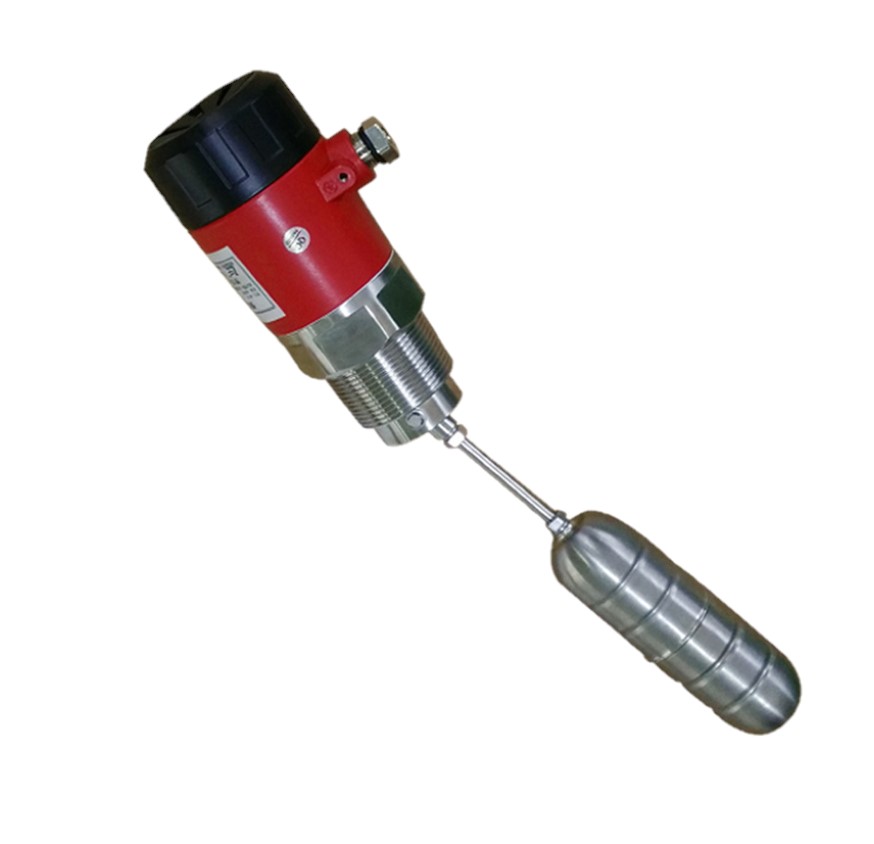
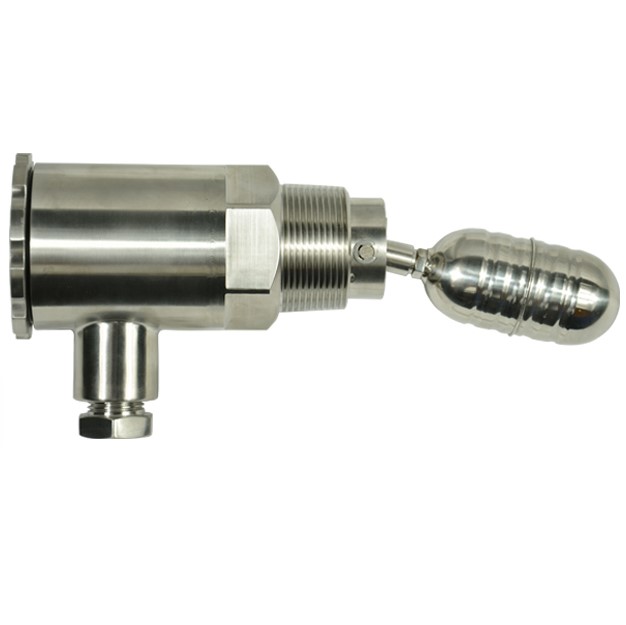
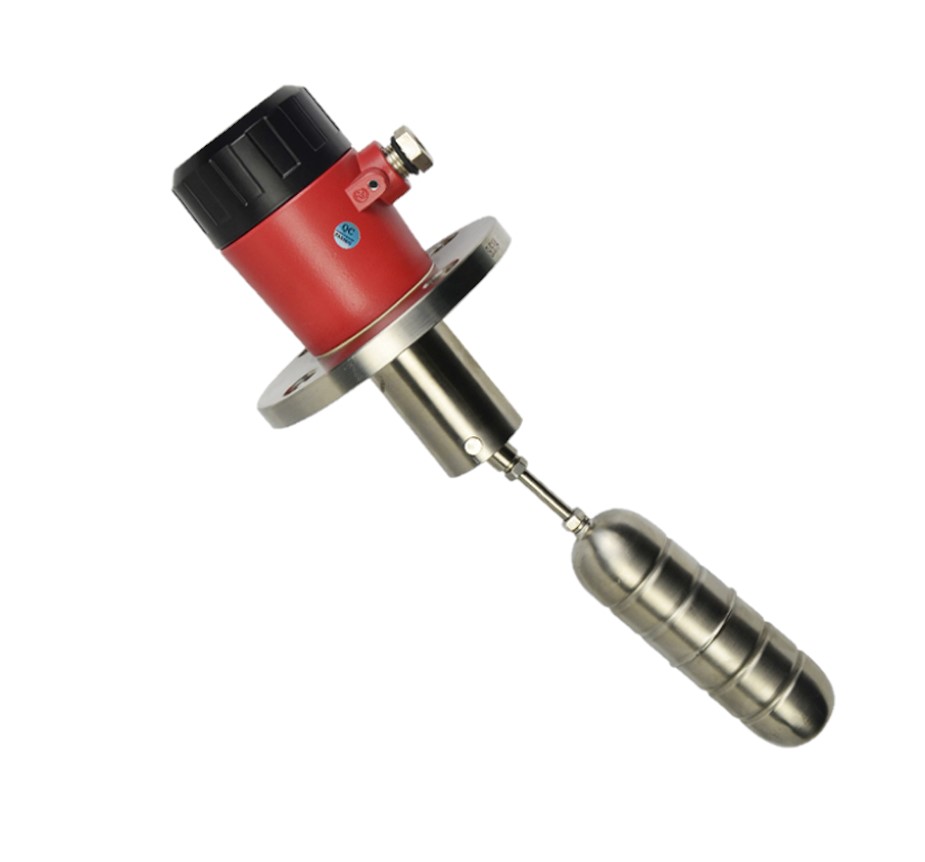
Floating Level Switch
$ 225.00 – $ 485.00Price range: $ 225.00 through $ 485.00
A floating level switch is a device used to monitor and control liquid levels in tanks and vessels. It operates based on buoyancy: a float rises and falls with the liquid level, activating or deactivating a switch mechanism. The switch can be mechanical, where the float moves a lever to open or close a contact, or magnetic, where a magnet within the float triggers a reed switch. Floating level switches are valued for their simplicity, cost-effectiveness, and reliability in various applications, including water treatment, oil and gas, chemical processing, and agriculture. They are ideal for applications where cost and ease of maintenance are priorities, and where the liquid’s properties do not hinder float movement. However, they may struggle with highly viscous, foamy, or turbulent liquids and require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance. Despite these limitations, floating level switches are a popular choice for their robust construction and effective performance in managing liquid levels.
Description
Introduction
Floating level switches are essential components used in various industrial and commercial applications to monitor and control liquid levels. Also, these switches operate based on the principle of buoyancy, utilizing a float that rises and falls with the liquid level. The primary function of a floating level switch is to activate or deactivate a device or process when a liquid reaches a specific level. Furthermore, this article explores the design, operation, advantages, limitations, and applications of floating level switches, providing a comprehensive understanding of this critical technology.
How a Floating Level Switch Works
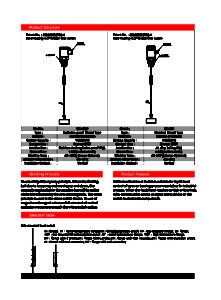
A floating level switch typically consists of a float, a switch mechanism, and sometimes a mounting assembly. In addition, manufacturers typically make the float from materials such as plastic or metal, designing it to be buoyant in the liquid. As the liquid level changes, the float moves up or down accordingly. Finally, attached to the float is a switch mechanism, which can be either a mechanical or a magnetic type.
Mechanical Switch Mechanism: In this type, the float is connected to a lever or a rod that operates a mechanical switch. In addition, as the float rises or falls, it moves the lever or rod, which in turn activates or deactivates the switch. Finally, mechanical switches are straightforward but can be prone to wear and require maintenance.
Magnetic Switch Mechanism: This mechanism uses a magnet within the float to operate a reed switch or other types of magnetic sensors. In addition, when the float moves with the liquid level, the magnet interacts with the reed switch, causing it to open or close. Finally, magnetic switches are often preferred for their durability and resistance to wear.
Design and Construction
The design of a floating level switch depends on several factors, including the type of liquid, operating environment, and application requirements. Key design considerations include:
Float Material: Make the float from a material compatible with the liquid it will contact. For example, use floats made from stainless steel or other resistant materials in corrosive environments.
Switch Type: Choosing between mechanical and magnetic switches depends on the application’s needs. Moreover, users favor magnetic switches for their reliability and longevity, while they use mechanical switches for simpler or cost-sensitive applications.
Mounting Assembly: The mounting assembly ensures that the switch is correctly positioned in the tank or vessel. It must be robust and secure to withstand the operational conditions.
Installation and Maintenance for a Floating Level Switch
Proper installation and maintenance are crucial for the effective operation of floating level switches. Here are some guidelines:
Installation: Mount the switch correctly according to the manufacturer’s specifications. Position the float where it can move freely with changes in the liquid level. Verify that the switch is compatible with the liquid and environmental conditions.
Calibration: Some floating level switches may require calibration to ensure accurate level detection. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for calibration procedures.
Maintenance: Regularly inspect the float and switch mechanism for signs of wear, damage, or fouling. Clean the float and ensure that the switch is functioning correctly. Replace any worn or damaged parts as needed.
Testing: Periodically test the floating level switch to ensure it is operating correctly. Check that it activates and deactivates at the intended levels.
Conclusion
Floating level switches are a versatile and cost-effective solution for monitoring and controlling liquid levels in various applications. Also, their simple design, reliability, and ease of use make them a popular choice in many industries. Furthermore, while they have limitations, such as sensitivity to certain liquid characteristics and mechanical wear. Other issues are proper installation, and maintenance can mitigate these issues. Finally, understanding the principles, advantages, limitations, and applications of floating level switches helps ensure their effective use. It’s effective use in managing liquid levels, contributing to efficient and safe operations across diverse processes.
Other Level Switches you may be interested in
Vibrionic Fork Level Sensor
Capacitance Level Sensor
Specifications
General Description
- Type: Floating Level Switch
- Application: Liquid level detection and control in tanks, vessels, and reservoirs
- Mounting Style: Vertical or horizontal mounting
Mechanical Specifications
- Float Material:
- Options: Polypropylene, Stainless Steel, PVC, PTFE
- Compatibility: Designed for use with specific liquids (e.g., water, oil, chemicals)
- Switch Mechanism:
- Type: Mechanical (lever-operated) or Magnetic (reed switch)
- Float Diameter:
- Range: 1.5 inches to 4 inches (38 mm to 100 mm)
- Float Length:
- Adjustable length depending on the application
Electrical Specifications
- Voltage Rating:
- AC Voltage: 110V, 220V, 240V
- DC Voltage: 12V, 24V
- Current Rating:
- Switch Output:
- Normally Open (NO) or Normally Closed (NC)
- Optional: SPST (Single Pole Single Throw), SPDT (Single Pole Double Throw)
- Wiring Connections:
- Type: Terminal block, pigtail leads, or cable with connectors
- Wire Gauge: 22 AWG to 16 AWG
Environmental Specifications
- Temperature Range:
- Operating: -20°C to 80°C (-4°F to 176°F)
- Storage: -40°C to 85°C (-40°F to 185°F)
- Pressure Rating:
- Maximum: 10 bar (145 psi)
- Ingress Protection:
- Rating: IP65 or IP67 (dust-tight and water-resistant)
Performance Specifications
- Switching Accuracy:
- Typically ±2 mm to ±10 mm (depending on model)
- Response Time:
- Activation/Deactivation: <1 second
- Cycle Life:
- Mechanical Switches: >1 million cycles
- Magnetic Switches: >10 million cycles
Construction and Material
- Body Material:
- Options: ABS, Stainless Steel, Aluminum
- Seals and Gaskets:
- Material: Nitrile (Buna-N), EPDM, Viton (depending on liquid compatibility)
- Mounting Options:
- Threaded: NPT, BSP
- Flanged: ANSI, DIN
- Clamp-on: Custom brackets
Compliance and Standards
- Certifications:
- CE (European Conformity)
- UL (Underwriters Laboratories) (for applicable models)
- RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances)
- Standards:
- IEC 61010 (Safety requirements for electrical equipment for measurement)
- ISO 9001 (Quality management systems)
Options and Accessories
- Adjustable Length Rods: For varying tank depths
- Extension Cables: For remote mounting
- Protective Guards: To prevent damage in harsh environments
- Mounting Brackets: For flexible installation
Installation and Maintenance
- Installation Instructions: Included with product
- Maintenance: Regular cleaning and inspection recommended; replacement parts available
These specifications provide a detailed overview of the key characteristics and options available for a floating level switch, ensuring it meets the requirements for various applications and environments.
Installation
Preparation
- Review Documentation: Before installation, review the manufacturer’s datasheet and installation instructions to understand the specific requirements and recommendations for your floating level switch model.
- Gather Tools and Materials: Ensure you have the necessary tools (e.g., wrench, screwdriver) and materials (e.g., mounting hardware, sealing materials) for installation.
- Verify Compatibility: Confirm that the floating level switch is compatible with the type of liquid, the tank or vessel size, and the environmental conditions where it will be installed.
Site Preparation
- Clean the Installation Area: Ensure the area where the switch will be mounted is clean and free of debris. This helps prevent any interference with the float’s movement.
- Check Liquid Level: Determine the appropriate mounting position based on the desired liquid levels. The switch should be installed where it can accurately detect the liquid level without interference.
Mounting the Switch
- Position the Mounting Assembly: Attach the mounting assembly to the tank or vessel at the desired location. Ensure it is securely fastened and aligned properly.
- Install the Float: Insert the float into the mounting assembly. Make sure the float can move freely with changes in liquid level and is not obstructed by other components or structures.
- Secure the Switch: If applicable, secure the switch mechanism to the float assembly, following the manufacturer’s guidelines. Ensure all connections are tight and correctly aligned.
Wiring and Connections
- Turn Off Power: Before making any electrical connections, ensure that power to the system is turned off to avoid any risk of electrical shock.
- Connect Wires: Connect the switch wires to the control system or relay according to the wiring diagram provided by the manufacturer. Follow proper electrical codes and standards for wiring.
- Verify Connections: Double-check all electrical connections to ensure they are secure and correctly configured.
Calibration and Testing
- Calibrate the Switch: If necessary, calibrate the floating level switch according to the manufacturer’s instructions to ensure accurate level detection. This may involve setting the activation or deactivation points.
- Test the Switch: Fill the tank or vessel to test the switch operation. Verify that the switch activates and deactivates at the correct liquid levels as intended.
- Check for Leaks: Ensure there are no leaks around the mounting assembly and connections. Tighten any fittings or seals as needed.
Final Checks and Documentation
- Inspect Installation: Conduct a final inspection of the installation to ensure everything is properly installed and functioning correctly.
- Document Installation: Record the installation details, including the switch model, mounting location, calibration settings, and any observations. This documentation will be useful for future maintenance and troubleshooting.
- Restore Power: Once everything is confirmed to be in order, restore power to the system and monitor the floating level switch during initial operation to ensure proper functionality.
7. Maintenance Recommendations
- Regular Inspections: Schedule periodic inspections to ensure the switch and float are functioning correctly. Check for signs of wear, corrosion, or fouling.
- Cleaning: Clean the float and mounting assembly as needed to prevent debris buildup that could affect performance.
- Adjustments: Make any necessary adjustments to the switch settings or positioning based on changes in liquid properties or operational requirements.
Following these installation procedures will help ensure that your floating level switch operates effectively and reliably, providing accurate liquid level monitoring and control.
Q&A
Q1: What is a floating level switch?
A1: A floating level switch is a device used to detect the level of a liquid within a tank or vessel. It consists of a buoyant float that moves with the liquid level and a switch mechanism that activates or deactivates based on the float’s position. This device helps control or monitor liquid levels to prevent overflows or dry running.
Q2: How does a floating level switch work?
A2: A floating level switch operates based on buoyancy. The float, which is buoyant, rises and falls with the liquid level. As the float moves, it either mechanically or magnetically triggers a switch mechanism to open or close an electrical circuit, signaling a high or low liquid level.
Q3: What are the different types of floating level switches?
A3: Floating level switches generally come in two types:
- Mechanical: Uses a lever or rod connected to the float to activate or deactivate a mechanical switch.
- Magnetic: Employs a magnet within the float to interact with a reed switch or other magnetic sensors, which triggers the switch mechanism.
Q4: What are the primary applications of floating level switches?
A4: Floating level switches are used in a variety of applications, including:
- Water treatment plants for monitoring water levels.
- Oil and gas industries to manage fluid levels in tanks.
- Chemical processing for controlling chemical levels.
- Food and beverage industries for managing processing and storage tanks.
- Agricultural systems for irrigation control.
Q5: What are the main advantages of using a floating level switch?
A5: Advantages include:
- Simplicity: Easy to install and operate.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Generally, less expensive compared to other level sensing technologies.
- Reliability: Robust design with minimal moving parts.
- Versatility: Suitable for a range of liquids and tank sizes.
- Low Power Consumption: Energy-efficient operation.
Q6: What are the limitations of floating level switches?
A6: Limitations include:
- Sensitivity to Liquid Properties: Not ideal for highly viscous, foamy, or turbulent liquids.
- Mechanical Wear: Mechanical switches may wear over time and require maintenance.
- Size Constraints: May not be suitable for very small or narrow tanks.
- Potential for Fouling: Floats can become coated with debris or sludge, affecting performance.
Q7: How should a floating level switch be installed?
A7: Installation steps include:
- Prepare the Site: Clean the installation area and verify compatibility with the liquid and tank.
- Mount the Switch: Attach the mounting assembly to the tank and install the float so it can move freely.
- Wiring: Connect the electrical wires according to the manufacturer’s wiring diagram.
- Calibrate and Test: Adjust settings as needed and test the switch for proper operation.
- Document: Record installation details and ensure all components are securely fastened.
Q8: What maintenance is required for floating level switches?
A8: Maintenance includes:
- Routine Inspections: Check for wear, damage, and proper operation.
- Cleaning: Remove debris and clean the float and surrounding area.
- Functional Testing: Verify operation and recalibrate if necessary.
- Adjustments: Adjust float position or switch settings as needed.
- Documentation: Log maintenance activities and update records.
Q9: How can you troubleshoot common issues with floating level switches?
A9: Troubleshooting involves:
- Checking Float Movement: Ensure the float moves freely without obstruction.
- Inspecting Connections: Verify all electrical connections are secure.
- Testing Calibration: Confirm that the switch activates and deactivates at the correct levels.
- Cleaning Components: Remove any buildup or debris affecting performance.
- Replacing Parts: Replace any damaged or worn components.
Q10: Can floating level switches be used in all types of liquids?
A10: Floating level switches can be used in many types of liquids, but their effectiveness may vary based on the liquid’s properties. They are generally suitable for clean liquids but may have limitations with viscous, foamy, or corrosive substances. For such applications, specialized floats and materials may be required.
Advantages / Disadvantages
Advantages of Floating Level Switches
Floating level switches offer several advantages, making them popular in various applications:
Simplicity: Floating level switches are straightforward in design and operation. Their simplicity contributes to ease of installation and maintenance.
Cost-Effectiveness: Compared to other level sensing technologies, floating level switches are relatively inexpensive, making them a cost-effective choice for many applications.
Reliability: With minimal moving parts and robust construction, floating level switches are reliable and can operate in harsh environments.
Versatility: They can be used in various liquids, including water, oils, and chemicals. Special designs can accommodate different tank shapes and sizes.
Low Power Consumption: Floating level switches typically consume very little power, making them energy efficient.
Limitations of Floating Level Switches
Despite their advantages, floating level switches have some limitations:
Sensitivity to Liquid Characteristics: Floating level switches may not perform well with highly viscous, foamy, or turbulent liquids. The float may become trapped or hindered in such conditions.
Mechanical Wear: Mechanical switches can experience wear and tear over time, leading to reduced accuracy or failure. Regular maintenance is required to ensure optimal performance.
Size Constraints: The size of the float and switch mechanism may limit their use in very small or narrow tanks.
Floating Issues: In certain applications, the float may become coated with debris or sludge, affecting its buoyancy and operation.
Applications
Applications of Floating Level Switches
Floating level switches find applications across a wide range of industries and processes:
Water Treatment Plants: Floating level switches are used to monitor water levels in tanks, wells, and reservoirs, ensuring proper operation and preventing overflows or dry running.
Oil and Gas Industry: In oil and gas operations, floating level switches help manage fluid levels in storage tanks, separators, and other equipment.
Chemical Processing: These switches are employed in chemical processing plants to monitor and control the levels of various chemicals, ensuring safe and efficient operations.
Food and Beverage Industry: Floating level switches are used in the food and beverage industry to manage liquid levels in processing tanks, fermentation vessels, and storage containers.
Automotive: In automotive applications, floating level switches monitor fuel levels in tanks, ensuring accurate readings and proper functioning of the vehicle.
Agriculture: Farmers use floating level switches in irrigation systems to maintain optimal water levels in reservoirs and ensure efficient water usage.
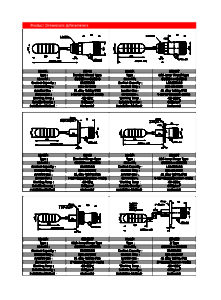
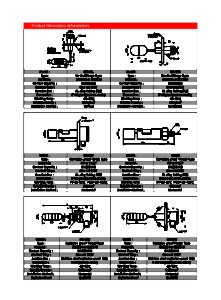
Drawings