature Ratings
- Maximum Pressure Rating: Up to 1000 psi (69 bar)
- Temperature Range: -20°F to 300°F (-29°C to 149°C) depending on material
Flow Characteristics
- Flow Coefficient (Cv): Typically ranges from 0.5 to 5.0 depending on valve size
- Flow Rate: Depends on size and pressure differential
Design Features
- Ball Type: Floating or Trunnion-mounted
- Handle Type: Lever or T-handle
- Operation: Manual, with quarter-turn operation
- Sealing Type: Soft-seated or metal-seated
- Blow-out Proof Stem: Ensures safety in high-pressure applications
- Mounting: Standard mounting pad available for actuator installation
Standards and Certifications
- Compliance: ANSI/ASME B16.34, API 608, or equivalent
- Certifications: ISO 9001 quality management, NSF/ANSI for potable water (if applicable)
Additional Features
- Locking Mechanism: Optional locking lever to prevent unauthorized operation
- End Connections: Options for different end fittings, including threaded, compression, or push-fit
- Drip-tight Seal: Ensures minimal leakage when closed
Applications
- Fluid Control: Suitable for controlling water, air, gas, and other fluids
- Industries: Plumbing, HVAC, automotive, chemical processing, and irrigation
Maintenance and Care
- Maintenance: Periodic inspection for leaks, checking handle operation, and ensuring proper sealing
- Cleaning: Use non-abrasive cleaners and avoid harsh chemicals to maintain valve integrity
By adhering to these specifications, the mini ball valve ensures efficient and reliable control of fluid flow in various small-scale applications.
Installation
Preparation
Verify Specifications:
- Ensure the mini ball valve is appropriate for your application in terms of size, pressure rating, and material compatibility.
Gather Tools and Materials:
- Tools may include wrenches, pipe cutters, thread sealant, and pipe fittings. Materials should include the valve and any necessary piping or connectors.
Check Local Codes:
- Review any local regulations or standards for valve installation that may apply.
Site Inspection
Location:
- Select an accessible location for installation, ensuring adequate space for operation and maintenance. Avoid placing the valve where it will be subject to excessive vibration or temperature extremes.
Pipe Alignment:
- Verify that the pipes are aligned properly and that there is sufficient space for the valve. The valve should be installed in a straight section of the pipe.
Check Pipe Size:
- Ensure that the pipe size matches the valve’s inlet and outlet connections.
Preparation of Piping
Shut Off System:
- Turn off the fluid supply to the section where the valve will be installed. Drain any remaining fluid from the pipes.
Clean Pipe Ends:
- Clean the ends of the pipes to remove debris, rust, or old sealant. This helps ensure a good seal and proper valve installation.
Inspect for Damage:
- Check the pipes and fittings for any damage that could affect installation or valve performance.
Valve Installation
Orientation:
- Install the valve according to the manufacturer’s recommended orientation. Ensure the flow direction arrow on the valve matches the direction of the fluid flow.
Attach Valve:
- For threaded connections, apply thread sealant to the male threads of the pipe. Screw the valve onto the pipe by hand, then tighten with a wrench. Avoid over-tightening to prevent damage.
- For compression fittings, ensure the pipe ends are properly aligned with the valve fittings. Tighten the compression nut securely.
- For push-fit connections, simply push the valve onto the pipe until it is firmly seated.
Secure the Valve:
- Ensure the valve is securely mounted. Use support brackets or straps if necessary to prevent movement or vibration.
System Testing
Reopen System:
- Slowly turn on the fluid supply to the system. This helps prevent sudden pressure surges that could damage the valve or piping.
Check for Leaks:
- Inspect all connections and fittings for leaks. Tighten any loose connections but avoid over-tightening.
Test Operation:
- Open and close the valve to ensure smooth operation. Verify that the valve is fully opening and closing and that there are no obstructions or resistance.
Final Checks
Verify Function:
- Confirm that the valve operates correctly and controls the flow as intended. Check for proper sealing and operation under normal operating conditions.
Record Installation Details:
- Document the installation date, valve model, serial number, and any relevant observations. This information is useful for future reference and maintenance.
Inform Users:
- If applicable, inform relevant personnel of the new valve installation and any changes in operation or maintenance procedures.
Maintenance and Follow-Up
Schedule Maintenance:
- Establish a regular maintenance schedule to inspect the valve and ensure it remains in good working condition.
Monitor Performance:
- Periodically check the valve’s performance and address any issues promptly to maintain optimal operation.
By following these installation procedures, you ensure that the mini ball valve is installed correctly and functions reliably in your system.
Maintenance
Routine Inspection
Visual Check:
- Regularly inspect the valve for any visible signs of damage, leakage, or wear. Look for corrosion, rust, or any unusual markings.
Verify Operation:
- Operate the valve periodically to ensure it opens and closes smoothly. The handle should turn easily without excessive force, and the valve should fully open and close.
Check for Leaks:
- Examine all connections and fittings for any signs of leakage. Look for water or fluid around the valve body and connections.
Cleaning
External Cleaning:
- Wipe the valve’s exterior with a clean, dry cloth to remove dirt and debris. For more stubborn stains, use a mild detergent and water, avoiding harsh chemicals that could damage the valve.
Internal Cleaning:
- If the valve is subject to build-up or contamination, follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for internal cleaning. In many cases, flushing the valve with clean water or another suitable solvent can help remove debris.
Lubrication
Check Lubrication:
- For valves with lubrication requirements, check the condition of the lubricant. Use the manufacturer-recommended lubricant to ensure smooth operation.
Apply Lubricant:
- Apply lubricant to the valve stem and any moving parts according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. Avoid over-lubricating, as excess lubricant can attract dirt and debris.
Inspection of Mechanical Components
Examine Moving Parts:
- Inspect the ball and stem for wear or damage. Ensure that the ball rotates smoothly and that the stem does not show signs of excessive wear or damage.
Check Seals and Seats:
- Examine the seat materials for signs of deterioration or damage. Replace any worn or damaged seals or seats to prevent leakage and ensure proper sealing.
Valve Operation
Operate Regularly:
- Even if the valve is not frequently used, operate it periodically to prevent the seals and moving parts from seizing or becoming stiff.
Test for Proper Function:
- Open and close the valve to ensure it functions correctly. Verify that it fully stops flow when closed and allows full flow when open.
Addressing Issues
Leakage:
- If leaks are detected, tighten fittings or connections as needed. If leakage persists, inspect and replace seals, gaskets, or other components.
Sticking or Hard Operation:
- If the valve becomes difficult to operate, check for debris or build-up. Clean the valve and apply lubricant as necessary. If problems persist, inspect for mechanical damage.
Documentation
Record Maintenance Activities:
- Document all maintenance activities, including inspections, cleaning, lubrication, and repairs. Keep records of any parts replaced and any issues identified.
Review Performance:
- Periodically review the valve’s performance and maintenance history to identify any recurring issues or patterns that may need addressing.
Professional Service
Seek Expert Assistance:
- For complex repairs or if the valve shows significant wear or damage, consult a professional service provider or the manufacturer’s support team for expert assistance.
Follow Manufacturer’s Guidelines:
- Adhere to the manufacturer’s maintenance guidelines to ensure proper care and to avoid voiding warranties.
Safety Considerations
Follow Safety Protocols:
- Always follow safety procedures when performing maintenance, including wearing appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and ensuring that the system is safely shut off.
Avoid Hazardous Conditions:
- Be cautious of hazardous fluids or high-pressure conditions when working with or around the valve.
By following these maintenance procedures, you can ensure that your mini ball valve remains in good working condition, providing reliable performance and extending its operational life.
Q&A
Q1: What is a mini ball valve used for?
A1: A mini ball valve is used to control the flow of fluids in small-diameter piping systems. It is ideal for applications where precise flow control is needed, such as in plumbing, HVAC systems, and small-scale chemical processes. Its compact size makes it suitable for tight spaces.
Q2: How does a mini ball valve work?
A2: A mini ball valve works by using a spherical ball with a hole through the center. When the handle is turned, the ball rotates to either open or close the flow path. When the ball’s hole aligns with the pipe, fluid flows through. When the ball is rotated so that the hole is perpendicular to the flow direction, the valve closes and stops the flow.
Q3: What materials are commonly used for mini ball valves?
A3: Mini ball valves are commonly made from materials such as:
- Body Material: Stainless Steel (316), Brass, or Plastic (PVC/CPVC)
- Ball Material: Stainless Steel (316), Brass, or Plastic (PVC/CPVC)
- Seat Material: PTFE (Teflon), Nylon, or EPDM
Q4: What are the typical sizes for mini ball valves?
A4: Mini ball valves typically range from 1/4 inch to 1 inch (6 mm to 25 mm) in nominal size. The size should be chosen based on the pipe diameter and the flow requirements of your system.
Q5: What pressure and temperature ratings should I consider?
A5: Mini ball valves generally have a maximum pressure rating of up to 1000 psi (69 bar). Temperature ratings can vary, but they typically range from -20°F to 300°F (-29°C to 149°C). Always check the manufacturer’s specifications to ensure the valve is suitable for your specific application.
Q6: How do I install a mini ball valve?
A6: To install a mini ball valve:
- Shut Off the System: Turn off the fluid supply and drain the system.
- Clean Pipe Ends: Remove debris from the pipe ends.
- Attach the Valve: Apply thread sealant if using threaded connections, then screw the valve onto the pipe. For compression or push-fit connections, align and secure the valve accordingly.
- Check for Leaks: Reopen the system slowly, check for leaks, and ensure the valve operates smoothly.
Q7: What maintenance is required for a mini ball valve?
A7: Regular maintenance includes:
- Visual Inspections: Check for damage, leaks, or wear.
- Cleaning: Wipe the exterior and, if necessary, flush the valve internally.
- Lubrication: Apply lubricant to moving parts as per manufacturer guidelines.
- Inspecting Mechanical Components: Examine the ball, stem, and seats for wear or damage.
- Documenting Activities: Keep records of inspections, maintenance, and repairs.
Q8: How can I troubleshoot common issues with mini ball valves?
A8: Common issues and their troubleshooting steps include:
- Leaks: Tighten fittings or replace seals if leaks persist.
- Difficulty in Operation: Clean the valve and lubricate moving parts. If problems continue, check for mechanical damage.
- Sticking: Ensure the valve is free of debris and properly lubricated.
Q9: What are the benefits of using a mini ball valve?
A9: Mini ball valves offer several benefits, including:
- Compact Size: Ideal for small spaces and tight installations.
- Precise Control: Provides accurate flow control.
- Durability: Reliable in various fluid control applications.
- Ease of Operation: Simple quarter-turn operation.
Q10: Where can I find replacement parts or professional service for my mini ball valve?
A10: Replacement parts and professional services can be sourced from the valve manufacturer, authorized distributors, or specialized valve service providers. Always use genuine parts and follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for repairs and maintenance.
Advantages / Disadvantages
Advantages
Compact Size:
- Advantage: Mini ball valves are designed to fit in tight spaces and small-diameter piping systems, making them ideal for applications where space is limited.
- Benefit: This compact design allows for flexible installation in confined areas.
Precise Flow Control:
- Advantage: The ball valve mechanism provides precise control over fluid flow with a simple quarter-turn operation.
- Benefit: This precision is crucial in applications requiring accurate flow regulation.
Durability:
- Advantage: Mini ball valves are typically constructed from robust materials like stainless steel, brass, or high-quality plastics, ensuring long-term reliability.
- Benefit: They withstand harsh operating conditions, including high pressures and temperatures.
Ease of Operation:
- Advantage: The quarter-turn operation is straightforward and requires minimal effort to open or close the valve.
- Benefit: This simplicity enhances user convenience and reduces the likelihood of operational errors.
Low Maintenance:
- Advantage: Mini ball valves generally require minimal maintenance compared to other types of valves.
- Benefit: Reduced maintenance needs result in lower operational costs and less downtime.
Leak-proof Design:
- Advantage: The design of the ball valve ensures a tight seal when closed, minimizing the risk of leakage.
- Benefit: This feature is essential for maintaining system integrity and preventing fluid loss.
Versatility:
- Advantage: Mini ball valves can handle a wide range of fluids, including water, gases, and chemicals.
- Benefit: Their versatility makes them suitable for various industrial, commercial, and residential applications.
Disadvantages
Limited Flow Capacity:
- Disadvantage: Due to their small size, mini ball valves may not be suitable for applications requiring high flow rates.
- Impact: This limitation restricts their use in larger systems or high-volume applications.
Potential for Clogging:
- Disadvantage: In applications with particulates or viscous fluids, the small passage of a mini ball valve can become clogged.
- Impact: Clogging can affect valve performance and require more frequent maintenance.
Temperature and Pressure Limits:
- Disadvantage: Mini ball valves have specific temperature and pressure ratings that may not suit all applications.
- Impact: Exceeding these limits can lead to valve failure or reduced performance.
Wear and Tear:
- Disadvantage: Frequent use or operation in harsh conditions can cause wear on the ball and seat, potentially leading to leaks.
- Impact: This wear may necessitate more frequent inspections and replacements.
Cost of High-Quality Materials:
- Disadvantage: High-quality mini ball valves made from materials like stainless steel or brass can be relatively expensive.
- Impact: The initial cost may be higher compared to plastic or lower-quality alternatives.
Limited Automation Options:
- Disadvantage: While manual mini ball valves are straightforward, automating them can be more complex and costly.
- Impact: This can limit their use in automated systems where electronic control is preferred.
Not Suitable for All Fluids:
- Disadvantage: Some mini ball valves may not be compatible with aggressive chemicals or extreme temperatures.
- Impact: Choosing the wrong material or valve type for specific fluids can lead to premature failure or safety hazards.
By understanding these advantages and disadvantages, you can better assess whether a mini ball valve is suitable for your specific application and make informed decisions regarding its use and maintenance.
Applications
Mini ball valves are versatile components used in various industries and applications due to their compact size and precise control capabilities. Here are some common applications:
Plumbing Systems
- Residential and Commercial Plumbing: Used to control water flow in small-diameter pipes for fixtures like sinks, showers, and toilets.
- Shut-Off Valves: Ideal for providing a reliable shut-off mechanism in plumbing lines where space is limited.
HVAC Systems
- Heating and Cooling: Employed in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems to regulate the flow of water or refrigerants in small-diameter piping.
- Balancing Valves: Useful for balancing flow rates in HVAC systems to ensure even distribution of heating or cooling.
Automotive Applications
- Fluid Control: Utilized in vehicles for controlling coolant, fuel, and other fluids in automotive systems.
- Small Engine Applications: Ideal for use in small engines and equipment where space is constrained.
Industrial Processes
- Chemical Processing: Used to control the flow of chemicals in small-scale processing systems.
- Fluid Handling: Suitable for handling various fluids in industrial settings, including lubricants and solvents.
Agriculture and Irrigation
- Irrigation Systems: Employed in irrigation systems to control water flow to various parts of a field or garden.
- Fertilizer Application: Used in systems that apply fertilizers and other additives to crops.
Laboratories
- Fluid Control in Experiments: Used in laboratory settings to control the flow of liquids in experiments and processes.
- Analytical Equipment: Employed in analytical and diagnostic equipment for precise fluid handling.
Medical Equipment
- Fluid Management: Utilized in medical devices and equipment to control the flow of fluids, such as in infusion pumps and dialysis machines.
- Compact Valve Solutions: Ideal for applications where space is limited, and precise flow control is crucial.
Home Appliances
- Dishwashers and Washing Machines: Used to control water flow in household appliances.
- Water Purifiers: Employed in water filtration systems to regulate the flow of water through filters.
Food and Beverage Industry
- Beverage Dispensing: Used in dispensing systems for beverages, controlling flow rates in bars and restaurants.
- Food Processing: Employed in food processing equipment for precise control of ingredients and liquids.
Marine Applications
- Marine Systems: Used in boat and ship systems to control the flow of water, fuel, and other fluids.
- Compact Marine Equipment: Suitable for small, space-constrained marine applications.
Aerospace
- Aircraft Systems: Employed in aircraft for controlling the flow of fluids in hydraulic and fuel systems.
- Spacecraft: Used in spacecraft for fluid management in various systems.
Energy Sector
- Oil and Gas: Used in small-scale energy applications for controlling the flow of oil, gas, and other fluids.
- Renewable Energy Systems: Employed in renewable energy systems such as solar water heaters and small wind turbines.
Summary
Mini ball valves are adaptable and useful across a broad spectrum of applications where space constraints and precise flow control are important. Their versatility makes them valuable in both every day and specialized scenarios, ensuring reliable operation in diverse environments.
 Mini ball valves are compact and versatile valves commonly used in various industrial applications where space is limited, or precise flow control is required. In addition, manufacturers construct these from high-quality materials like 304 stainless steel (304SS) or 316 stainless steels (316SS). This material is known for its corrosion resistance and durability in demanding environments. The choice of material depends on the specific requirements of the application, with 316SS offering greater resistance to corrosion and pitting compared to 304SS.
Mini ball valves are compact and versatile valves commonly used in various industrial applications where space is limited, or precise flow control is required. In addition, manufacturers construct these from high-quality materials like 304 stainless steel (304SS) or 316 stainless steels (316SS). This material is known for its corrosion resistance and durability in demanding environments. The choice of material depends on the specific requirements of the application, with 316SS offering greater resistance to corrosion and pitting compared to 304SS.