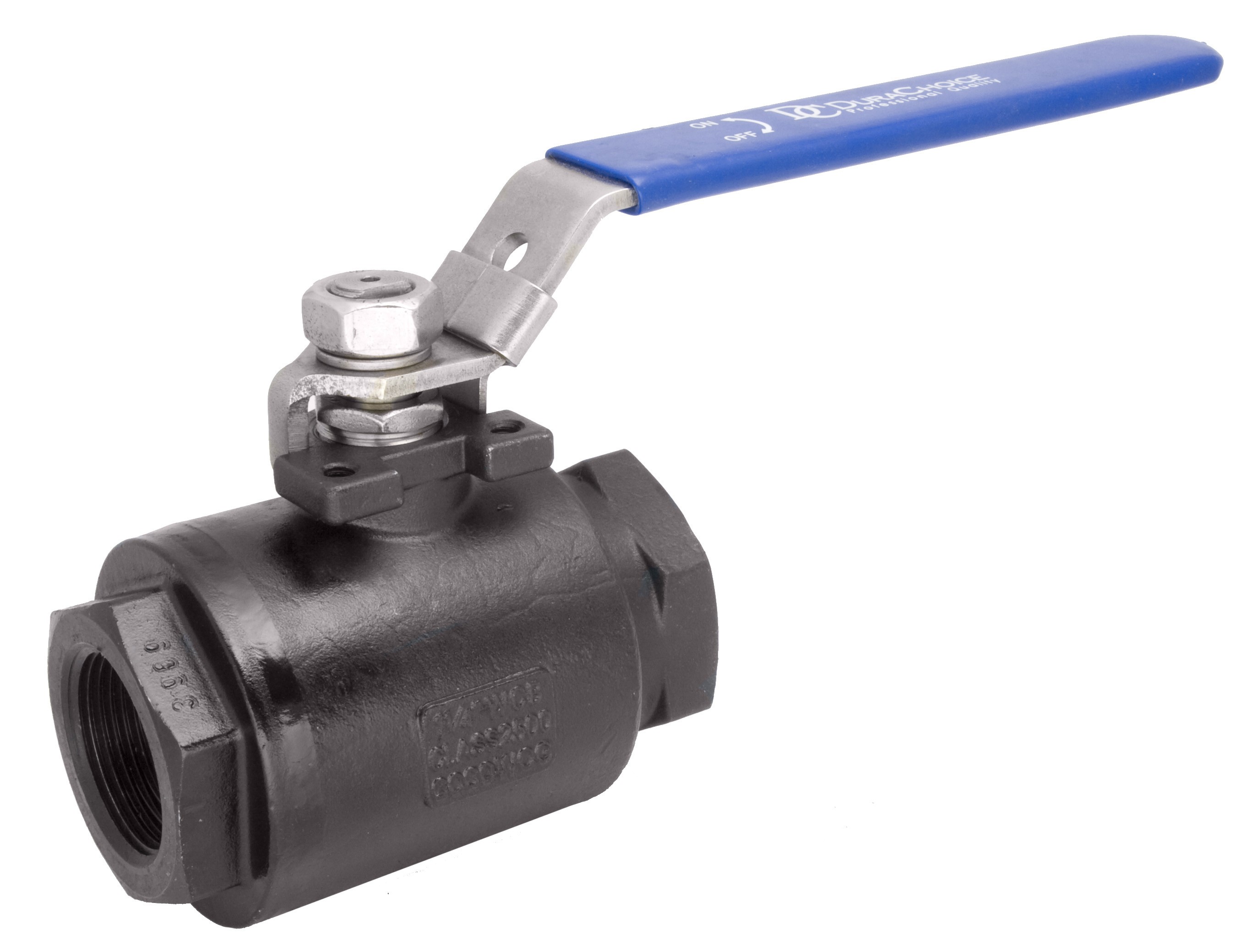
Ball Valves
$ 22.00 – $ 2,122.00
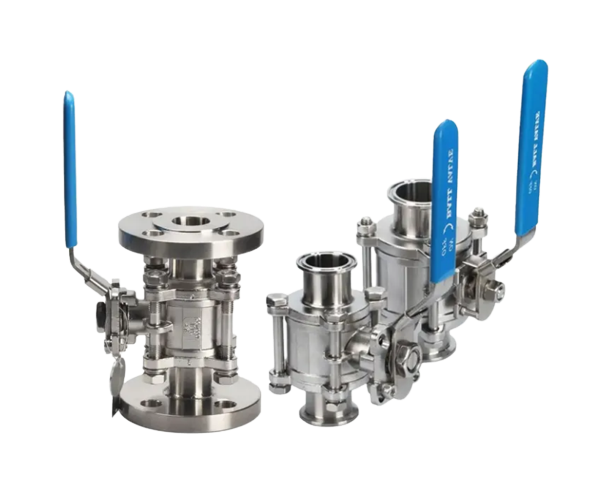
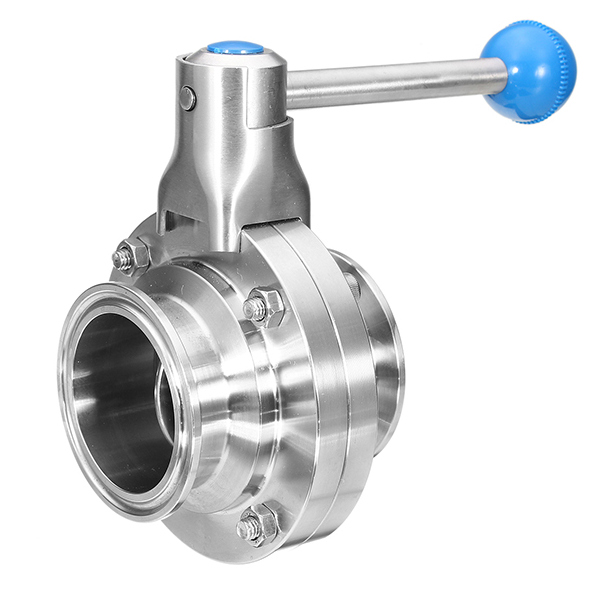
Ball valves are vital components used for controlling the flow of liquids or gases in industrial settings. They are available in different constructions, including 1-piece, 2-piece, and 3-piece designs, each offering specific benefits in terms of maintenance and versatility. 1-piece ball valves are compact and straightforward, while 2-piece valves allow for easier disassembly and repair. 3-piece ball valves provide superior maintenance flexibility with their modular design. These valves come with various connection ends to accommodate different piping systems, such as FNPT, flanged, and sanitary Tri-clamp ends, catering to diverse installation needs. Materials like carbon steel, 304 stainless steel (304SS), and 316 stainless steels (316SS) are commonly used in ball valve construction, each offering unique strengths including durability, corrosion resistance, and suitability for specific industrial applications. Proper selection of ball valves based on their design, connection ends, and materials is crucial for efficient flow control and system integrity in industrial processes.
Description
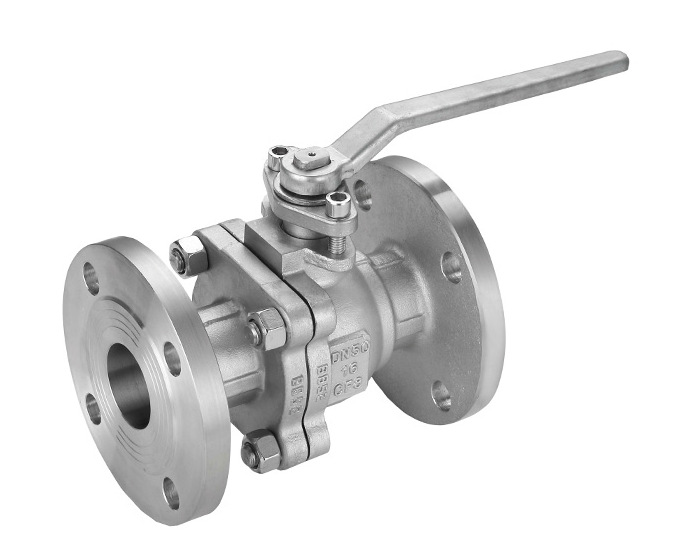 Ball valves are versatile flow control valves commonly used in various industrial applications to regulate the flow of liquids or gases. They are categorized based on their construction as 1-piece, 2-piece, or 3-piece ball valves, each offering specific advantages and applications. Additionally, ball valves come with different connection ends, including FNPT, flanged, and sanitary Tri-clamp ends, catering to diverse installation requirements. Materials such as carbon steel, 304 stainless steel (304SS), and 316 stainless steels (316SS) are commonly used for their construction, providing properties like strength, corrosion resistance, and durability.
Ball valves are versatile flow control valves commonly used in various industrial applications to regulate the flow of liquids or gases. They are categorized based on their construction as 1-piece, 2-piece, or 3-piece ball valves, each offering specific advantages and applications. Additionally, ball valves come with different connection ends, including FNPT, flanged, and sanitary Tri-clamp ends, catering to diverse installation requirements. Materials such as carbon steel, 304 stainless steel (304SS), and 316 stainless steels (316SS) are commonly used for their construction, providing properties like strength, corrosion resistance, and durability.
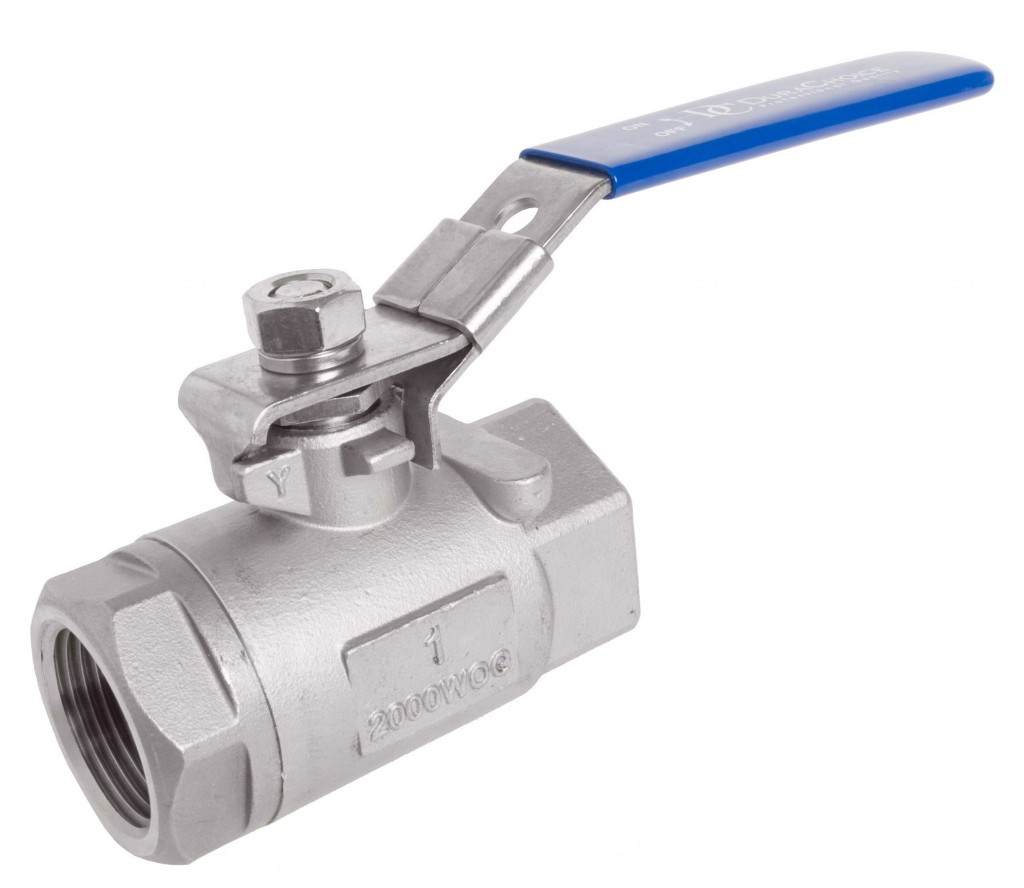

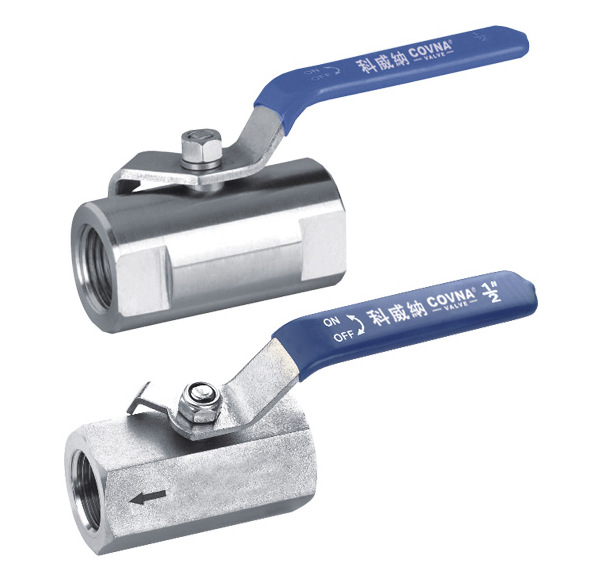
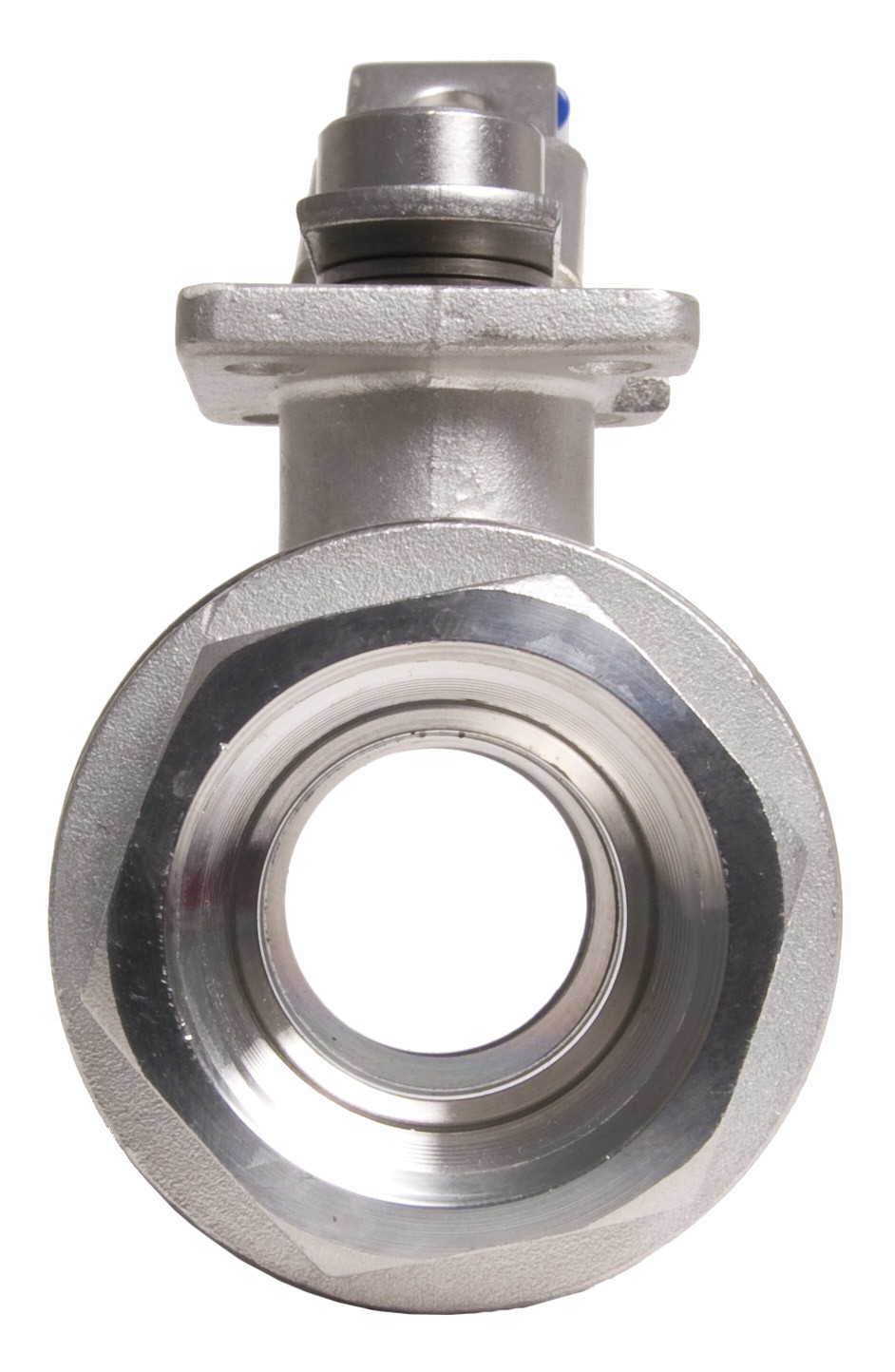
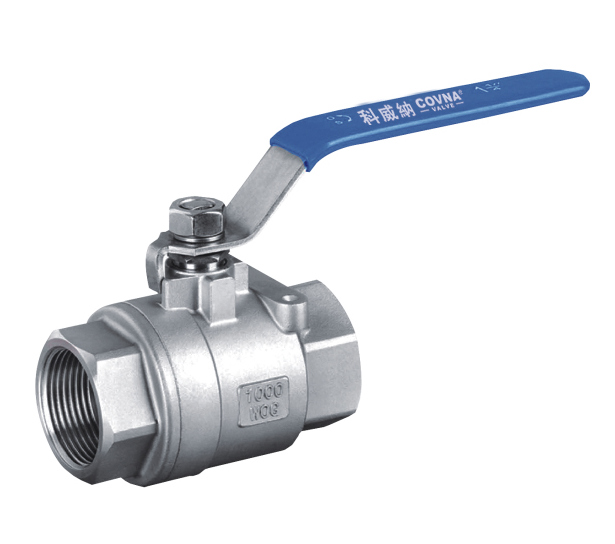
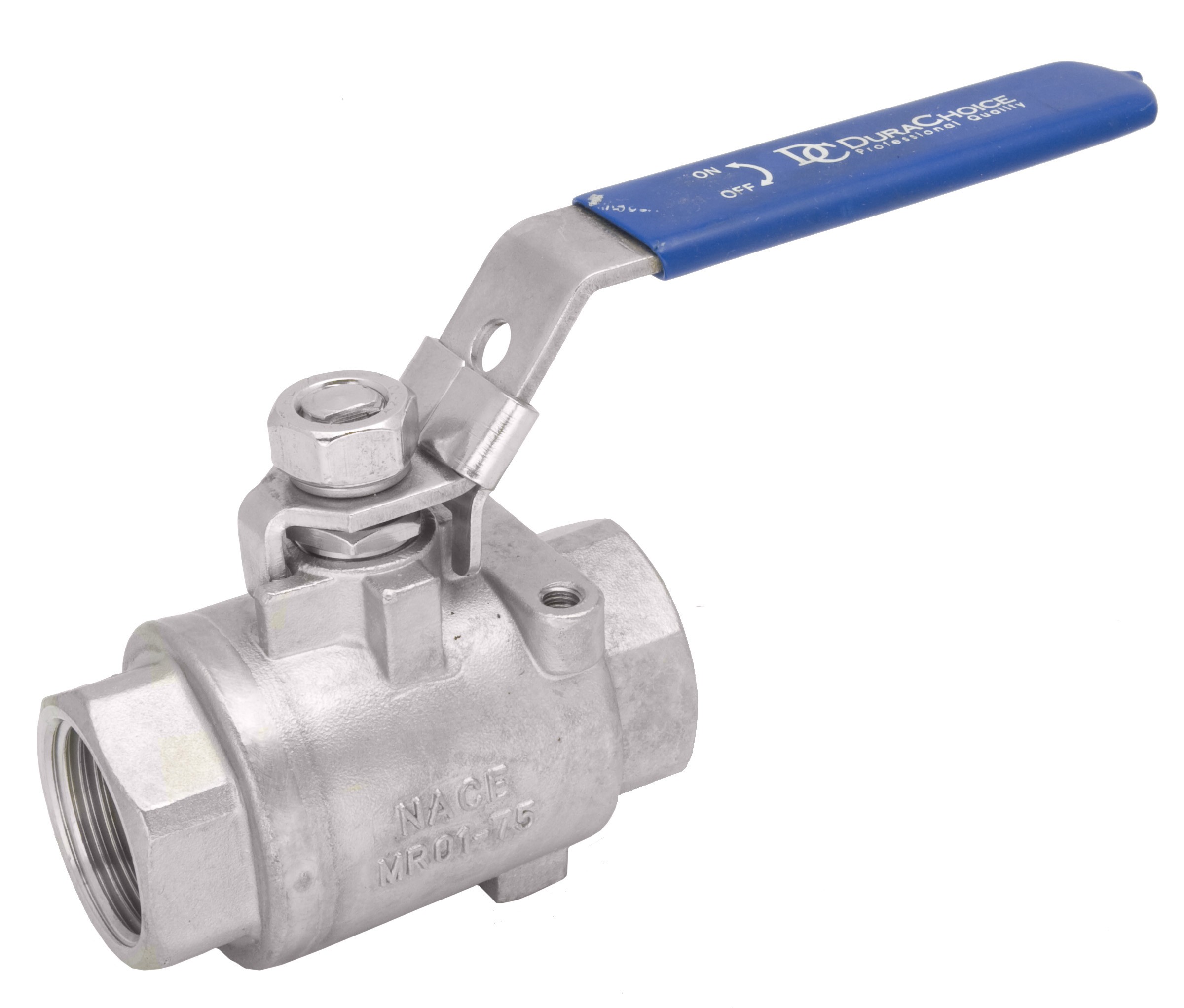
1-Piece Ball Valves
1-piece units consist of a single housing that integrates the ball and seat. They are compact, lightweight, and generally cost-effective. Engineers design these valves for simple on/off flow control applications, and they make them easy to install and maintain. However, they offer limited flexibility for repair or maintenance due to their one-piece design.

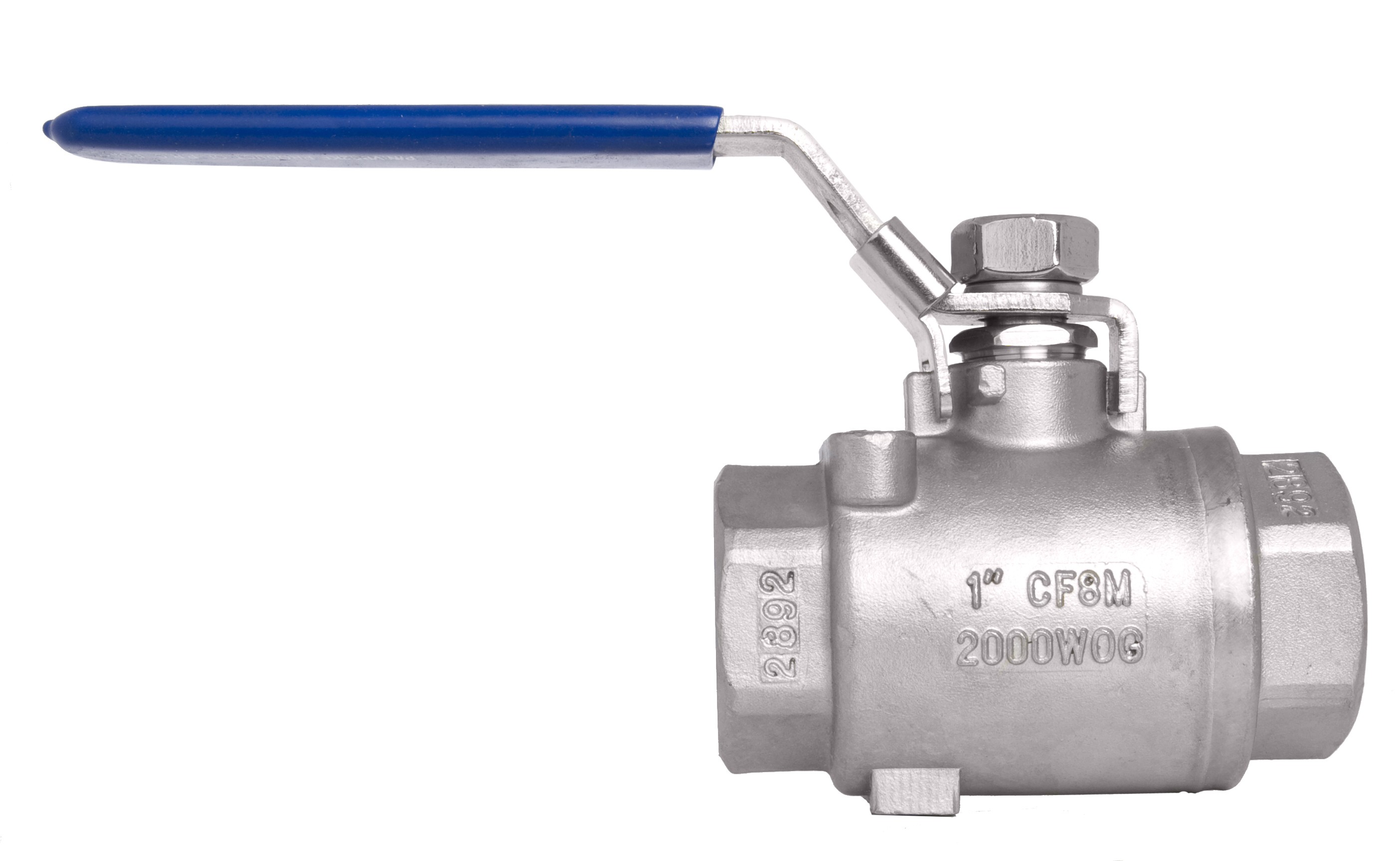
2-Piece Ball Valves
Engineers construct 2-piece ball valves with two separate pieces: one containing the ball and stem assembly and the other housing the seat. This design allows for easier disassembly, maintenance, and repair compared to 1-piece ball valves. They are suitable for a wider range of applications and offer greater flexibility in terms of customization and end connections.
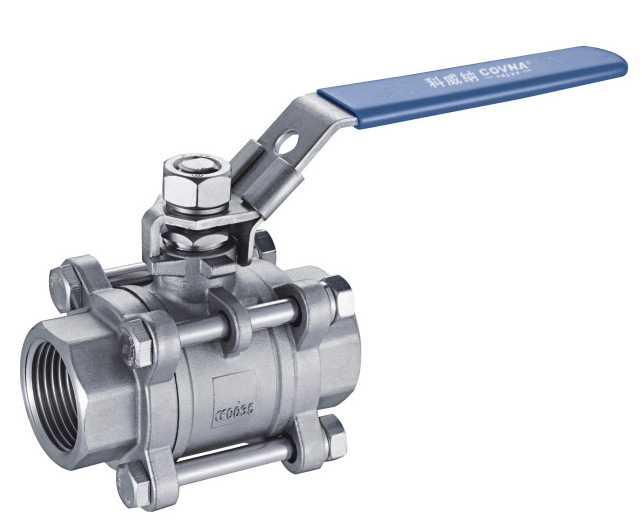
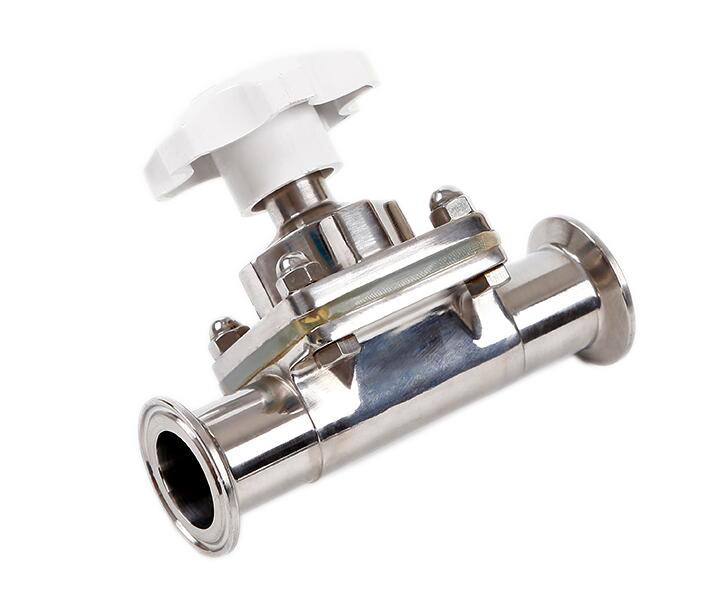
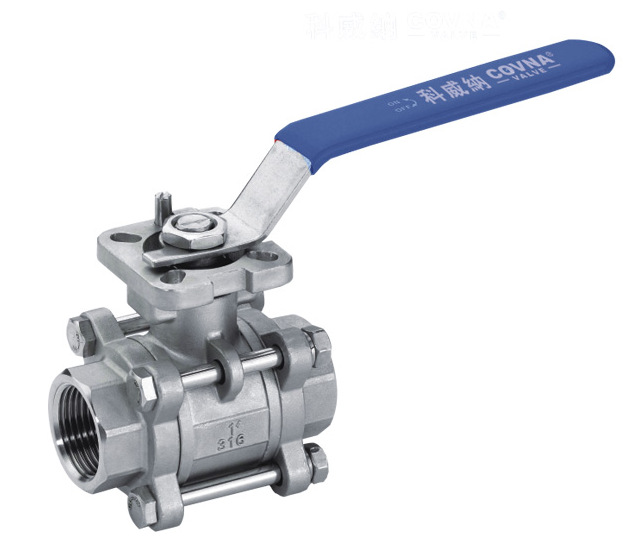
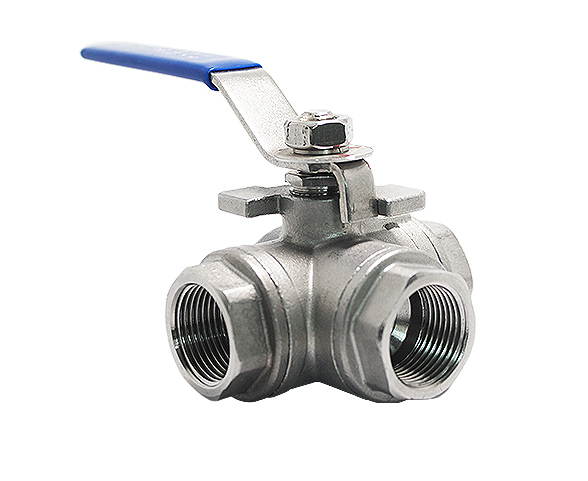
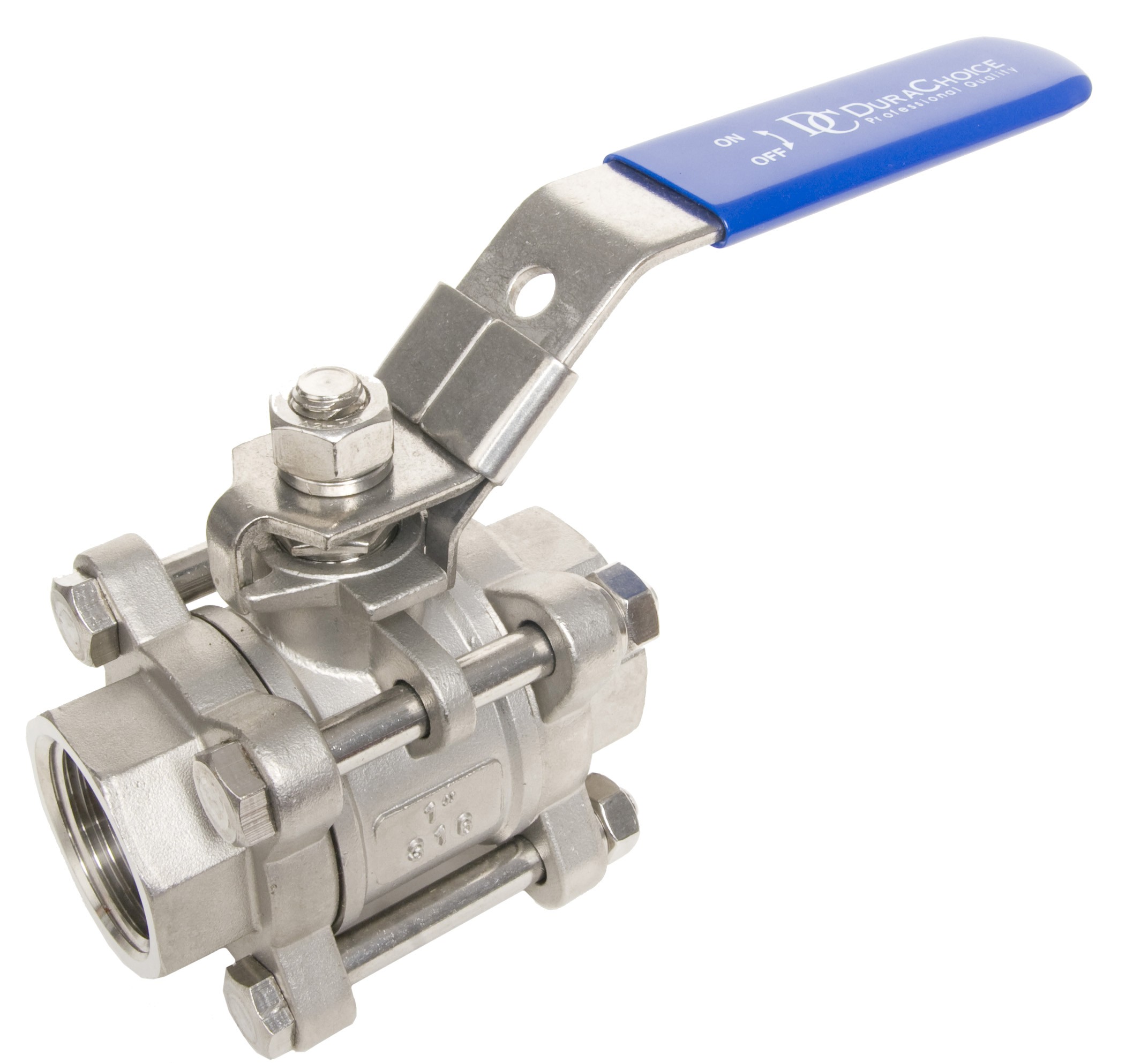
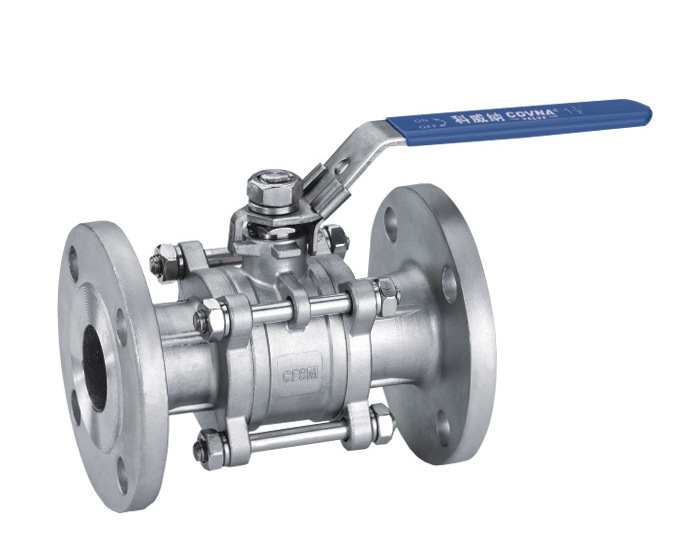 3-Piece Ball Valves
3-Piece Ball Valves
The design of 3-piece units includes a body and two end caps, allowing you to remove the middle section without disturbing the piping connections. This design facilitates easy maintenance, cleaning, and servicing, making these units ideal for applications that require regular upkeep. 3-piece ball valves offer superior versatility and durability compared to 1-piece and 2-piece valves.
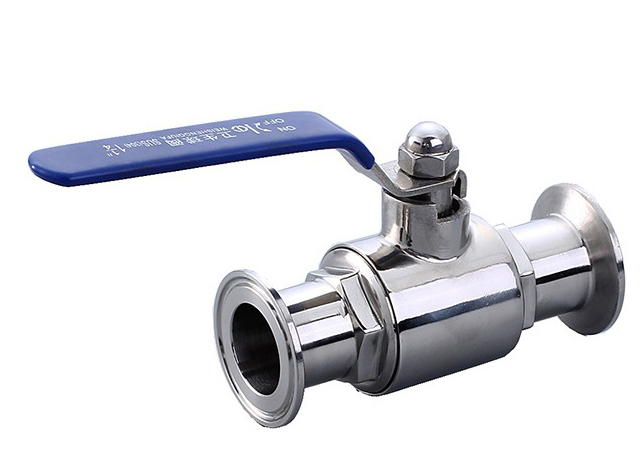
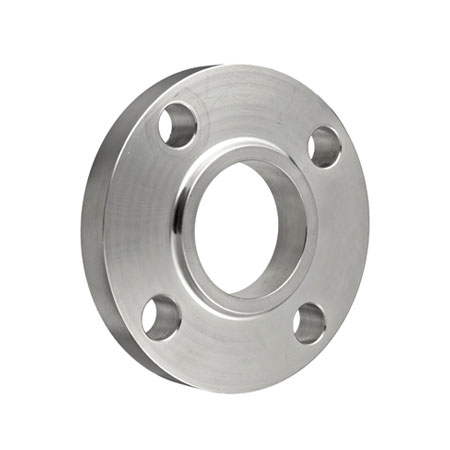 Connection Ends
Connection Ends
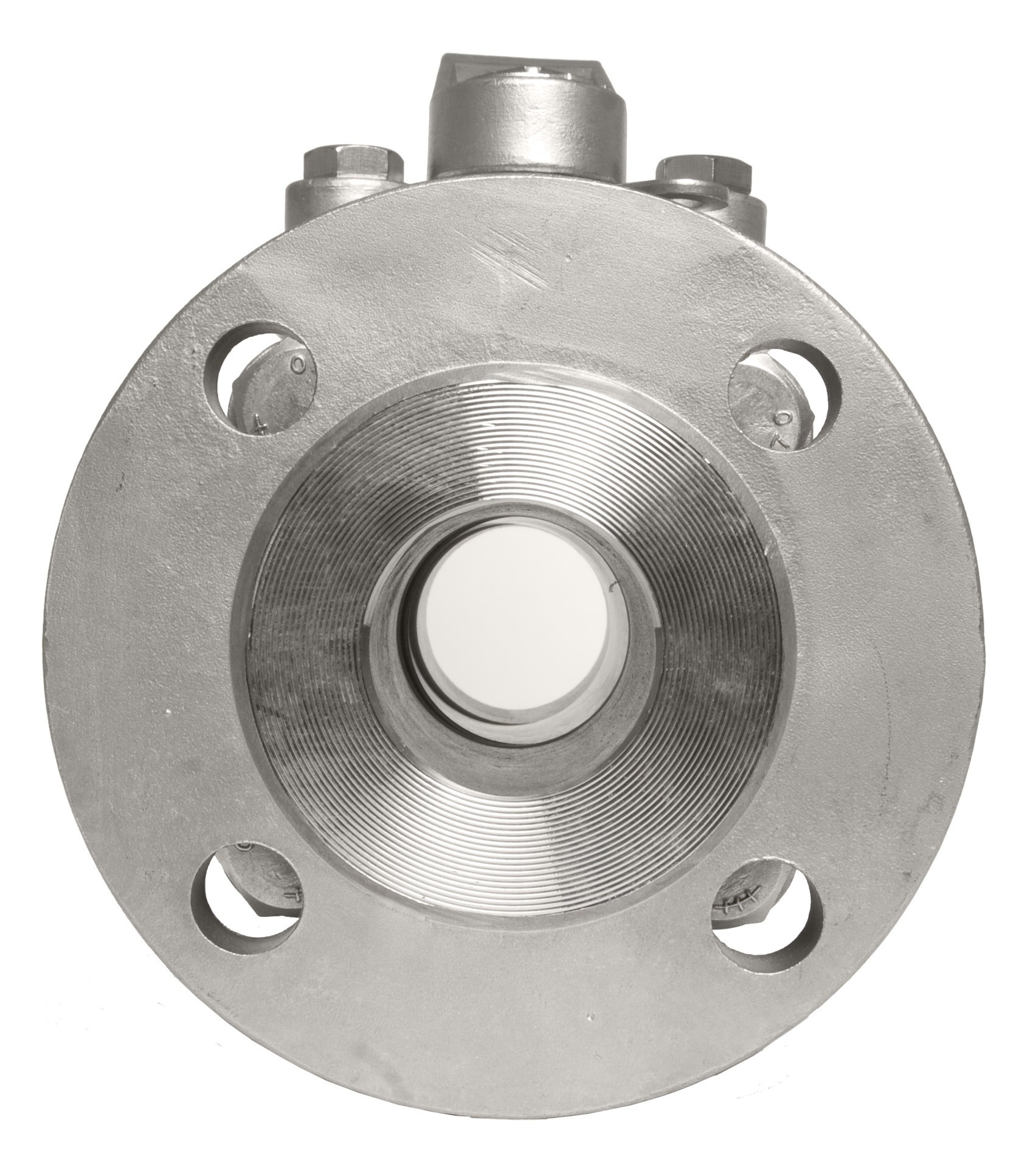
Valves come with different connection ends to suit various piping systems. FNPT (Female National Pipe Thread) connections provide a threaded connection for easy installation into female threaded pipes or fittings. Flanged connections feature flat discs with holes for bolting onto flanged pipes, providing a secure and leak-proof attachment. Designers create sanitary Tri-clamp ends for hygienic applications in industries such as food and pharmaceuticals, ensuring cleanliness and enabling easy disassembly for cleaning and sterilization.
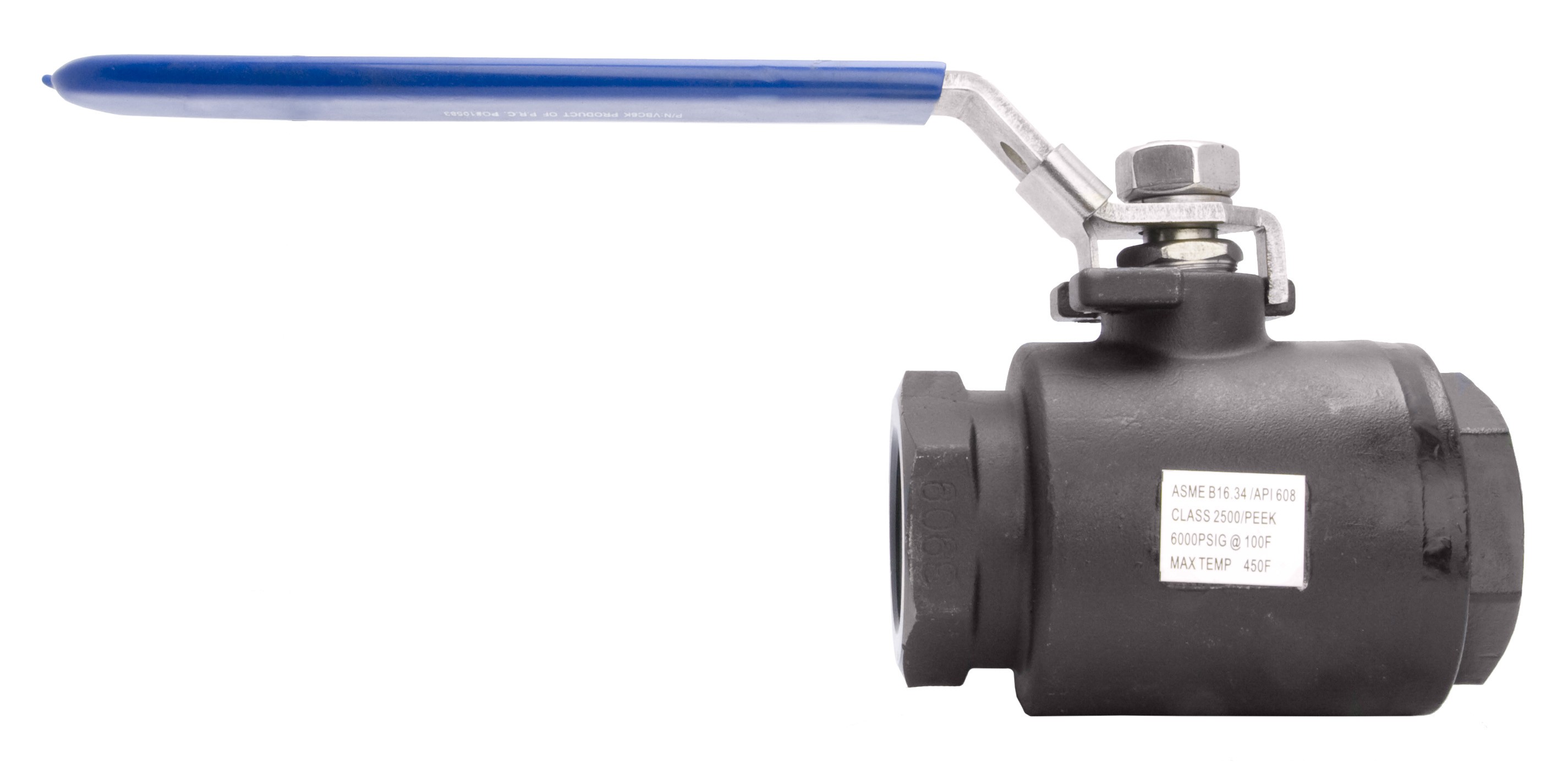
Materials
We are manufactures using different materials to suit specific application requirements. Carbon steel ball valves are durable and cost-effective, suitable for applications with moderate pressure and temperature conditions. 304 stainless steel (304SS) provides good corrosion resistance and industries commonly use it in general industrial applications. 316 stainless steel (316SS) provides superior corrosion resistance and is ideal for applications requiring high chemical resistance or exposure to harsh environments.
In conclusion, they are essential components for flow control in industrial systems. Also, with varying designs such as 1-piece, 2-piece, and 3-piece valves catering to different needs. The choice of connection ends and materials, including FNPT, flanged, sanitary Tri-clamp ends. Furthermore, other materials include carbon steel, 304SS, or 316SS, depends on the specific application requirements for durability, compatibility, and performance.
Specifications
The specifications of a ball valve typically include key details that define its design, construction, and operational capabilities. Here are the typical specifications you might find for a ball valve:
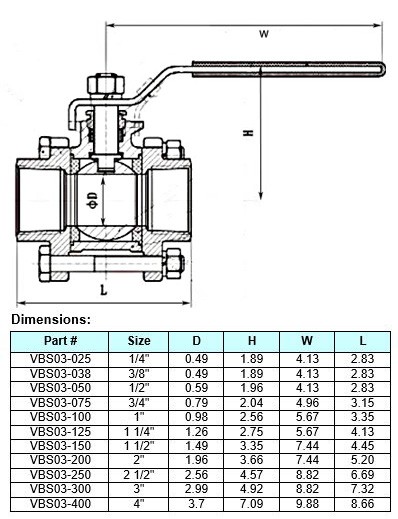
Size: The size specification indicates the nominal diameter of the valve, usually expressed in inches or millimeters, and denotes the size of the pipeline for which the valve is designed.
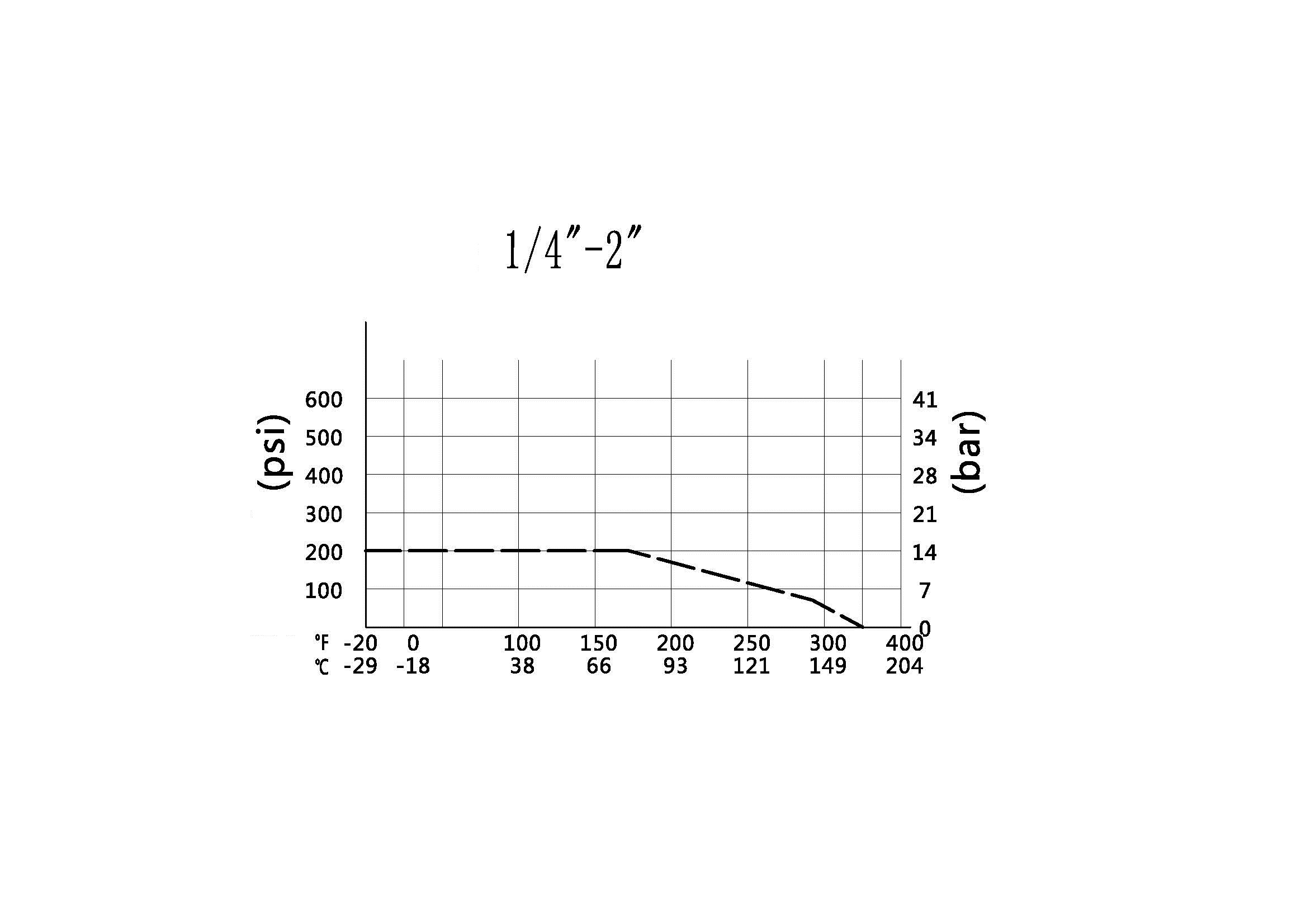
Pressure rating: This specification defines the maximum pressure at which the valve can safely operate, often specified in pounds per square inch (psi) or bars. It is crucial to ensure the valve is compatible with the operating pressure of the system.
Temperature rating: The temperature rating specifies the range of temperatures within which the valve can effectively function without compromising its integrity or performance. The temperature rating is typically expressed in degrees Celsius or Fahrenheit.
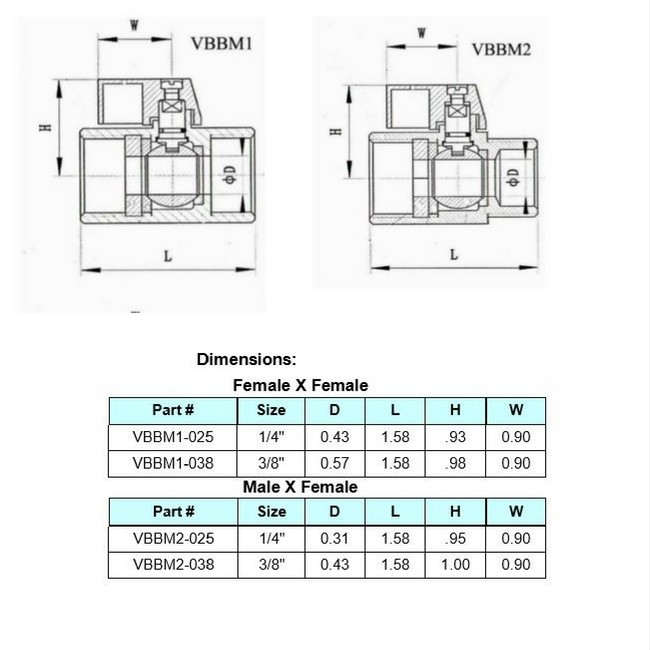
Dimensions
| Pipe Size |
1/2″ – 6″. Above that call for price. |
Details
| Body Material |
Carbon Steel, 304, 316 Stainless Steel |
| Body Style |
Inline |
| Max. Pressure |
600 PSIG CWP (Default), up to 2500 PSIG |
| Body Seal Material |
PTFE |
| Compliance |
RoHs |
| Stem Type |
Blowout Proof |
| Ball Valve Basic Body Material |
Stainless Steel |
| Seat Material |
PTFE |
| Handle Type |
Lever |
| Standards |
MSS-SP-110 |
| Connection Type |
Threaded FNPT x FNPT, Flanged Class 150, Socket, Tri-Clamps |
| Ball Valve Product Group |
Manual |
| Temp. Range |
-60 Degrees to 450 Degrees F |
| Ball Material |
316 stainless steel |
| Item |
Ball Valve |
| Handle Material |
Stainless Steel |
| Port |
Full |
| Valve Structure |
1, 2, and 3-Piece |
| Max. Steam Pressure |
150 PSI WSP |
| Stem Material |
316 Stainless Steel |
| General Connection Type |
Female NPT, RF Class 150 Flanged, Tri-Clamp |
| Sub-Category |
Stainless Steel Ball Valves |
|
Installation
Proper installation of ball valves is crucial to ensure reliable performance and longevity. Here’s a detailed guide to installing 1-piece, 2-piece, and 3-piece ball valves:
General Preparation
Verify Specifications:
- Action: Check that the ball valve’s size, pressure rating, and material are appropriate for the intended application.
- Purpose: Ensures compatibility with the system’s requirements and prevents installation issues.
Inspect the Valve:
- Action: Examine the ball valve for any visible damage or defects.
- Purpose: Identifies any issues before installation that could affect valve performance.
Prepare the Piping:
- Action: Clean the pipe ends to remove any debris, dirt, or rust.
- Purpose: Ensures a clean, smooth surface for sealing and proper valve connection.
Installation of 1-Piece Ball Valves
Align the Valve:
- Action: Position the valve between the two pipe ends, ensuring that it is aligned correctly with the flow direction marked on the valve body.
- Purpose: Prevents stress on the valve and ensures proper flow direction.
Secure the Valve:
- Action: Use pipe wrenches to tighten the valve into place, applying even pressure to avoid damage.
- Purpose: Ensures a secure fit and prevents leaks.
Check for Leaks:
- Action: After installation, open the valve slowly and check for any signs of leakage around the joints.
- Purpose: Identifies any leaks that may need to be addressed before full operation.
Test the Valve:
- Action: Operate the valve through its full range to ensure smooth operation.
- Purpose: Confirms that the valve is functioning correctly and free from obstructions.
Installation of 2-Piece Ball Valves
Align and Assemble the Valve:
- Action: Position the valve between the pipe ends. Ensure that the valve is aligned and then secure the body sections together by threading or bolting them.
- Purpose: Ensures proper alignment and connection of the valve to the pipe system.
Tighten Connections:
- Action: Use the appropriate tools to tighten the connections, making sure to avoid overtightening.
- Purpose: Ensures a leak-proof seal without damaging the valve or pipe.
Check for Leaks:
- Action: After installation, slowly open the valve and inspect for any leaks around the body and connection points.
- Purpose: Ensures that all connections are secure and leak-free.
Test the Valve:
- Action: Operate the valve fully to confirm that it opens and closes smoothly.
- Purpose: Verifies that the valve operates correctly within the system.
Installation of 3-Piece Ball Valves
Position the Valve:
- Action: Insert the central body of the valve between the pipe ends, ensuring correct alignment with the flow direction.
- Purpose: Ensures proper installation and function of the valve.
Attach End Pieces:
- Action: Align and secure the end pieces to the central body using bolts or clamps, making sure the seals are properly positioned.
- Purpose: Provides a secure and leak-proof connection.
Tighten and Secure:
- Action: Tighten the end pieces evenly to the central body, following the manufacturer’s torque specifications.
- Purpose: Ensures a secure fit and prevents leakage.
Check for Leaks:
- Action: Open the valve slowly and check for any leaks around the joints and connections.
- Purpose: Identifies any potential issues that need to be addressed.
Test Operation:
- Action: Operate the valve through its full range to ensure smooth and proper functioning.
- Purpose: Confirms that the valve operates correctly and without obstruction.
Final Checks
Verify Alignment and Support:
- Action: Ensure the valve is properly aligned and supported to prevent stress on the valve and piping.
- Purpose: Avoids damage and ensures longevity.
Documentation:
- Action: Record installation details, including valve type, size, and location.
- Purpose: Provides a reference for future maintenance or inspections.
Clean Up:
- Action: Remove any debris or tools from the installation area.
- Purpose: Ensures a safe and clean work environment.
Inform Users:
- Action: Brief users or operators on the valve’s operation and maintenance requirements.
- Purpose: Ensures proper usage and upkeep of the valve.
Summary
- 1-Piece Ball Valves: Simple installation with fewer components, suitable for smaller, lower-pressure applications.
- 2-Piece Ball Valves: Allows for easier maintenance with a two-part design, suitable for a range of sizes and pressures.
- 3-Piece Ball Valves: Provides flexibility and ease of maintenance with a modular design, ideal for high-pressure and large-diameter applications.
Proper installation is key to ensuring the reliability and efficiency of ball valves in various systems. Following these procedures will help achieve optimal performance and longevity of the valve.
Maintenance
Maintaining ball valves properly ensures their longevity, reliability, and optimal performance. Here’s a detailed guide to the maintenance procedures for 1-piece, 2-piece, and 3-piece ball valves:
General Maintenance Guidelines
Regular Inspection:
- Action: Periodically inspect the valve for signs of wear, leaks, or other issues.
- Purpose: Early detection of potential problems to prevent failure or damage.
Clean the Valve:
- Action: Regularly clean the external surfaces of the valve to remove dust, dirt, and other contaminants.
- Purpose: Prevents accumulation of debris that could affect the valve’s operation.
Check for Leaks:
- Action: Inspect around the valve’s connections and body for any signs of leakage.
- Purpose: Identifies leaks that need immediate attention to avoid fluid loss and damage.
Verify Valve Operation:
-
- Action: Operate the valve through its full range (open and close) to ensure smooth operation.
- Purpose: Ensures that the valve functions correctly and is not obstructed or jammed.
Maintenance for 1-Piece Ball Valves
Inspect Valve Body:
- Action: Check the valve body and pipe connections for any signs of corrosion, cracking, or damage.
- Purpose: Identifies structural issues that could lead to valve failure.
Lubricate Moving Parts:
- Action: If applicable, apply a lubricant to the valve’s moving parts to ensure smooth operation.
- Purpose: Prevents sticking and ensures the valve operates correctly.
Replace the Valve (if needed):
- Action: If the valve shows signs of significant wear or damage that cannot be repaired, replace the entire valve.
- Purpose: Maintains system integrity and performance.
Check Seals and Gaskets:
- Action: Examine seals and gaskets for wear or damage.
- Purpose: Ensures that these components are in good condition to prevent leaks.
Disassemble the Valve
Maintenance for 2-Piece Ball Valves:
- Action: For thorough inspection or repairs, disassemble the valve by separating the two body sections.
- Purpose: Allows access to internal components for detailed inspection and maintenance.
Inspect Internal Components:
- Action: Check the ball, seats, and seals for wear or damage.
- Purpose: Identifies issues that could affect valve performance and requires replacement or repair.
Clean Internal Parts:
- Action: Clean internal components using appropriate solvents and tools to remove any buildup or contaminants.
- Purpose: Ensures smooth operation and prevents blockages.
Reassemble and Tighten:
- Action: Reassemble the valve, ensuring all bolts or threads are properly tightened to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Purpose: Maintains valve integrity and prevents leaks at the joint.
Test the Valve:
- Action: After reassembly, test the valve for leaks and proper operation.
- Purpose: Confirms that the valve is functioning correctly and is free from issues.
Maintenance for 3-Piece Ball Valves
Disassemble the Valve:
- Action: Carefully disassemble the valve by removing the end pieces from the central body.
- Purpose: Facilitates detailed inspection and maintenance of internal components.
Inspect and Clean Internal Components:
- Action: Check the ball, seats, and seals for damage, wear, or buildup. Clean components as needed.
- Purpose: Ensures all parts are in good condition and free from obstructions.
Replace Worn Components:
- Action: Replace any worn or damaged internal components such as seals, seats, or the ball itself.
- Purpose: Restores proper function and prevents leaks or operational issues.
Check Seals and Gaskets:
- Action: Examine and replace seals and gaskets as needed to ensure a leak-proof assembly.
- Purpose: Maintains a proper seal and prevents fluid leakage.
Reassemble the Valve:
- Action: Reassemble the valve by securely attaching the end pieces to the central body.
- Purpose: Ensures that all components are correctly aligned and securely fastened.
Tighten Connections:
- Action: Ensure all bolts or connections are tightened to the specified torque settings.
- Purpose: Prevents leaks and maintains valve integrity.
Test for Leaks and Function:
- Action: Open and close the valve fully, checking for any leaks or issues in operation.
- Purpose: Verifies that the valve is functioning correctly and is leak-free.
Additional Tips
Follow Manufacturer’s Instructions:
- Action: Always refer to and follow the manufacturer’s maintenance guidelines and recommendations.
- Purpose: Ensures that maintenance procedures are appropriate for the specific valve model.
Use Proper Tools and Parts:
- Action: Use the correct tools for maintenance and replacement parts that meet the valve’s specifications.
- Purpose: Avoids damage and ensures compatibility.
Regular Maintenance Schedule:
- Action: Establish and adhere to a regular maintenance schedule based on the valve’s usage and environmental conditions.
- Purpose: Prevents unexpected failures and extends the valve’s service life.
Summary
1-Piece Ball Valves: Maintenance focuses on external inspections, lubrication, and replacement if needed. These valves require fewer maintenance steps due to their simpler design.
2-Piece Ball Valves: Maintenance involves disassembly, internal inspection, cleaning, and reassembly. They offer more flexibility for repairs and replacements compared to 1-piece valves.
3-Piece Ball Valves: Require thorough disassembly, detailed internal inspection and cleaning, and careful reassembly. They are suited for high-pressure and critical applications where ease of maintenance is crucial.
Proper maintenance ensures optimal performance and longevity of ball valves, reducing downtime and extending the valve’s service life.
Q&A
Q1: What are the main differences between 1-piece, 2-piece, and 3-piece ball valves?
A1: The primary differences are in their construction and ease of maintenance:
- 1-Piece Ball Valves: Made from a single piece of material. They are compact, cost-effective, and have fewer potential leakage points but are less flexible in maintenance.
- 2-Piece Ball Valves: Consist of two separate body sections that are bolted or threaded together. They offer easier maintenance and a wider range of sizes and pressures but have potential for leakage at the joint.
- 3-Piece Ball Valves: Comprise a central body section and two end pieces that can be disassembled. They are highly flexible for maintenance, suitable for high-pressure and large-diameter applications, but are generally more expensive and bulkier.
Q2: What are the advantages of using a 1-piece ball valve?
A2: The advantages of a 1-piece ball valve include:
- Compact Size: Ideal for applications with limited space.
- Cost-Effective: Generally, less expensive due to its simple construction.
- Leak-Proof: Fewer joints and seams reduce the risk of leaks.
- Durability: Robust construction with fewer components.
Q3: When should I choose a 2-piece ball valve over a 1-piece or 3-piece valve?
A3: Choose a 2-piece ball valve if:
- Maintenance Needs: You need a valve that can be easily disassembled for maintenance without replacing the entire unit.
- Cost vs. Performance: You require a balance between cost and ease of maintenance, and you do not need the high flexibility of a 3-piece valve.
- Size and Pressure Requirements: The application fits within the range of sizes and pressures that 2-piece valves can handle.
Q4: What are the key benefits of a 3-piece ball valve?
A4: The benefits of a 3-piece ball valve include:
- Ease of Maintenance: Can be serviced and repaired without removing the valve from the pipeline by disassembling the end pieces.
- Flexibility: Suitable for high-pressure and large-diameter applications.
- Modular Design: Allows for customization and easy replacement of internal components.
- Durability: Robust design capable of withstanding demanding conditions.
Q5: What applications are best suited for 1-piece ball valves?
A5: 1-piece ball valves are best suited for:
- Residential Plumbing: For fixtures like sinks and toilets where space is limited.
- Small-Scale Industrial Processes: Where a simple, reliable valve is needed.
- HVAC Systems: In compact or smaller HVAC applications.
- Food and Beverage Equipment: Where cost-effectiveness and simplicity are priorities.
Q6: What applications are best suited for 2-piece ball valves?
A6: 2-piece ball valves are ideal for:
- Commercial Plumbing: For water and gas distribution in commercial settings.
- Chemical Processing: Where the ability to disassemble for cleaning or repairs is important.
- Agricultural Irrigation: For controlling water flow in irrigation systems.
- Hydraulic Systems: For medium-pressure hydraulic fluid control.
Q7: What applications are best suited for 3-piece ball valves?
A7: 3-piece ball valves are best suited for:
- High-Pressure Systems: Such as oil and gas industries where high-pressure handling is required.
- Large-Diameter Piping: In industrial processes, chemical processing, and water treatment.
- Critical Industrial Processes: Where reliable performance and ease of maintenance are crucial.
- Utility Plants: For managing large volumes of fluids in water and utility systems.
Q8: How do I determine which type of ball valve is right for my application?
A8: To determine the right ball valve type:
- Assess Space Constraints: Choose 1-piece for tight spaces, 2-piece for moderate space with maintenance needs, and 3-piece for applications requiring flexibility and high performance.
- Consider Maintenance Needs: Opt for 2-piece or 3-piece valves if frequent maintenance or component replacement is anticipated.
- Evaluate Pressure and Size Requirements: Select a valve type that matches the pressure and size specifications of your application.
- Budget: Factor in the cost of the valve and its maintenance requirements to fit within your budget.
Q9: Can ball valves handle both high and low temperatures?
A9: Yes, ball valves can handle a range of temperatures, but the specific temperature range depends on the valve material and design. Always check the manufacturer’s specifications to ensure the valve is suitable for the temperature conditions of your application.
Q10: What materials are commonly used for ball valves and how do they affect performance?
A10: Common materials for ball valves include:
- Stainless Steel (e.g., 304SS, 316SS): Offers excellent corrosion resistance and durability, suitable for harsh environments.
- Brass: Good for general-purpose applications with moderate corrosive resistance.
- Plastic (e.g., PVC, CPVC): Ideal for corrosive fluids and lower pressure applications but less durable than metal options. The material affects the valve’s resistance to corrosion, temperature tolerance, and overall durability. Choose the material based on the fluid characteristics and operating conditions.
This Q&A provides a comprehensive overview of ball valve types, their advantages, applications, and considerations for choosing the right valve for specific needs.
Advantages / Disadvantages
1-Piece Ball Valves
Advantages:
Compact Design:
- Advantage: The single-piece construction allows for a compact design, making it suitable for applications with limited space.
- Benefit: Ideal for residential plumbing and small-scale applications.
Cost-Effective:
- Advantage: Generally less expensive due to simpler manufacturing processes and fewer parts.
- Benefit: Provides a budget-friendly option for basic fluid control needs.
Leak-Proof:
- Advantage: The absence of joints or seams reduces the risk of leaks.
- Benefit: Ensures a tight seal, reducing the likelihood of fluid loss and improving reliability.
Durability:
- Advantage: Fewer components mean fewer potential points of failure.
- Benefit: Enhanced durability and strength for low to moderate pressure applications.
Disadvantages:
Limited Maintenance:
- Disadvantage: If internal components need repair or replacement, the entire valve often has to be replaced.
- Impact: Higher replacement costs and potential downtime.
Size and Pressure Constraints:
- Disadvantage: Not suitable for large diameters or high-pressure applications due to manufacturing limitations.
- Impact: Limits use to smaller, lower-pressure systems.
Less Flexibility:
- Disadvantage: The single-piece design provides limited options for customization and modification.
- Impact: May not be suitable for applications requiring specific configurations.
2-Piece Ball Valves
Advantages:
Ease of Maintenance:
- Advantage: The ability to disassemble the valve into two sections facilitates easier maintenance and repairs.
- Benefit: Simplifies the process of replacing internal components or cleaning the valve.
Versatility:
- Advantage: Available in a wide range of sizes and pressure ratings.
- Benefit: Suitable for various applications, including commercial plumbing and chemical processing.
Cost-Effective Balance:
- Advantage: Provides a balance between cost and performance.
- Benefit: Offers a good middle ground for applications that require regular maintenance without the higher cost of a 3-piece valve.
Customizable:
- Advantage: Can be modified or adapted for specific needs more easily than 1-piece valves.
- Benefit: Provides flexibility in application-specific requirements.
Disadvantages:
Potential for Leakage:
- Disadvantage: The joint between the two body sections may be a potential leakage point.
- Impact: Requires careful assembly and maintenance to prevent leaks.
Size and Weight:
- Disadvantage: Generally larger and heavier than 1-piece valves.
- Impact: May not be suitable for applications with very tight space constraints.
Maintenance Complexity:
- Disadvantage: While maintenance is easier compared to 1-piece valves, it still requires disassembly of the valve body.
- Impact: Involves more steps than 1-piece valves for routine checks and repairs.
3-Piece Ball Valves
Advantages:
Ease of Maintenance and Service:
- Advantage: The valve can be disassembled into three parts for easy inspection, cleaning, or replacement of internal components.
- Benefit: Minimizes downtime and repair costs since only the end pieces need to be removed, leaving the piping connections intact.
High Pressure and Size Capability:
- Advantage: Suitable for large-diameter and high-pressure applications.
- Benefit: Provides reliable performance in demanding conditions, including industrial and high-pressure environments.
Modular Design:
- Advantage: Allows for customization and configuration adjustments.
- Benefit: Offers flexibility for specific applications and systems.
Durability:
- Advantage: Robust construction capable of withstanding harsh environments.
- Benefit: Long service life and reliability in critical applications.
Disadvantages:
Higher Cost:
- Disadvantage: Generally more expensive due to the complexity of the design and additional components.
- Impact: May be over budget for applications where a simpler valve would suffice.
Bulkiness:
- Disadvantage: Typically, larger and heavier than 1-piece and 2-piece valves.
- Impact: Can be challenging to fit into compact or constrained spaces.
Assembly and Maintenance:
- Disadvantage: While maintenance is facilitated, the valve requires proper reassembly to ensure no leakage.
- Impact: Potentially more complex than simpler valve designs, requiring careful handling during reassembly.
Summary
- 1-Piece Ball Valves: Ideal for cost-sensitive applications with space constraints and lower pressure needs. They are durable but limited in maintenance flexibility and size range.
- 2-Piece Ball Valves: Offer a balance of cost, maintenance ease, and versatility, suitable for various applications. They have potential leakage points and are bulkier than 1-piece valves.
- 3-Piece Ball Valves: Best for high-pressure and large-diameter applications where ease of maintenance and durability are crucial. They come at a higher cost and are bulkier but provide significant advantages in terms of flexibility and long-term performance.
Applications
Applications for 1-Piece, 2-Piece, and 3-Piece Ball Valves
1-Piece Ball Valves
Residential Plumbing:
- Application: Often used in home plumbing systems to control water flow to fixtures like sinks, toilets, and showers.
- Benefit: Compact size and cost-effectiveness make them ideal for space-constrained areas in residential settings.
Small-Scale Industrial Processes:
- Application: Suitable for small-diameter piping systems in light industrial processes, such as water or air flow control.
- Benefit: Reliable and durable for non-critical applications where simplicity and lower cost are advantageous.
HVAC Systems:
- Application: Used to control the flow of water or refrigerants in small HVAC systems.
- Benefit: Provides precise control in compact and space-limited installations.
Food and Beverage Equipment:
- Application: Employed in small food and beverage processing systems for controlling liquid flow.
- Benefit: Suitable for applications requiring simple, cost-effective valves.
Water Filtration Systems:
- Application: Utilized in residential or small commercial water filtration systems to control the flow of water through filters.
- Benefit: Easy to install and operate in confined spaces.
2-Piece Ball Valves
Commercial Plumbing:
- Application: Commonly used in commercial buildings for water and gas distribution systems.
- Benefit: Provides a good balance between cost, ease of maintenance, and reliability.
Chemical Processing:
- Application: Suitable for handling chemicals in small to medium-scale processing systems where maintenance is necessary.
- Benefit: The ability to disassemble for repairs or replacement of internal parts makes it ideal for handling aggressive fluids.
Agricultural Irrigation:
- Application: Used in irrigation systems to control water flow to various parts of an agricultural field.
- Benefit: Offers reliable control and the flexibility to replace components if needed.
Hydraulic Systems:
- Application: Employed in hydraulic systems for controlling the flow of hydraulic fluids in machinery.
- Benefit: Provides good performance in medium-pressure applications.
Marine Applications:
- Application: Used in small marine systems for controlling water and fuel flow.
- Benefit: Provides reliable service in marine environments where maintenance is a factor.
3-Piece Ball Valves
High-Pressure Systems:
- Application: Ideal for high-pressure applications such as those found in oil and gas industries, where reliable control is crucial.
- Benefit: The robust construction and flexibility for maintenance make it suitable for demanding conditions.
Large-Diameter Piping:
- Application: Suitable for large-diameter piping systems in industrial settings, including chemical processing and water treatment facilities.
- Benefit: Allows for easy servicing and repair without disrupting the entire system.
Critical Industrial Processes:
- Application: Used in critical processes where downtime must be minimized and reliability is essential, such as in petrochemical or pharmaceutical industries.
- Benefit: The ability to replace internal components quickly and easily makes it valuable for high-uptime environments.
HVAC Systems with High Pressure:
- Application: Employed in large-scale HVAC systems where high pressure and large flow rates are involved.
- Benefit: Offers durability and flexibility for maintenance in high-pressure environments.
Utility and Water Treatment Plants:
- Application: Used in utility and water treatment plants to manage large volumes of water and other fluids.
- Benefit: The 3-piece design facilitates easy maintenance and provides reliable performance in large-scale operations.
Summary
1-Piece Ball Valves: Ideal for applications with space constraints and lower pressure requirements, including residential plumbing and small-scale industrial uses.
2-Piece Ball Valves: Offer a good balance of cost and maintenance ease, suitable for commercial plumbing, chemical processing, and agricultural irrigation.
3-Piece Ball Valves: Best suited for high-pressure and large-diameter applications where reliability, ease of maintenance, and flexibility are crucial, such as in critical industrial processes and utility plants.
Download
Drawings
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.
 Ball valves are versatile flow control valves commonly used in various industrial applications to regulate the flow of liquids or gases. They are categorized based on their construction as 1-piece, 2-piece, or 3-piece ball valves, each offering specific advantages and applications. Additionally, ball valves come with different connection ends, including FNPT, flanged, and sanitary Tri-clamp ends, catering to diverse installation requirements. Materials such as carbon steel, 304 stainless steel (304SS), and 316 stainless steels (316SS) are commonly used for their construction, providing properties like strength, corrosion resistance, and durability.
Ball valves are versatile flow control valves commonly used in various industrial applications to regulate the flow of liquids or gases. They are categorized based on their construction as 1-piece, 2-piece, or 3-piece ball valves, each offering specific advantages and applications. Additionally, ball valves come with different connection ends, including FNPT, flanged, and sanitary Tri-clamp ends, catering to diverse installation requirements. Materials such as carbon steel, 304 stainless steel (304SS), and 316 stainless steels (316SS) are commonly used for their construction, providing properties like strength, corrosion resistance, and durability. 3-Piece Ball Valves
3-Piece Ball Valves Connection Ends
Connection Ends






























Reviews
There are no reviews yet.