Description
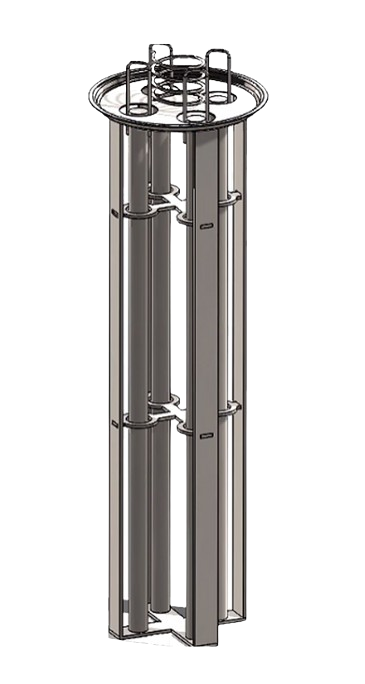 The innovative Magnetic Bag Filter Housings are set to transform magnetic filtration. Suitable for virtually any pipe size, these housings are ideal for small commercial systems. Also, large industrial setups in factories, hospitals, and building complexes. In addition, the design allows for full-flow or inline use, or as a side stream filter, adapting to various needs and applications. Furthermore, leveraging advanced Magnetic Strainer technology, they remove nearly 100% of magnetite and other unwanted debris from hydronic systems. Finally, the housings use long, high-intensity Neodymium magnetic rods to capture visible and submicronic magnetite (iron oxide) and non-magnetic contaminants (scale), collecting them efficiently.
The innovative Magnetic Bag Filter Housings are set to transform magnetic filtration. Suitable for virtually any pipe size, these housings are ideal for small commercial systems. Also, large industrial setups in factories, hospitals, and building complexes. In addition, the design allows for full-flow or inline use, or as a side stream filter, adapting to various needs and applications. Furthermore, leveraging advanced Magnetic Strainer technology, they remove nearly 100% of magnetite and other unwanted debris from hydronic systems. Finally, the housings use long, high-intensity Neodymium magnetic rods to capture visible and submicronic magnetite (iron oxide) and non-magnetic contaminants (scale), collecting them efficiently.
Prevent Destructive Corrosion and Heating System Damage
Magnetic Bag Filter Housings capture existing contamination, prevent further buildup, increase system efficiency, lower costs, protect boilers and ECM heat pumps, prevent “cold spots” in systems, extend system lifespan, and reduce overall maintenance.
How It Works
The core feature of the Magnetic Bag Filter Housings is a set of powerful, high-intensity magnetic rods. A filtration bag, available in various micron tolerances, also contains it. Also, as water flows through the filter, the magnets draw in and collect magnetite and other particles. The cleaned water continues to flow through. Moreover, you can easily clean the housings by periodically removing the magnet assembly and washing off the collected sludge. The filtration bag is also replaced with a new one during this process.
Innovative Features of Magnetic Bag Filter Housings
Three Systems in One:
The manufacturer makes these housings from stainless steel and offers them in various sizes. In addition, each unit includes the longest, most powerful magnet assembly available, a bag filter, and can serve as a pot feeder for chemical dosing in hydronic systems.
Built for Large Pipes:
Unlike current magnetic filter systems that cannot accommodate pipes larger than 12″, you can use Magnetic Bag Filter Housings in systems ranging from 12″ to 32″. Larger systems can be custom-built, mounted on skids, and delivered to your location.
High Pressure / High Temperature Models:
Designed to handle extremely high pressures (300 psi +) and temperatures (306º to 450ºF / 150º to 232ºC).
Completely Customizable:
You can customize these housings to meet unique requirements such as specific water pressure, temperature, different inflow and outflow pipe sizes, and unique size needs. A wide range of housing styles is available, including portable units and those on skids.
Specifications
Compatible with all heating systems
Very easy to install
Low system downtime during installation
Easy to maintain
Includes bag filter
Also serves as a chemical pot feeder
Includes bag filter for capturing other debris
Easy to clean
Rare Earth Neodymium Magnets (12,000 Gauss)
Full flow inline or Sidestream filter
Flow Rate ranges up to 3500 gpm for 32”
Fits into horizontal pipe systems
All valves and fittings included
Available in all ranges of pipe
Customizable
Temperature: -32º to 450ºF / -35.5º – 232ºC
Operating pressure: 0 to 300
Large collection reservoir
Installation
Preparation
Review Manufacturer’s Instructions: Carefully read the installation manual provided by the manufacturer to understand specific requirements and recommendations.
Gather Tools and Equipment: Ensure you have all necessary tools and equipment, including wrenches, pipe cutters, sealant, and any mounting hardware provided with the housing.
Safety Measures: Wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves, safety glasses, and protective clothing. Ensure the system is depressurized and drained before starting the installation.
Installation Site Preparation
Location Selection: Choose an appropriate location for the filter housing, typically on the return circuit near the boiler or a critical point where fluid re-enters the system. Ensure there is adequate space for installation and maintenance.
Pipe Cutting: Measure and mark the section of pipe where the housing will be installed. Cut the pipe cleanly and remove any burrs or debris to ensure a proper fit.
Installing the Filter Housing
Position the Housing: Position the filter housing in the intended location, ensuring that the inlet and outlet align with the existing piping. The magnetic rods and filtration bag should be accessible for maintenance.
Connect the Inlet Pipe: Apply pipe sealant or thread tape to the threads of the inlet pipe. Connect the inlet pipe to the housing’s inlet port, ensuring a secure and leak-free connection.
Connect the Outlet Pipe: Repeat the same process for the outlet pipe, ensuring it is securely connected to the housing’s outlet port.
Secure the Housing: If the housing has mounting brackets or supports, secure it to a solid surface or frame to prevent movement and vibration during operation.
Final Checks and Testing
Inspect Connections: Check all connections for tightness and ensure there are no leaks. Tighten any fittings as necessary.
System Refill: Gradually refill the system with fluid, checking for any leaks around the housing and connections. Ensure the system is properly vented to remove any air pockets.
Pressure Test: Slowly pressurize the system and inspect the housing and connections for leaks under pressure. Address any leaks immediately by tightening fittings or applying additional sealant.
Initial Operation
Start the System: Start the fluid system and monitor the operation of the Magnetic Bag Filter Housing. Ensure that fluid is flowing smoothly and that the housing is effectively capturing contaminants.
Initial Cleaning: After a short period of operation, perform an initial cleaning of the housing to remove any captured debris. This helps to establish a baseline for maintenance intervals.
Maintenance and Documentation
Document Installation: Record the installation details, including the location of the housing, date of installation, and any observations during the initial operation.
Set Maintenance Schedule: Establish a regular maintenance schedule based on the manufacturer’s recommendations and the observed performance of the housing. This includes periodic inspections, cleaning, and replacement of the magnetic rods and filtration bag if necessary.
By following these detailed installation instructions, you can ensure that the Magnetic Bag Filter Housing is correctly installed and operates effectively, providing optimal protection for your fluid system.
Maintenance
Regular Inspections
Safety First: Ensure the system is depressurized and fluid flow is stopped before beginning any maintenance. Wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves, safety glasses, and protective clothing.
Visual Inspection: Perform a visual inspection of the housing, connections, and surrounding areas. Look for signs of leaks, corrosion, or damage.
Check Pressure Gauges: Verify the pressure differential across the housing. A significant increase in pressure drop indicates the need for cleaning.
Cleaning the Housing
Depressurize and Drain: Safely depressurize the system and drain the fluid from the housing to prevent spills and ensure safe access.
Remove Housing Lid: Carefully open the housing lid according to the manufacturer’s instructions. This usually involves loosening bolts or clamps that secure the lid.
Extract Magnetic Rods: Remove the magnetic rods from the housing. Be cautious, as they will have accumulated ferrous particles.
Clean Magnetic Rods: Wipe down the magnetic rods with a clean cloth to remove collected particles. If necessary, use a soft brush to remove stubborn debris. Inspect the rods for signs of wear or damage and replace if necessary.
Remove and Replace Filtration Bag: Remove the used filtration bag from the housing. Dispose of it according to your facility’s waste management protocols. Install a new filtration bag, ensuring it fits securely within the housing.
Inspect Seals and Gaskets: Check the seals and gaskets for wear or damage. Replace any that are worn or compromised to prevent leaks during operation.
Reassemble and Test
Reassemble the Housing: Carefully reinsert the clean magnetic rods and new filtration bag into the housing. Ensure all components are properly seated and aligned.
Secure Housing Lid: Close and secure the housing lid, making sure all bolts or clamps are tightened evenly to prevent leaks.
Refill and Pressurize: Gradually refill the system with fluid, checking for leaks around the housing lid and connections. Slowly repressurize the system while monitoring for any signs of leakage.
Function Test: Start the system and observe the housing’s performance. Ensure that fluid flows smoothly and there are no unusual noises or vibrations. Verify that the pressure differential returns to normal levels after cleaning.
Periodic Maintenance
Schedule Regular Cleaning: Based on system usage and contamination levels, establish a regular cleaning schedule. More frequent cleaning may be required in systems with high levels of contaminants.
Replace Worn Components: Periodically inspect and replace magnetic rods, seals, gaskets, and other components that are subject to wear. Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for replacement intervals.
Record Maintenance Activities: Keep detailed records of all maintenance activities, including dates, actions taken, and any observations. This helps track the housing’s performance and identify any recurring issues.
Advanced Maintenance
Magnet Strength Check: Periodically check the strength of the magnetic rods to ensure they are still effective at capturing ferrous particles. Replace any rods that have lost significant magnetic strength.
System Flush: Occasionally perform a full system flush to remove any accumulated contaminants that may not be captured by the housing alone. This helps maintain overall system cleanliness and efficiency.
Consult Manufacturer: If you encounter persistent issues or need specialized maintenance, consult the manufacturer for guidance. They may provide additional maintenance procedures or recommend specific replacement parts.
By following these comprehensive maintenance procedures, you can ensure that the Magnetic Bag Filter Housing continues to operate efficiently, providing optimal protection for your fluid system and extending the life of your equipment.
Q&A
Q1: What is a Magnetic Bag Filter Housing?
A1: A Magnetic Bag Filter Housing is a filtration device used in fluid systems to remove ferrous particles and other contaminants. It uses high-intensity magnetic rods within a bag filter to capture magnetite and other debris, ensuring clean fluid flow and protecting downstream equipment.
Q2: How does a Magnetic Bag Filter Housing work?
A2: The housing contains magnetic rods that attract and hold ferrous particles. As fluid flows through the filter, these particles are drawn to the magnetic rods, while non-magnetic debris is collected in the bag filter. The clean fluid then continues through the system.
Q3: What are the benefits of using a Magnetic Bag Filter Housing?
A3: Benefits include efficient removal of ferrous and non-magnetic particles, extended equipment life, reduced maintenance costs, improved system efficiency, protection of critical components like boilers and pumps, and reduced operational costs.
Q4: What types of systems can use Magnetic Bag Filter Housings?
A4: These housings are suitable for a wide range of systems, including small commercial setups, large industrial systems in factories, hospitals, and building complexes. They can be used in hydronic heating systems, HVAC, manufacturing processes, and more.
Q5: How often should the Magnetic Bag Filter Housing be cleaned?
A5: Cleaning frequency depends on the system’s usage and contamination levels. Regular inspections and monitoring of pressure differentials can help determine when cleaning is necessary. Following the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule is advisable.
Q6: Can Magnetic Bag Filter Housings capture non-magnetic particles?
A6: Yes, while primarily designed to capture ferrous particles, the bag filter also collects non-magnetic contaminants such as scale and other debris, providing comprehensive filtration.
Q7: Where should a Magnetic Bag Filter Housing be installed in a system?
A7: It is typically installed on the return circuit near the boiler or at a critical point where fluid re-enters the system. In larger systems, additional units can be placed at various points to provide extra protection.
Q8: What maintenance is required for a Magnetic Bag Filter Housing?
A8: Maintenance includes regular inspections, cleaning of magnetic rods and the bag filter, checking and replacing seals and gaskets, and ensuring all connections are secure. Periodic checks of magnet strength and occasional system flushes are also recommended.
Q9: Are there any limitations to using Magnetic Bag Filter Housings?
A9: Limitations include the initial cost, the need for regular maintenance, and their effectiveness primarily for ferrous particles. For comprehensive filtration, additional methods may be needed for non-magnetic contaminants.
Q10: How do I know if the Magnetic Bag Filter Housing is working effectively?
A10: Effective operation is indicated by a consistent low-pressure differential across the housing, clean fluid output, and the absence of ferrous particles in downstream equipment. Regular monitoring and maintenance ensure optimal performance.
Q11: What makes Magnetic Bag Filter Housings unique compared to other filtration systems?
A11: They combine magnetic and bag filtration, capturing both ferrous and non-magnetic particles. They are highly efficient, versatile, and customizable to fit various system requirements, including handling large pipe sizes and extreme pressure and temperature conditions.
Q12: Can Magnetic Bag Filter Housings be customized for specific applications?
A12: Yes, they can be built to suit unique requirements such as specific water pressure, temperature, and different sized inflow and outflow pipes. A wide range of housing styles, including portable units and those on skids, is available to meet diverse needs.
Advantages / Disadvantages
Advantages:
Efficient Particle Removal: Magnetic Bag Filter Housings effectively capture both ferrous and non-magnetic particles, ensuring high levels of fluid cleanliness.
Extended Equipment Life: By removing harmful contaminants, these housings protect pumps, valves, boilers, and other system components, prolonging their lifespan.
Reduced Maintenance Costs: The magnetic rods and filtration bags are easily cleaned and reused, reducing the need for frequent replacements and lowering maintenance costs.
Improved System Efficiency: Cleaner fluids enhance the overall efficiency and performance of the system, leading to lower operational costs and improved energy efficiency.
Versatile Applications: Suitable for a wide range of systems, from small commercial setups to large industrial installations, including factories, hospitals, and building complexes.
Environmentally Friendly: Reusable magnetic rods and reduced filter waste contribute to more sustainable operations.
High Pressure and Temperature Tolerance: Models are available to handle extreme pressures and temperatures, making them suitable for demanding applications.
Customizable: Magnetic Bag Filter Housings can be customized to meet specific requirements such as different pipe sizes, pressure levels, and temperature ranges.
Ease of Installation and Maintenance: Designed for straightforward installation and maintenance, minimizing downtime and operational disruptions.
Prevention of Corrosion and Damage: By capturing magnetite and other debris, these housings help prevent destructive corrosion and heating system damage, reducing the risk of costly repairs.
Disadvantages:
Initial Cost: The upfront investment for Magnetic Bag Filter Housings can be higher than traditional filtration systems, which may be a consideration for budget-conscious operations.
Limited to Magnetic Particles: While they capture non-magnetic debris in the bag filter, the primary advantage is the removal of ferrous particles. Additional filtration methods may be required for comprehensive contaminant removal.
Regular Maintenance Required: Despite lower maintenance costs, regular cleaning and inspections are necessary to maintain optimal performance, requiring ongoing labor and attention.
Magnet Strength Degradation: Over time, the strength of the magnetic rods can degrade, reducing their effectiveness and necessitating periodic checks and replacements.
Space Requirements: Adequate space is needed for installation and maintenance, which can be a constraint in some system setups.
Potential for Magnet Damage: Magnetic rods can be damaged by impact or extreme conditions, requiring careful handling and potential replacement.
Flow Rate Limitations: Some magnetic filtration systems may impose limitations on flow rates, which can be a drawback in high-flow applications.
Dependency on Proper Installation: The effectiveness of the magnetic bag filter housing is heavily dependent on proper installation. Incorrect placement or orientation can significantly reduce its filtration efficiency.
Complexity for Non-Magnetic Contaminants: In systems with a mix of magnetic and non-magnetic contaminants, a combination of filtration methods may be required, adding to system complexity and cost.
Monitoring and Maintenance Knowledge: Effective use of magnetic filtration requires knowledge of monitoring and maintenance procedures to ensure consistent performance, which may necessitate additional training for personnel.
Applications
Hydronic Heating Systems
Magnetic Bag Filter Housings are used in hydronic heating systems to remove magnetite and other debris, preventing blockages and corrosion in pipes, pumps, and boilers. This ensures efficient heat transfer and prolongs the life of the system.
HVAC Systems
In heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems, these filters help maintain clean circulating fluids, which improves system efficiency, reduces wear on components, and minimizes maintenance requirements.
Industrial Cooling Systems
Used in cooling systems for machinery and industrial processes, Magnetic Bag Filter Housings remove contaminants from cooling fluids, protecting heat exchangers, compressors, and other critical equipment from fouling and damage.
Manufacturing Processes
In manufacturing, particularly in metalworking and machining operations, these filters capture ferrous particles from cutting fluids and coolants, enhancing the quality of finished products and extending the life of tools and equipment.
Power Generation
Magnetic Bag Filter Housings are used in power plants to filter boiler feedwater and cooling water, reducing the risk of scale and corrosion in turbines, condensers, and other vital components, thus improving efficiency and reliability.
Chemical Processing
In chemical processing industries, these filters help maintain the purity of process fluids by removing contaminants, ensuring the quality of chemical products, and protecting sensitive equipment from damage.
Water Treatment
They are employed in water treatment facilities to remove iron and other contaminants from water before it is distributed for industrial or residential use, ensuring water quality and protecting infrastructure.
Food and Beverage Industry
In the food and beverage industry, Magnetic Bag Filter Housings are used to maintain the purity of process fluids, ensuring that products meet safety and quality standards and preventing contamination of final products.
Pharmaceutical Manufacturing
These filters are essential in pharmaceutical manufacturing to ensure that process fluids are free from contaminants, maintaining the integrity of pharmaceutical products and complying with strict regulatory standards.
Automotive Industry
Used in the automotive industry to filter fluids in production lines, these housings help maintain the cleanliness of paints, lubricants, and other fluids, ensuring the quality of automotive parts and finished vehicles.
Oil and Gas
In oil and gas operations, Magnetic Bag Filter Housings remove contaminants from drilling fluids, completion fluids, and produced water, protecting equipment and ensuring smooth operation of extraction and processing activities.
Pulp and Paper Industry
These filters are utilized in the pulp and paper industry to remove contaminants from process water and chemicals, improving product quality and protecting equipment from wear and fouling.
Electronics Manufacturing
In electronics manufacturing, they help maintain the purity of process fluids, preventing contamination that could affect the performance and reliability of electronic components and devices.
Marine Applications
Magnetic Bag Filter Housings are used in marine environments to filter ballast water, cooling water, and other onboard fluids, protecting ship systems from corrosion and fouling.
Renewable Energy Systems
In renewable energy systems, such as geothermal and solar thermal plants, these filters remove contaminants from heat transfer fluids, ensuring efficient operation and protecting system components from damage.
These diverse applications demonstrate the versatility and effectiveness of Magnetic Bag Filter Housings in maintaining fluid cleanliness, protecting equipment, and ensuring the efficient operation of various systems across different industries.
Downloads
Drawings
 The innovative Magnetic Bag Filter Housings are set to transform magnetic filtration. Suitable for virtually any pipe size, these housings are ideal for small commercial systems. Also, large industrial setups in factories, hospitals, and building complexes. In addition, the design allows for full-flow or inline use, or as a side stream filter, adapting to various needs and applications. Furthermore, leveraging advanced Magnetic Strainer technology, they remove nearly 100% of magnetite and other unwanted debris from hydronic systems. Finally, the housings use long, high-intensity Neodymium magnetic rods to capture visible and submicronic magnetite (iron oxide) and non-magnetic contaminants (scale), collecting them efficiently.
The innovative Magnetic Bag Filter Housings are set to transform magnetic filtration. Suitable for virtually any pipe size, these housings are ideal for small commercial systems. Also, large industrial setups in factories, hospitals, and building complexes. In addition, the design allows for full-flow or inline use, or as a side stream filter, adapting to various needs and applications. Furthermore, leveraging advanced Magnetic Strainer technology, they remove nearly 100% of magnetite and other unwanted debris from hydronic systems. Finally, the housings use long, high-intensity Neodymium magnetic rods to capture visible and submicronic magnetite (iron oxide) and non-magnetic contaminants (scale), collecting them efficiently.

